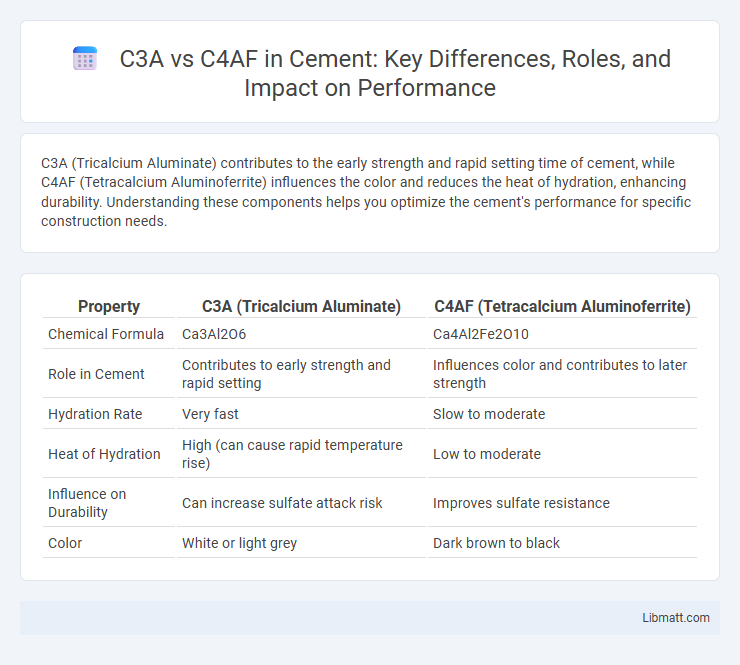
C3A (Tricalcium Aluminate) contributes to the early strength and rapid setting time of cement, while C4AF (Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite) influences the color and reduces the heat of hydration, enhancing durability. Understanding these components helps you optimize the cement's performance for specific construction needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | C3A (Tricalcium Aluminate) | C4AF (Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Ca3Al2O6 | Ca4Al2Fe2O10 |
| Role in Cement | Contributes to early strength and rapid setting | Influences color and contributes to later strength |
| Hydration Rate | Very fast | Slow to moderate |
| Heat of Hydration | High (can cause rapid temperature rise) | Low to moderate |
| Influence on Durability | Can increase sulfate attack risk | Improves sulfate resistance |
| Color | White or light grey | Dark brown to black |
Introduction to Cement Compounds: C3A and C4AF
C3A (tricalcium aluminate) and C4AF (tetracalcium aluminoferrite) are two essential hydraulic compounds in Portland cement responsible for key hydration reactions. C3A reacts rapidly with water and gypsum, influencing early setting time and heat generation, while C4AF contributes to color and provides moderate strength through slower hydration. The proportion of C3A and C4AF directly impacts cement's durability, sulfate resistance, and overall cement performance in construction applications.
Chemical Composition of C3A and C4AF
C3A, or tricalcium aluminate (Ca3Al2O6), primarily consists of calcium oxide and aluminum oxide, with minor amounts of iron oxide and other impurities influencing its reactivity and hydration properties. C4AF, or tetracalcium aluminoferrite (Ca4Al2Fe2O10), contains calcium oxide, aluminum oxide, and a significant proportion of iron oxide, which imparts its characteristic dark color and affects its hydraulic behavior. The distinct chemical compositions of C3A and C4AF impact their roles in cement hydration, strength development, and resistance to sulfate attack.
Structural Differences Between C3A and C4AF
C3A (tricalcium aluminate) and C4AF (tetracalcium aluminoferrite) differ structurally in their chemical composition and crystalline arrangement, impacting cement hydration and performance. C3A primarily consists of calcium and aluminum in a cubic crystal system, while C4AF incorporates both aluminum and iron within a more complex, orthorhombic lattice. These structural differences influence their reactivity rates and contribute differently to the color and heat evolution of Portland cement.
Hydration Reactions: C3A vs C4AF
C3A (tricalcium aluminate) hydrates rapidly with water, forming calcium aluminate hydrates and releasing significant heat, which influences early strength development in cement. C4AF (tetracalcium aluminoferrite) reacts more slowly, producing hydrated iron aluminates with lower heat evolution, contributing to long-term strength and color in cement. Understanding the distinct hydration reactions of C3A and C4AF helps optimize Your cement mix for desired setting times and durability.
Role of C3A in Cement Setting and Strength
C3A (tricalcium aluminate) significantly influences cement setting time due to its rapid hydration, which generates heat and contributes to early strength development. It reacts quickly with water and gypsum to form ettringite, controlling the initial set and preventing flash setting. Your cement's early strength and setting characteristics largely depend on the proportion of C3A relative to C4AF (tetracalcium aluminoferrite), which hydrates more slowly and affects later strength and color.
Functions of C4AF in Cement Performance
C4AF, or tetracalcium aluminoferrite, plays a crucial role in cement by influencing setting time and contributing to the color of the final product. It reacts relatively slowly compared to C3A, improving the workability of cement and reducing heat generation during hydration. Your cement's durability and resistance to sulfate attack are enhanced by the stable compounds formed from C4AF hydration.
Impact on Durability and Sulfate Resistance
C3A (Tricalcium Aluminate) significantly influences cement's sulfate resistance due to its high reactivity with sulfate ions, often leading to expansion and cracking in sulfate-rich environments. In contrast, C4AF (Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite) contributes less to sulfate attack, enhancing overall durability by providing moderate resistance and stabilizing the cement matrix. Understanding the balance of C3A and C4AF in your cement mix is crucial for optimizing durability and sulfate resistance in aggressive environmental conditions.
Heat Generation: Comparing C3A and C4AF
C3A generates more heat during the hydration process compared to C4AF, significantly influencing the temperature rise in concrete curing. C4AF contributes less to heat evolution but plays a crucial role in color and sulfate resistance. Understanding these differences helps optimize your mix design for thermal control in mass concrete applications.
Influence on Concrete Color and Appearance
C3A and C4AF are key mineral components in cement that significantly influence the color and appearance of concrete. C3A typically contributes to a lighter, more uniform gray tone, while C4AF imparts darker hues, often resulting in a browner or more varied surface coloration. Your choice of cement with differing C3A and C4AF content will affect the aesthetic finish and visual consistency of concrete structures.
Summary: Selecting Cement Based on C3A and C4AF Content
C3A (tricalcium aluminate) and C4AF (tetracalcium aluminoferrite) significantly influence cement properties, with higher C3A content accelerating setting time and increasing sulfate sensitivity, while C4AF contributes to the color and moderate strength development. When selecting cement, evaluating C3A and C4AF levels can help optimize durability and resistance to chemical attacks, especially in environments prone to sulfate exposure. Your choice should balance these compounds to achieve desired performance in specific construction conditions.
C3A vs C4AF Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com