Cement fineness directly affects the rate of hydration and strength development, with finer cement particles increasing surface area for reaction. Your choice of particle size distribution influences workability and durability, as a well-graded range ensures better packing density and reduced voids in the final mix.
Table of Comparison
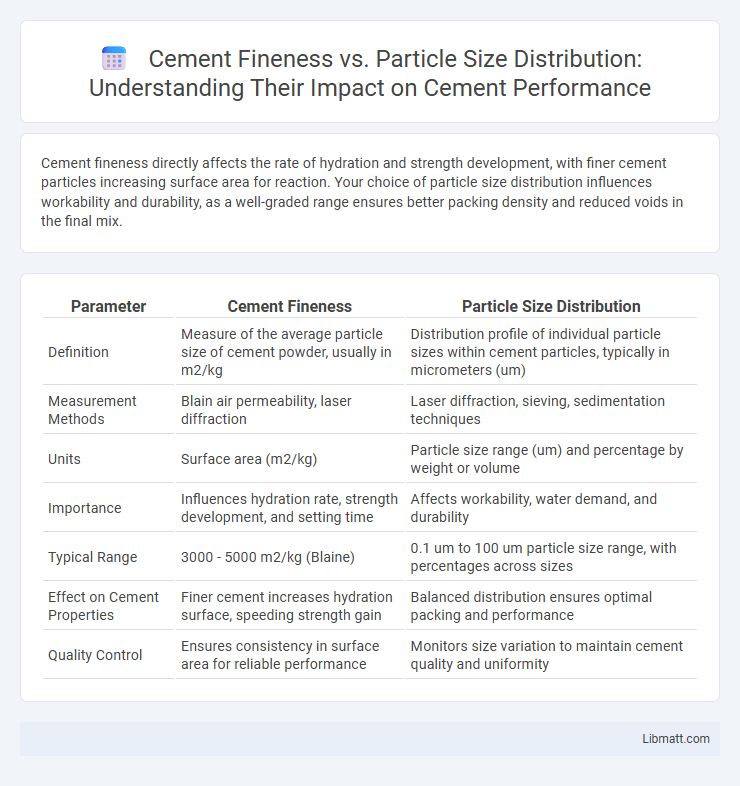
| Parameter | Cement Fineness | Particle Size Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of the average particle size of cement powder, usually in m2/kg | Distribution profile of individual particle sizes within cement particles, typically in micrometers (um) |
| Measurement Methods | Blain air permeability, laser diffraction | Laser diffraction, sieving, sedimentation techniques |
| Units | Surface area (m2/kg) | Particle size range (um) and percentage by weight or volume |
| Importance | Influences hydration rate, strength development, and setting time | Affects workability, water demand, and durability |
| Typical Range | 3000 - 5000 m2/kg (Blaine) | 0.1 um to 100 um particle size range, with percentages across sizes |
| Effect on Cement Properties | Finer cement increases hydration surface, speeding strength gain | Balanced distribution ensures optimal packing and performance |
| Quality Control | Ensures consistency in surface area for reliable performance | Monitors size variation to maintain cement quality and uniformity |
Introduction to Cement Fineness and Particle Size Distribution
Cement fineness directly influences the rate of hydration and strength development by determining the surface area available for chemical reactions. Particle size distribution (PSD) represents the range and proportion of different particle sizes within the cement powder, impacting workability and durability. Precise control of cement fineness and PSD enables optimization of concrete performance, ensuring better mechanical properties and long-term stability.
Importance of Cement Fineness in Construction
Cement fineness directly affects the hydration rate and strength development of concrete, making it crucial for construction quality. A finer cement particle size distribution enhances the surface area available for chemical reactions, leading to improved early strength and durability. Understanding your cement's fineness ensures optimal mix design and long-lasting structural performance.
Defining Particle Size Distribution in Cement
Particle size distribution (PSD) in cement quantifies the range and proportion of particle sizes within a cement sample, directly impacting hydration rate and strength development. Cement fineness, often measured by Blaine air permeability or sieve analysis, is derived from the PSD and influences setting time and workability of your concrete mix. Understanding PSD allows optimization of cement performance for specific applications by balancing surface area and particle packing efficiency.
Methods for Measuring Cement Fineness
Cement fineness is primarily measured using methods such as the Blaine air permeability test, which estimates the specific surface area of cement particles, and laser diffraction techniques that provide detailed particle size distribution analysis. The Blaine method assesses the resistance of a known volume of air passing through a compacted cement sample, offering results expressed in m2/kg. Laser diffraction, on the other hand, produces precise particle size distribution curves, identifying proportions of fine and coarse particles that critically influence cement hydration and strength development.
Techniques for Analyzing Particle Size Distribution
Laser diffraction and sieve analysis are precise techniques commonly used to evaluate cement fineness by measuring particle size distribution. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) offers detailed imaging to assess particle morphology and improve the reliability of particle size analysis in cement. Blaine air permeability testing remains a standard method to indirectly determine cement fineness based on particle surface area measurement.
Relationship Between Fineness and Particle Size Distribution
The relationship between cement fineness and particle size distribution is crucial for determining cement performance in concrete. Fineness directly affects the surface area of cement particles, influencing hydration rate and strength development, with finer particles accelerating the process. Your choice of cement fineness impacts particle size distribution, which in turn controls setting time, durability, and workability of the final mix.
Effects of Fineness on Cement Hydration and Strength
Cement fineness, measured by particle size distribution, critically influences hydration rate and ultimate strength development in concrete. Finer cement particles increase the surface area available for water contact, accelerating hydration reactions and enhancing early strength gain. However, excessively fine cement may lead to rapid water consumption and reduced workability, necessitating optimized particle size distribution for balanced performance.
Impact of Particle Size Distribution on Workability and Durability
Particle size distribution (PSD) significantly influences cement fineness, affecting both workability and durability of concrete. A well-graded PSD enhances flowability by optimizing particle packing, reducing water demand, and improving cement hydration, which strengthens the concrete matrix. Your choice of cement with an appropriate PSD ensures better consistency and long-term resistance to environmental stresses, crucial for structural performance.
Comparative Analysis: Fineness vs. Particle Size Distribution
Cement fineness measures the average size of particles, often quantified by specific surface area (m2/kg), while particle size distribution (PSD) provides a detailed profile of particle sizes across a range, influencing hydration and strength development. A finer cement with higher specific surface area generally accelerates strength gain but may increase water demand, whereas a well-graded PSD optimizes packing density and reduces voids for improved durability. Understanding the comparative impact of fineness and PSD on your concrete mix design allows precise control over performance characteristics like setting time and compressive strength.
Optimizing Cement Performance through Fineness and Particle Size Control
Optimizing cement performance relies on precise control of cement fineness and particle size distribution, which directly influence hydration rate and strength development. Finer cement particles increase the surface area available for reaction, enhancing early strength and reducing setting time, while well-graded particle size distribution improves packing density and durability. Balancing these parameters ensures improved workability, reduced water demand, and enhanced long-term mechanical properties in concrete applications.
Cement fineness vs Particle size distribution Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com