Cementitious coating provides excellent durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for concrete surfaces exposed to harsh environments, while epoxy coating offers superior chemical resistance and a glossy finish, perfect for areas requiring high aesthetic appeal and strong adhesion. Your choice depends on the specific application needs, such as exposure conditions and desired surface properties.
Table of Comparison
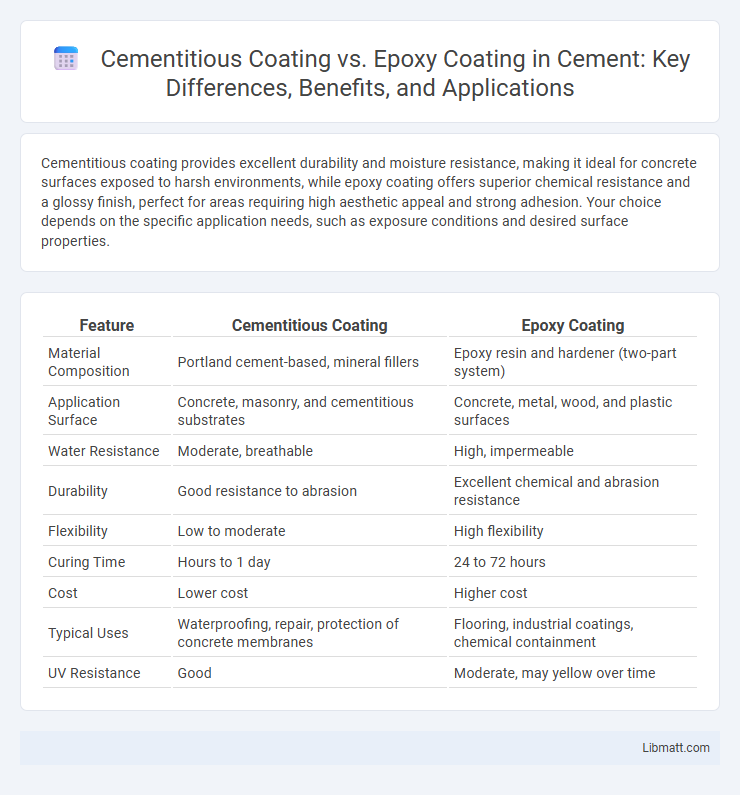
| Feature | Cementitious Coating | Epoxy Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Portland cement-based, mineral fillers | Epoxy resin and hardener (two-part system) |
| Application Surface | Concrete, masonry, and cementitious substrates | Concrete, metal, wood, and plastic surfaces |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, breathable | High, impermeable |
| Durability | Good resistance to abrasion | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate | High flexibility |
| Curing Time | Hours to 1 day | 24 to 72 hours |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Uses | Waterproofing, repair, protection of concrete membranes | Flooring, industrial coatings, chemical containment |
| UV Resistance | Good | Moderate, may yellow over time |
Introduction to Cementitious and Epoxy Coatings
Cementitious coatings are mineral-based protective layers primarily composed of cement and fine aggregates, designed for high durability and water resistance on concrete surfaces. Epoxy coatings consist of synthetic resin and hardeners that chemically bond to substrates, offering exceptional adhesion, chemical resistance, and a glossy finish ideal for industrial and commercial floors. Both coatings serve distinct purposes in construction and maintenance, with cementitious coatings favored for structural protection and epoxy coatings preferred for aesthetic and chemical-resistant applications.
Composition and Material Properties
Cementitious coatings consist primarily of cement, sand, and polymer additives, offering excellent adhesion, permeability, and resistance to water and chemicals, which makes them ideal for concrete protection and repair. Epoxy coatings are composed of epoxy resins and hardeners that create a dense, durable, and chemically resistant film, providing superior abrasion resistance and waterproofing for various surfaces. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and breathability (cementitious) or toughness and chemical resistance (epoxy).
Key Differences Between Cementitious and Epoxy Coatings
Cementitious coatings are mineral-based, providing excellent fire resistance and vapor permeability, making them ideal for concrete substrates requiring breathability. Epoxy coatings offer superior chemical resistance, durability, and adhesion, creating a tough, impermeable surface suitable for high-traffic and industrial environments. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right coating based on the project's environmental conditions and performance requirements.
Application Methods and Surface Preparation
Cementitious coatings require a clean, roughened concrete surface, often achieved through sandblasting or acid etching, and are typically applied using trowels or brushes to ensure proper adhesion and thickness. Epoxy coatings demand meticulous surface preparation including degreasing, grinding, and vacuum cleaning to remove contaminants, followed by roller or spray application for a smooth, durable finish. Both coatings rely on precise substrate preparation; however, epoxy applications are more sensitive to moisture and require strict environmental controls during curing.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cementitious coatings offer high durability with excellent resistance to moisture, impact, and abrasion, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and environments prone to cracking. Epoxy coatings provide superior chemical resistance and bonding strength, resulting in a longer lifespan under conditions of heavy traffic, chemical exposure, and mechanical wear. While cementitious coatings excel in flexibility and thermal resistance, epoxy coatings generally deliver enhanced longevity in industrial and commercial settings due to their robust adhesion and protective properties.
Chemical and Water Resistance Capabilities
Cementitious coatings offer moderate chemical resistance and superior water resistance, making them ideal for substrates exposed to moisture but not harsh chemicals. Epoxy coatings exhibit excellent chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and solvents, alongside outstanding waterproofing properties, suitable for environments with aggressive chemical exposure. Choosing the right coating depends on your specific chemical and water resistance requirements for long-term durability.
Typical Uses and Industry Applications
Cementitious coatings are primarily used for waterproofing and corrosion protection in concrete structures such as tunnels, bridges, and wastewater treatment plants due to their excellent adhesion and permeability resistance. Epoxy coatings are widely applied in industrial floors, chemical storage tanks, and marine environments for their superior chemical resistance, durability, and abrasion protection. Both coatings serve critical roles in construction and infrastructure maintenance, with cementitious coatings favored for concrete substrate protection and epoxy coatings preferred for high-performance surface finishes.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Cementitious coatings offer ease of maintenance with simple cleaning and patching for minor surface cracks, making them suitable for environments where routine upkeep is minimal. Epoxy coatings require more specialized repair methods to address peeling or abrasion, involving surface preparation and recoating to ensure durability and performance. Your choice between these coatings should consider the frequency and complexity of maintenance tasks needed to sustain optimal protective qualities.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Cementitious coatings generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to epoxy coatings, making them a budget-friendly option for large surface applications or projects with tight financial constraints. Epoxy coatings, while more expensive initially, provide superior durability and chemical resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses and overall lifecycle costs. Your choice should balance immediate budget considerations with the expected performance and longevity requirements of the coating application.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Project
Selecting the right coating depends on the project's exposure conditions and durability requirements; cementitious coatings offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and moisture, making them ideal for industrial and marine environments. Epoxy coatings provide superior chemical resistance and a smooth, high-gloss finish, suited for flooring and surfaces requiring high abrasion resistance. Evaluating factors like substrate type, environmental exposure, and maintenance needs is crucial for optimizing performance and longevity.
Cementitious Coating vs Epoxy Coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com