Cement retarders slow down the setting time of concrete, allowing more time for mixing, transportation, and placement, which is essential in hot weather or large pours. Cement accelerators speed up the curing process, enabling faster strength gain and reducing construction time, ideal for cold climates or quick turnaround projects.
Table of Comparison
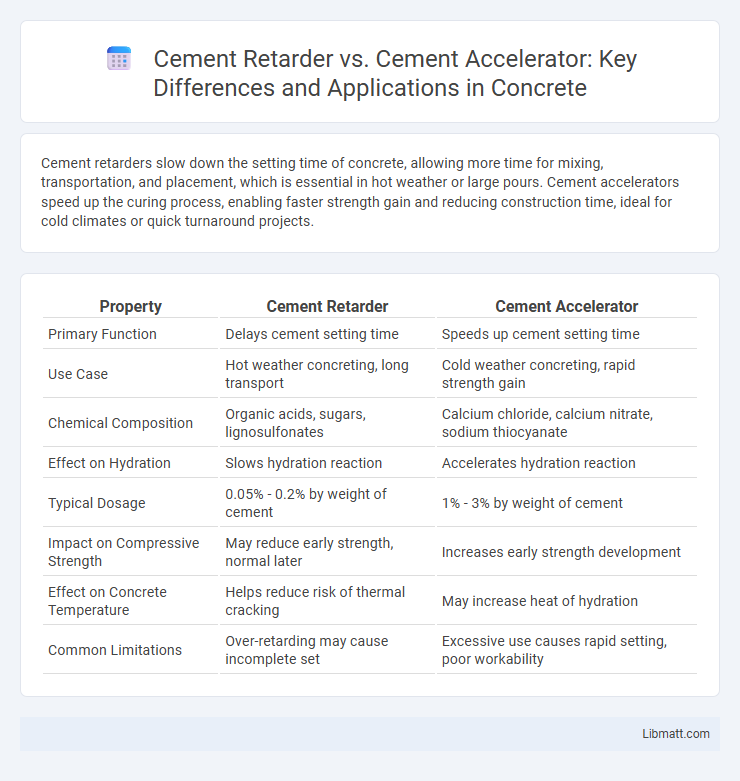
| Property | Cement Retarder | Cement Accelerator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Delays cement setting time | Speeds up cement setting time |
| Use Case | Hot weather concreting, long transport | Cold weather concreting, rapid strength gain |
| Chemical Composition | Organic acids, sugars, lignosulfonates | Calcium chloride, calcium nitrate, sodium thiocyanate |
| Effect on Hydration | Slows hydration reaction | Accelerates hydration reaction |
| Typical Dosage | 0.05% - 0.2% by weight of cement | 1% - 3% by weight of cement |
| Impact on Compressive Strength | May reduce early strength, normal later | Increases early strength development |
| Effect on Concrete Temperature | Helps reduce risk of thermal cracking | May increase heat of hydration |
| Common Limitations | Over-retarding may cause incomplete set | Excessive use causes rapid setting, poor workability |
Introduction to Cement Retarder and Accelerator
Cement retarders and accelerators are chemical additives used in concrete to control the setting time of cement. Retarders delay the hydration process, allowing more time for mixing and placing concrete in hot weather or large-scale projects. Accelerators speed up cement setting, improving early strength and reducing curing time in cold conditions or fast-track construction.
Understanding the Role of Cement Retarders
Cement retarders are chemical additives used in concrete to delay the setting time, enhancing workability and preventing premature hardening during hot weather or long transportation. Their primary role is to slow down the hydration process of cement, allowing more time for mixing, placing, and finishing, which improves the durability and strength of the final structure. In contrast, cement accelerators speed up setting time to achieve rapid strength gain, making retarders essential for projects requiring extended working time and controlled curing conditions.
Key Functions of Cement Accelerators
Cement accelerators primarily enhance the hydration process, significantly reducing the setting time of concrete and enabling faster strength development in construction projects. These additives are crucial for cold weather concreting, preventing delays caused by low temperatures and ensuring structural integrity. By improving early strength, cement accelerators facilitate quicker formwork removal and accelerate project timelines.
Chemical Composition: Retarder vs Accelerator
Cement retarders commonly contain lignosulfonates, sugars, or hydroxycarboxylic acids that slow the hydration process by interfering with calcium ion activity. In contrast, cement accelerators often include calcium chloride, sodium silicate, or triethanolamine, which speed up cement setting by enhancing calcium silicate hydrate formation. The fundamental chemical difference lies in retarders' ability to delay the exothermic reactions of cement hydration, while accelerators promote early strength gain through rapid crystal nucleation.
Mechanism of Action: How Retarders and Accelerators Work
Cement retarders work by chemically delaying the hydration process of cement, slowing down the setting time and allowing more time for placement and finishing. In contrast, cement accelerators increase the rate of hydration, promoting rapid strength development and quicker setting. These mechanisms optimize construction timelines by controlling the cement curing process according to project needs.
Major Applications in Construction
Cement retarders are primarily used in hot weather concreting to delay the setting time, preventing premature hardening and ensuring longer workability for large-scale pours. Cement accelerators speed up the hydration process, enabling faster strength gain, which is essential for cold weather concreting and rapid repair works. Your choice between a cement retarder or accelerator depends on specific project conditions such as temperature, timeframe, and desired strength development.
Advantages and Limitations of Cement Retarders
Cement retarders slow down the hydration process of cement, allowing for extended working time and preventing premature setting in large concrete pours or hot weather conditions. Their advantages include improved workability, reduced risk of cold joints, and enhanced durability of concrete structures. Limitations involve potential delays in construction schedules and the need for precise dosage control to avoid compromised strength development.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Cement Accelerators
Cement accelerators speed up the setting time of concrete, enabling faster construction progress and early strength development, which is essential in cold weather conditions and time-sensitive projects. However, their use can increase the risk of thermal cracking due to rapid hydration and may reduce long-term strength if over-applied. Proper dosage control is critical to maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks such as reduced workability and potential durability concerns.
Factors Influencing the Choice: Retarder or Accelerator
The choice between cement retarder and cement accelerator depends primarily on ambient temperature, desired setting time, and specific project requirements such as concrete thickness and curing conditions. Retarders are preferred in hot weather to slow hydration and prevent premature setting, while accelerators are used in cold climates to speed up curing and achieve early strength. Chemical composition, compatibility with cement type, and the impact on concrete durability also influence the decision.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Cement Retarder and Accelerator
Choosing between cement retarder and cement accelerator depends on your project's specific requirements for setting time and workability. Cement retarders are ideal for hot climates or large pours where extended workability is necessary, while accelerators are best for cold weather conditions or when rapid strength development is crucial. Understanding your environmental conditions and project timeline ensures optimal concrete performance by selecting the appropriate admixture.
Cement Retarder vs Cement Accelerator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com