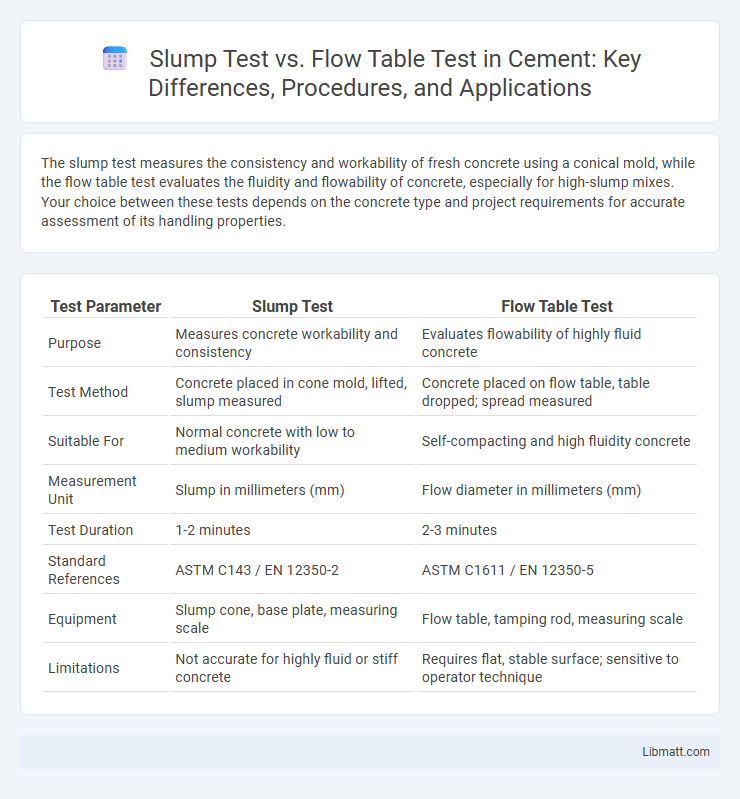
The slump test measures the consistency and workability of fresh concrete using a conical mold, while the flow table test evaluates the fluidity and flowability of concrete, especially for high-slump mixes. Your choice between these tests depends on the concrete type and project requirements for accurate assessment of its handling properties.
Table of Comparison
| Test Parameter | Slump Test | Flow Table Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures concrete workability and consistency | Evaluates flowability of highly fluid concrete |
| Test Method | Concrete placed in cone mold, lifted, slump measured | Concrete placed on flow table, table dropped; spread measured |
| Suitable For | Normal concrete with low to medium workability | Self-compacting and high fluidity concrete |
| Measurement Unit | Slump in millimeters (mm) | Flow diameter in millimeters (mm) |
| Test Duration | 1-2 minutes | 2-3 minutes |
| Standard References | ASTM C143 / EN 12350-2 | ASTM C1611 / EN 12350-5 |
| Equipment | Slump cone, base plate, measuring scale | Flow table, tamping rod, measuring scale |
| Limitations | Not accurate for highly fluid or stiff concrete | Requires flat, stable surface; sensitive to operator technique |
Introduction to Concrete Workability Tests
Concrete workability tests measure the ease with which concrete can be mixed, placed, and finished. The Slump Test evaluates the consistency and fluidity of fresh concrete by measuring the vertical settlement of a concrete cone after lifting it. The Flow Table Test, on the other hand, determines the flowability and spreadability of concrete by observing how far the mix spreads on a flat table, helping you assess the material's suitability for various construction applications.
Overview of Slump Test
The Slump Test measures the workability and consistency of fresh concrete by assessing the vertical settlement of a concrete sample in a conical mold. It provides a quick indication of the concrete's fluidity, critical for ensuring proper mixing and placement. This test is widely used on construction sites for its simplicity and effectiveness in gauging concrete slump and overall usability.
Overview of Flow Table Test
The Flow Table Test measures the workability and flow of concrete by placing a sample on a flow table and lifting it repeatedly to assess spreading diameter. This test is suitable for concrete with low to medium workability, especially in consistency ranges where the slump test is less effective. The flow table provides quantitative data on the fluidity of concrete, aiding in quality control and mix design adjustments.
Key Differences Between Slump Test and Flow Table Test
The Slump Test measures the consistency and workability of fresh concrete by evaluating its vertical deformation, while the Flow Table Test assesses the flowability and spread of concrete by measuring its horizontal flow diameter. You can use the Slump Test primarily for medium to stiff concrete mixes, whereas the Flow Table Test is suitable for highly fluid or self-compacting concrete. These tests differ in both procedure and application, providing complementary insights into concrete's fresh state properties.
Equipment Used in Each Test
Slump test equipment includes a slump cone, a base plate, a tamping rod, and a measuring scale to assess the consistency and workability of fresh concrete. Flow table test requires a flow table, a standardized cone mold, a measuring tray, and a tamping rod to determine the flowability and deformability of concrete mixtures. Both tests utilize specialized molds and tamping tools, but the slump test emphasizes vertical settlement measurement, whereas the flow table test focuses on horizontal spread measurement.
Step-by-Step Procedure: Slump Test
The Slump Test procedure involves filling a standard cone mold with fresh concrete in three layers, each tamped 25 times with a steel rod to ensure compaction. Once the mold is filled and leveled, it is carefully lifted vertically, allowing the concrete to slump freely. You then measure the vertical distance between the top of the mold and the top of the slumped concrete to determine consistency and workability.
Step-by-Step Procedure: Flow Table Test
The Flow Table Test involves placing a specific amount of concrete on a flow table, then raising the table by a standard height 25 times within 15 seconds to simulate concrete flow. After the prescribed jolts, the spread diameter of the concrete is measured to assess its workability and flowability. This procedure helps determine the consistency of concrete mixes, particularly for highly fluid and self-compacting concrete.
Applications of Slump Test in Construction
The Slump Test is widely used in construction to assess the consistency and workability of fresh concrete on-site, ensuring it meets project specifications for structural integrity. This test helps determine the water-cement ratio and detect any variations in mix quality, which is critical for foundations, beams, and slabs. Understanding your concrete's slump allows you to predict its behavior during placement and compaction, ultimately improving durability and performance in various construction applications.
Applications of Flow Table Test in Construction
The Flow Table Test is widely used in construction to evaluate the workability of concrete mixes, especially for medium to high slump concretes that require easy consolidation without segregation. It is essential for assessing the consistency of concrete in precast elements, pavements, and flooring where uniform flow and spreadability determine the final surface quality and durability. This test provides quantitative data to optimize mix designs for improved pumping, placement, and compaction efficiency on construction sites.
Choosing the Right Test for Concrete Mix Analysis
Selecting the appropriate test for concrete mix analysis depends on the mix's consistency and workability requirements. The Slump Test is ideal for measuring the workability of medium to high slump concretes, providing quick, reliable results on the fluidity of the mix. Your choice between the Slump Test and Flow Table Test should consider factors such as aggregate size, admixtures, and the desired flow characteristics to ensure accurate assessment of the concrete's performance.
Slump Test vs Flow Table Test Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com