Cement paste is a mixture of cement and water that acts as the binding agent in concrete, while concrete is a composite material comprising cement paste, aggregates like sand and gravel, which provides strength and durability for construction. Your choice depends on whether you need just the adhesive component or a fully structural material.
Table of Comparison
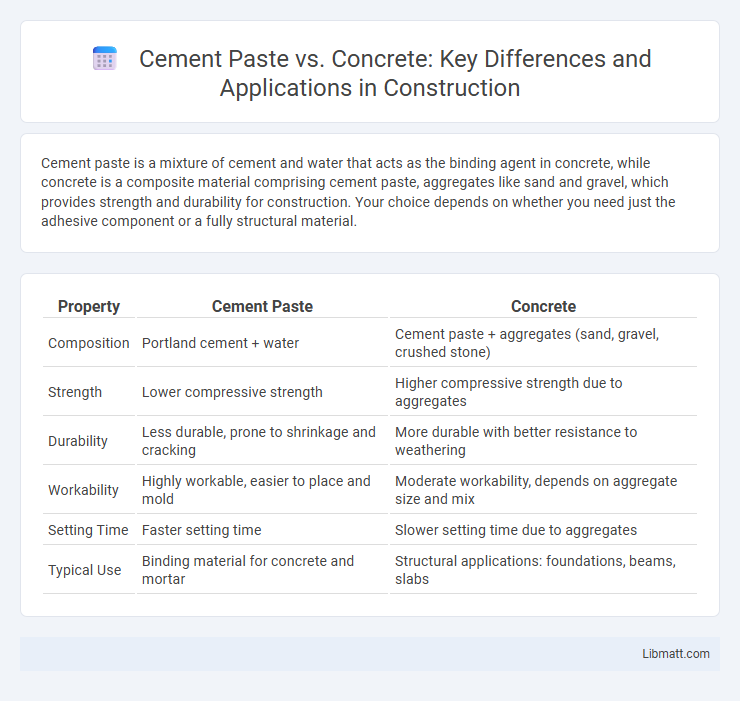
| Property | Cement Paste | Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Portland cement + water | Cement paste + aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone) |
| Strength | Lower compressive strength | Higher compressive strength due to aggregates |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to shrinkage and cracking | More durable with better resistance to weathering |
| Workability | Highly workable, easier to place and mold | Moderate workability, depends on aggregate size and mix |
| Setting Time | Faster setting time | Slower setting time due to aggregates |
| Typical Use | Binding material for concrete and mortar | Structural applications: foundations, beams, slabs |
Introduction to Cement Paste and Concrete
Cement paste is a mixture of cement and water that forms the binding matrix in concrete, playing a crucial role in its strength and durability. Concrete is a composite material consisting of cement paste combined with aggregates such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone, which provides structural support and reduces shrinkage. The interaction between cement paste and aggregates determines concrete's mechanical properties and its performance in construction applications.
Composition Differences: Cement Paste vs Concrete
Cement paste consists of cement and water, forming a smooth, sticky binder when mixed, while concrete includes cement paste combined with aggregates like sand, gravel, or crushed stone to enhance strength and durability. The addition of aggregates in concrete significantly reduces shrinkage and improves load-bearing capacity compared to cement paste alone. Understanding these composition differences helps you choose the appropriate material for construction projects, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Key Properties Comparison
Cement paste is a mixture of cement and water that binds aggregates in concrete, characterized by its high plasticity and low strength when alone. Concrete combines cement paste with aggregates like sand and gravel, resulting in significantly enhanced compressive strength, durability, and reduced shrinkage. The inclusion of aggregates in concrete improves load-bearing capacity and dimensional stability compared to cement paste, making it suitable for structural applications.
Roles in Construction Applications
Cement paste acts as the binding agent in concrete, providing the primary adhesive force that holds aggregates together, crucial for structural integrity in construction. Concrete's composite nature, combining cement paste with sand, gravel, and water, delivers enhanced compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for foundations, bridges, and buildings. The synergy between cement paste and aggregates directly influences concrete's performance characteristics such as workability, setting time, and long-term strength essential for diverse construction applications.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Cement paste, composed primarily of cement and water, exhibits lower strength and durability compared to concrete, which integrates aggregates to form a composite material with enhanced mechanical properties. The inclusion of coarse and fine aggregates in concrete significantly improves its compressive strength and resistance to environmental degradation, making it suitable for structural applications. Concrete's improved microstructure reduces permeability, thereby increasing durability against chemical attacks and freeze-thaw cycles compared to the more porous cement paste.
Workability and Setting Time
Cement paste, composed of cement and water, has higher workability but longer setting time due to the absence of aggregates. Concrete includes aggregates like sand and gravel, improving structural strength while reducing workability compared to plain paste. Your choice depends on whether ease of placement or faster initial setting is the priority for your project.
Cost Implications
Cement paste, composed primarily of water and cement, tends to have a higher material cost due to its concentrated binder content compared to concrete, which includes aggregates that reduce overall expense. Concrete's incorporation of sand, gravel, or crushed stone significantly lowers the price per cubic meter while maintaining adequate performance for most structural applications. Understanding the cost implications helps you make informed decisions when balancing budget constraints and project requirements.
Environmental Impact
Cement paste consists primarily of hydrated cement, which has a high carbon footprint due to CO2 emissions during the cement production process. Concrete combines cement paste with aggregates, which dilutes the overall cement content and reduces the per-unit environmental impact compared to pure cement paste. Understanding the differences in material composition can help you make more sustainable construction choices by optimizing cement usage and minimizing carbon emissions.
Common Usage Scenarios
Cement paste is primarily used as a binding agent in construction applications, playing a crucial role in forming mortar and grout for masonry and repairs. Concrete, a composite material consisting of cement paste, aggregates, and water, is extensively used in structural elements such as foundations, slabs, beams, and columns for buildings, bridges, and roads. The inclusion of aggregates in concrete enhances its strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty and load-bearing construction projects.
Choosing Between Cement Paste and Concrete
Choosing between cement paste and concrete depends on the application's structural requirements and durability needs, as cement paste is a mix of cement and water while concrete includes aggregates like sand and gravel. Concrete provides enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for construction projects such as foundations, pavements, and structural elements. Cement paste is primarily used as a binder within concrete or for specific repair materials, where high fluidity and bonding are essential but not load-bearing capacity.
Cement paste vs Concrete Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com