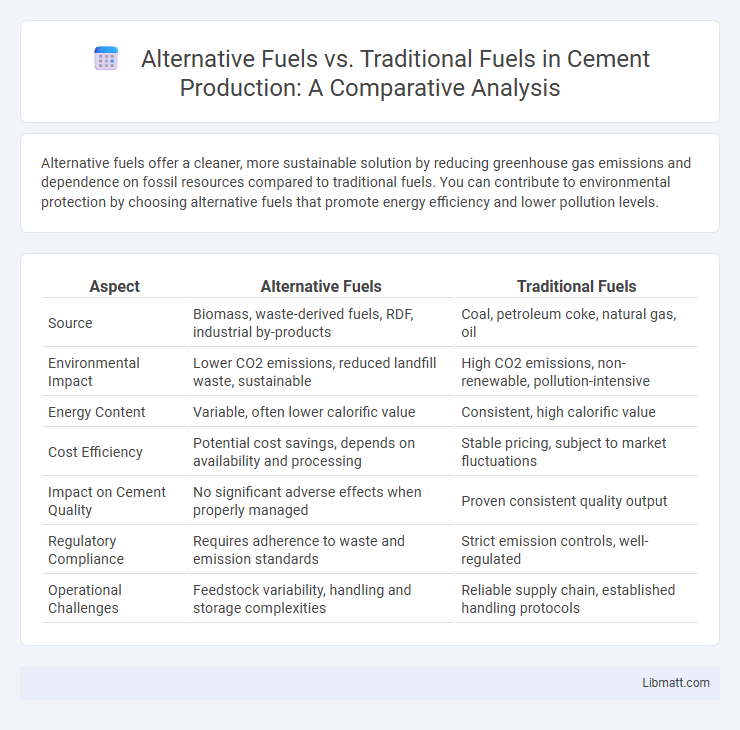
Alternative fuels offer a cleaner, more sustainable solution by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil resources compared to traditional fuels. You can contribute to environmental protection by choosing alternative fuels that promote energy efficiency and lower pollution levels.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alternative Fuels | Traditional Fuels |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Biomass, waste-derived fuels, RDF, industrial by-products | Coal, petroleum coke, natural gas, oil |
| Environmental Impact | Lower CO2 emissions, reduced landfill waste, sustainable | High CO2 emissions, non-renewable, pollution-intensive |
| Energy Content | Variable, often lower calorific value | Consistent, high calorific value |
| Cost Efficiency | Potential cost savings, depends on availability and processing | Stable pricing, subject to market fluctuations |
| Impact on Cement Quality | No significant adverse effects when properly managed | Proven consistent quality output |
| Regulatory Compliance | Requires adherence to waste and emission standards | Strict emission controls, well-regulated |
| Operational Challenges | Feedstock variability, handling and storage complexities | Reliable supply chain, established handling protocols |
Overview of Alternative and Traditional Fuels
Traditional fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, and coal, have dominated energy consumption due to their high energy density and established infrastructure, but they contribute significantly to environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Alternative fuels include biofuels, hydrogen, electricity, and natural gas, offering cleaner and renewable energy sources that reduce carbon footprints and reliance on finite resources. Your choice between these fuel types impacts environmental sustainability and energy efficiency in transportation and industry.
Key Differences Between Alternative and Traditional Fuels
Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electricity, differ from traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel in their environmental impact, energy sources, and emissions profiles. Whereas traditional fuels are derived from finite fossil resources with higher carbon footprints, alternative fuels utilize renewable resources or cleaner technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on oil. Your choice between these fuels influences energy sustainability, vehicle performance, and long-term cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electricity, produce significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change effects. Traditional fuels contribute to higher carbon dioxide emissions and release harmful pollutants, including sulfur oxides and particulate matter, which negatively impact air quality and human health. Choosing alternative fuels can significantly reduce your environmental footprint by promoting cleaner energy sources with sustainable production and consumption cycles.
Economic Implications and Costs
Alternative fuels often have higher upfront infrastructure costs but can lead to significant savings through lower fuel prices and reduced environmental penalties compared to traditional fuels. Your long-term expenses may decrease with alternative fuels due to improved energy efficiency and government incentives promoting cleaner energy. Economic implications include fluctuating fossil fuel prices and potential carbon taxes, which can increase the cost of traditional fuels over time.
Availability and Infrastructure Challenges
Alternative fuels such as hydrogen, biodiesel, and electric energy face significant availability and infrastructure challenges compared to traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel, which benefit from widespread distribution networks and established refueling stations. The limited number of charging points and specialized equipment for alternative fuels restricts their accessibility, impacting your ability to rely on them for long-distance travel or in rural areas. Expanding infrastructure for alternative fuels requires substantial investment and coordination, hindering their immediate adoption despite environmental advantages.
Performance and Efficiency Analysis
Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen show varying performance and efficiency compared to traditional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, often delivering lower energy density but higher combustion efficiency. Your vehicle may experience improved emissions profiles and potentially lower fuel consumption with alternative fuels, although engine modifications can be required to optimize performance. Efficiency analysis reveals that while traditional fuels provide consistent power output, alternative fuels can offer better thermal efficiency and reduced environmental impact when tailored to specific engine designs.
Technological Advancements in Fuels
Technological advancements in alternative fuels have led to higher energy efficiency, lower carbon emissions, and improved storage solutions compared to traditional fossil fuels such as gasoline and diesel. Innovations in biofuels, hydrogen fuel cells, and electric battery technology are driving the transition toward sustainable energy sources by reducing dependency on finite oil reserves. These developments enhance fuel performance, promote cleaner combustion processes, and support the integration of renewable energy into transportation and industrial applications.
Government Policies and Global Trends
Government policies increasingly support alternative fuels through subsidies, tax incentives, and strict emission regulations to reduce carbon footprints and combat climate change. Global trends show a shift towards electric vehicles, biofuels, and hydrogen energy, driven by international agreements like the Paris Accord and growing investments in renewable energy infrastructure. Traditional fuels face declining demand as nations aim to achieve net-zero emissions and enhance energy security through diversified fuel sources.
Future Prospects in the Fuel Industry
Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electric energy, present promising future prospects by reducing carbon emissions and enhancing sustainability in the fuel industry. Traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel face increasing regulatory pressures and resource depletion concerns, accelerating the shift toward cleaner alternatives. Your choices in fuel consumption will influence the industry's evolution toward greener, more efficient energy solutions.
Consumer Adoption and Market Outlook
Consumer adoption of alternative fuels is accelerating due to growing environmental awareness and stricter emissions regulations, driving market demand for electric vehicles, hydrogen, and biofuels. Traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel remain dominant but face declining long-term prospects as governments implement policies favoring cleaner energy sources. Your choice to switch to alternative fuels can contribute to reduced carbon footprints while benefiting from expanding refueling infrastructure and improved technology.
Alternative fuels vs Traditional fuels Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com