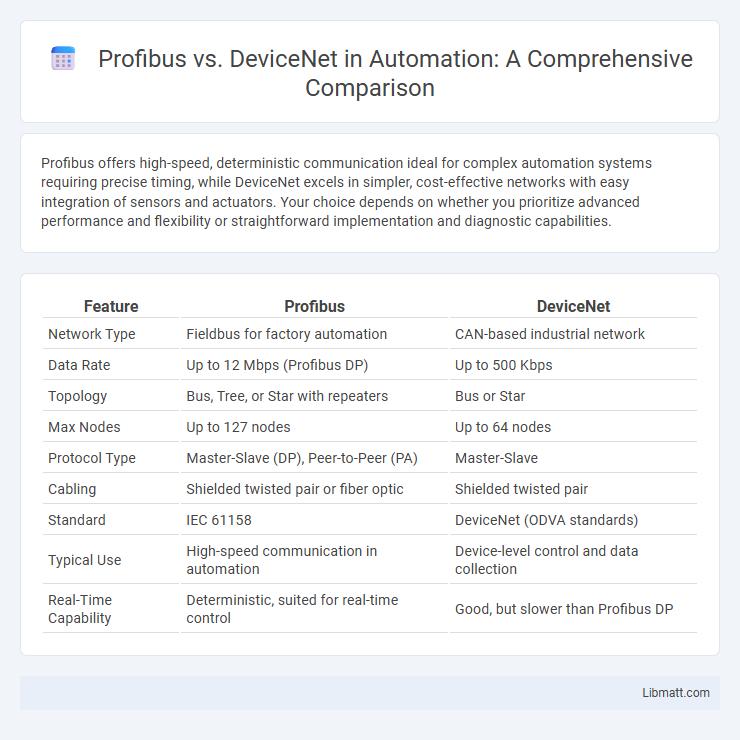
Profibus offers high-speed, deterministic communication ideal for complex automation systems requiring precise timing, while DeviceNet excels in simpler, cost-effective networks with easy integration of sensors and actuators. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize advanced performance and flexibility or straightforward implementation and diagnostic capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Profibus | DeviceNet |
|---|---|---|
| Network Type | Fieldbus for factory automation | CAN-based industrial network |
| Data Rate | Up to 12 Mbps (Profibus DP) | Up to 500 Kbps |
| Topology | Bus, Tree, or Star with repeaters | Bus or Star |
| Max Nodes | Up to 127 nodes | Up to 64 nodes |
| Protocol Type | Master-Slave (DP), Peer-to-Peer (PA) | Master-Slave |
| Cabling | Shielded twisted pair or fiber optic | Shielded twisted pair |
| Standard | IEC 61158 | DeviceNet (ODVA standards) |
| Typical Use | High-speed communication in automation | Device-level control and data collection |
| Real-Time Capability | Deterministic, suited for real-time control | Good, but slower than Profibus DP |
Introduction to Profibus and DeviceNet
Profibus (Process Field Bus) is a standardized, open digital communication system widely used in industrial automation for real-time data exchange between controllers and field devices, offering high-speed performance and robust networking capabilities. DeviceNet, developed by the Open DeviceNet Vendors Association (ODVA), is a network protocol based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus technology, primarily designed for industrial devices like sensors, actuators, and motor controllers, emphasizing ease of integration and device interoperability. Both Profibus and DeviceNet serve crucial roles in factory automation, with Profibus excelling in complex plant-wide networks and DeviceNet optimized for simple, device-level communication.
Key Differences Between Profibus and DeviceNet
Profibus and DeviceNet differ primarily in communication protocols and network topology; Profibus uses a master-slave protocol based on RS-485 or fiber optics, while DeviceNet operates on a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. Profibus supports higher data rates up to 12 Mbps and longer cable lengths, making it suitable for complex automation systems, whereas DeviceNet typically supports speeds up to 500 kbps and is optimized for device-level communication. Your choice depends on specific industrial automation needs, with Profibus favored for process control and DeviceNet for discrete manufacturing environments.
Architecture Overview: Profibus vs DeviceNet
Profibus features a hierarchical architecture with a Master-Slave communication model, supporting multiple devices on a single bus, ideal for factory automation. DeviceNet employs a peer-to-peer, token passing protocol enabling direct device communication with flexible node addition, suitable for control networks requiring real-time data exchange. Understanding these architectural differences helps optimize Your industrial network design for performance and scalability.
Communication Protocols and Standards
Profibus and DeviceNet are industrial communication protocols designed to connect automation devices, with Profibus based on the open IEC 61158 and IEC 61784 standards and supporting high-speed data transfer up to 12 Mbps. DeviceNet operates on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol, adhering to the DeviceNet specification defined by ODVA, and emphasizes ease of use in device-level networking with speeds up to 500 kbps. Profibus excels in complex, large-scale automation networks requiring deterministic communication, while DeviceNet is optimized for device-level integration with simpler wiring and standardized profiles.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Profibus offers data transfer rates up to 12 Mbps, enabling high-speed communication suitable for complex automation systems, while DeviceNet supports speeds up to 500 kbps, making it better suited for simpler device-level networks. Profibus uses a deterministic token-passing protocol that ensures timely and reliable data transmission, whereas DeviceNet employs a carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) mechanism, which can introduce latency under heavy traffic. This performance difference often positions Profibus as the preferred choice for applications requiring rapid and synchronized control, while DeviceNet is favored for cost-effective and lower-speed device integration.
Network Topology and Scalability
Profibus networks typically use a bus topology that supports high device counts, offering scalability through repeaters to extend segment length and increase the number of devices. DeviceNet employs a trunk-and-drop topology optimized for simpler device connections and easier expansion, but with limitations on maximum network size and node count compared to Profibus. Your choice depends on the required network size and complexity, with Profibus better suited for large-scale, complex industrial environments and DeviceNet ideal for smaller, modular systems.
Device Compatibility and Integration
DeviceNet offers broad compatibility with devices adhering to the CIP protocol, enabling seamless integration across multiple industrial automation systems. Profibus supports a wide range of devices through its well-established DP and PA standards, facilitating interoperability in complex process and factory automation environments. Both protocols ensure robust device integration, but DeviceNet excels in environments prioritizing network simplicity, while Profibus is favored for high-speed data exchange and extensive device variety.
Reliability and Fault Tolerance
Profibus offers high reliability with its deterministic communication protocol and fault-tolerant ring topology, which ensures continuous operation even if one segment fails. DeviceNet employs a token-passing method that provides robust fault detection and isolation but may be less reliable in highly complex networks due to potential bus collisions. Both protocols incorporate error-checking mechanisms, but Profibus's redundancy options typically yield superior fault tolerance in industrial automation environments.
Application Areas and Industry Use Cases
Profibus excels in complex manufacturing environments such as automotive and chemical industries where real-time communication and high-speed data exchange are critical for process automation. DeviceNet finds extensive use in packaging, food and beverage, and material handling sectors, leveraging its robust capabilities for device-level control and efficient integration with industrial Ethernet networks. Your choice between Profibus and DeviceNet should consider the specific industry's communication speed requirements and the level of device interoperability needed in the application area.
Choosing Between Profibus and DeviceNet
Choosing between Profibus and DeviceNet depends on the specific industrial application and network requirements. Profibus offers high-speed communication and robust performance for complex automation systems, ideal for process and factory automation with extensive device integration. Your decision should consider factors like network topology, data transmission speed, device compatibility, and industry standards to ensure optimal connectivity and control.
Profibus vs DeviceNet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com