Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, electricity, and hydrogen, offer cleaner emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel. Choosing alternative fuel options can enhance your vehicle's environmental impact while supporting sustainable energy sources.
Table of Comparison
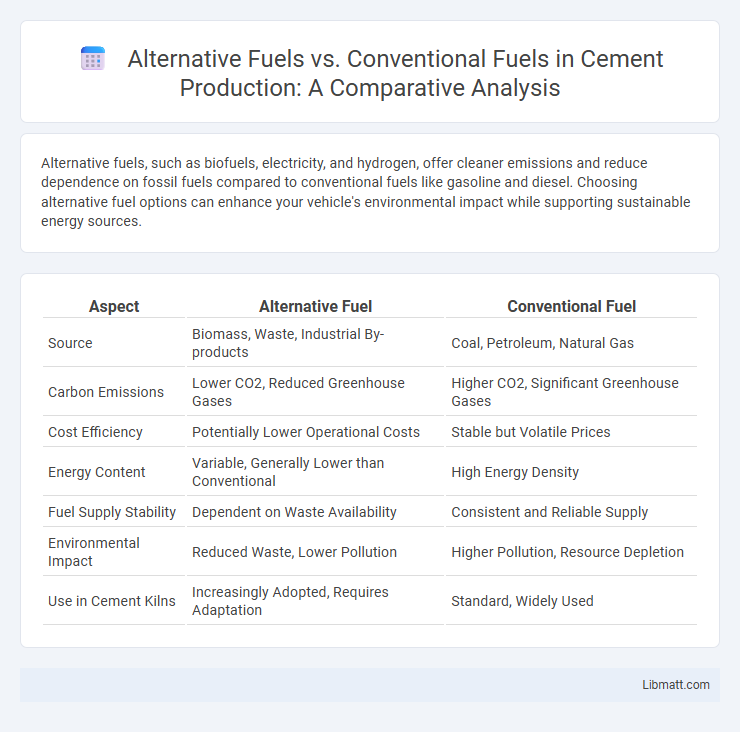
| Aspect | Alternative Fuel | Conventional Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Biomass, Waste, Industrial By-products | Coal, Petroleum, Natural Gas |
| Carbon Emissions | Lower CO2, Reduced Greenhouse Gases | Higher CO2, Significant Greenhouse Gases |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially Lower Operational Costs | Stable but Volatile Prices |
| Energy Content | Variable, Generally Lower than Conventional | High Energy Density |
| Fuel Supply Stability | Dependent on Waste Availability | Consistent and Reliable Supply |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced Waste, Lower Pollution | Higher Pollution, Resource Depletion |
| Use in Cement Kilns | Increasingly Adopted, Requires Adaptation | Standard, Widely Used |
Introduction to Alternative and Conventional Fuels
Alternative fuels include options like biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen, and electricity, designed to reduce environmental impact and reliance on fossil fuels. Conventional fuels, primarily gasoline and diesel derived from petroleum, remain widely used due to established infrastructure and energy density. Your choice between alternative and conventional fuels can influence vehicle emissions, fuel efficiency, and overall sustainability.
Defining Alternative Fuels: Types and Sources
Alternative fuels include biofuels, hydrogen, electricity, and natural gas, derived from renewable sources like biomass, solar energy, or water electrolysis. These fuels reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and coal, which originate from crude oil and natural deposits. Advancements in technology have diversified alternative fuel production methods, promoting sustainability and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Conventional Fuels: Overview and Market Dominance
Conventional fuels, primarily derived from fossil resources such as crude oil, natural gas, and coal, dominate the global energy market due to established extraction, refining, and distribution infrastructure. These fuels power the majority of transportation, industrial processes, and electricity generation worldwide, accounting for over 80% of global energy consumption according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). Your reliance on conventional fuels is linked to their high energy density and existing market availability, despite increasing environmental concerns driving the shift toward alternative energy sources.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Resource Depletion
Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen produce significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change. These renewable energy sources help conserve finite natural resources by decreasing reliance on crude oil extraction and refining processes that cause habitat destruction and soil degradation. Transitioning to alternative fuels supports sustainable energy consumption by minimizing carbon footprints and preserving ecosystems for future generations.
Economic Considerations: Costs and Market Trends
Alternative fuels often present higher upfront costs compared to conventional fuels due to limited production scale and infrastructure development but can lead to long-term savings through improved fuel efficiency and government incentives. Market trends indicate increasing investment in biofuels, electric energy, and hydrogen, driven by policy shifts and consumer demand for sustainable options, which gradually reduce costs and improve availability. Your decision between alternative and conventional fuels should factor in fluctuating oil prices, tax credits, and evolving technological advancements influencing overall economic feasibility.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen often provide higher energy efficiency and produce fewer emissions compared to conventional gasoline and diesel fuels. Conventional fuels have a well-established infrastructure but tend to have lower thermal efficiency, resulting in more energy lost as heat during combustion. Optimizing your vehicle for alternative fuel use can enhance fuel economy and reduce your carbon footprint significantly.
Infrastructure and Availability Challenges
Alternative fuel options often face significant infrastructure and availability challenges compared to conventional fuels, which benefit from extensive fueling stations and established supply chains. Electric vehicle charging stations and hydrogen fuel networks are less widespread, limiting accessibility for consumers and complicating long-distance travel. Addressing these gaps in infrastructure is crucial to ensure your seamless transition to alternative fuel vehicles and broader adoption.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological advancements in alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electric powertrains, have significantly improved energy efficiency and reduced emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel. Innovations in battery technology, fuel cells, and synthetic fuel production are driving the transition toward cleaner energy sources, offering your vehicle improved performance and sustainability. These developments position alternative fuels as viable solutions to meet stringent environmental regulations and decreasing reliance on finite conventional fuel resources.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies increasingly favor alternative fuels through subsidies, tax credits, and stricter emissions regulations to reduce carbon footprints and promote sustainable energy use. Incentives such as grants and rebates encourage consumers and manufacturers to adopt electric, hydrogen, and biofuel technologies, accelerating market penetration. Conventional fuels face higher regulatory costs and phasedown mandates under international agreements like the Paris Accord, driving a shift towards cleaner alternatives.
Future Outlook: Transitioning to Sustainable Energy
The future outlook for alternative fuel highlights a significant transition toward sustainable energy driven by innovations in biofuels, hydrogen, and electric technologies. Conventional fuels, primarily derived from fossil sources, face increasing regulatory constraints and environmental concerns that accelerate the shift to cleaner alternatives. Investment in renewable infrastructure and government policies supports the widespread adoption of alternative fuels, reducing carbon emissions and promoting energy security.
Alternative Fuel vs Conventional Fuel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com