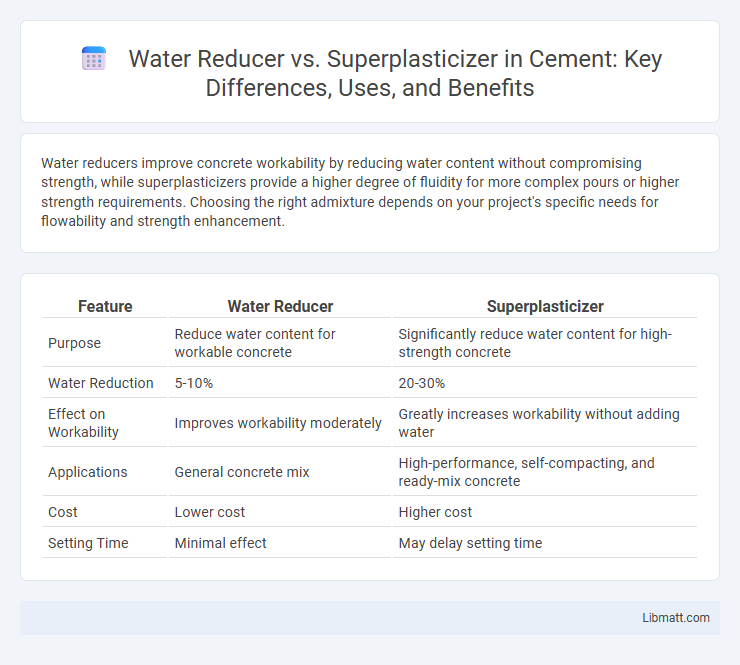
Water reducers improve concrete workability by reducing water content without compromising strength, while superplasticizers provide a higher degree of fluidity for more complex pours or higher strength requirements. Choosing the right admixture depends on your project's specific needs for flowability and strength enhancement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Water Reducer | Superplasticizer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce water content for workable concrete | Significantly reduce water content for high-strength concrete |
| Water Reduction | 5-10% | 20-30% |
| Effect on Workability | Improves workability moderately | Greatly increases workability without adding water |
| Applications | General concrete mix | High-performance, self-compacting, and ready-mix concrete |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Setting Time | Minimal effect | May delay setting time |
Introduction to Water Reducers and Superplasticizers
Water reducers and superplasticizers are advanced chemical admixtures used in concrete to improve workability and strength by reducing water content. Water reducers typically lower the water-cement ratio by up to 15%, enhancing durability and surface finish, while superplasticizers can reduce water content by 25-40%, enabling high-performance concrete with superior flowability. Understanding these admixtures helps you optimize concrete mix designs for specific structural requirements and environmental conditions.
Defining Water Reducers
Water reducers are chemical admixtures that improve concrete workability by reducing the water content needed without compromising strength, typically lowering water by 5-10%. Superplasticizers, a subset of water reducers, offer higher water reduction levels, often between 12-30%, enabling highly fluid concrete mixtures for advanced applications. Both enhance concrete durability and strength by optimizing the water-cement ratio, but superplasticizers provide superior dispersion of cement particles for improved performance.
Understanding Superplasticizers
Superplasticizers are advanced water reducers that significantly improve concrete workability while reducing water content by up to 30%. These high-range admixtures enhance strength, durability, and pumpability of concrete by dispersing cement particles more effectively than conventional water reducers. Understanding how superplasticizers interact with your mix design helps optimize concrete performance for demanding construction projects.
Key Differences Between Water Reducers and Superplasticizers
Water reducers and superplasticizers are both chemical admixtures used to improve concrete workability and strength but differ significantly in performance and dosage. Water reducers typically lower water content by 5-10% to enhance concrete's workability and strength, while superplasticizers can reduce water by 20-30%, providing high fluidity without compromising strength. Superplasticizers are more effective for high-performance concrete applications due to their advanced dispersion mechanisms and ability to maintain slump over extended periods.
Chemical Composition and Mechanisms
Water reducers typically contain lignosulfonates or hydroxylated carboxylic acids, which function by dispersing cement particles to reduce water content and improve workability. Superplasticizers, often composed of sulfonated melamine or naphthalene formaldehyde condensates, operate through electrostatic repulsion and steric hindrance, providing higher water reduction and improved flow without compromising strength. The distinct chemical compositions directly influence their mechanisms, with superplasticizers offering enhanced dispersion at lower dosages compared to traditional water reducers.
Impact on Concrete Workability
Water reducers improve concrete workability by reducing the water content needed for a given slump, enhancing consistency without compromising strength. Superplasticizers, as high-range water reducers, significantly increase fluidity and flowability, allowing for easier placement and finishing even in low water-to-cement ratio mixes. Both additives optimize workability but superplasticizers offer superior performance in producing highly workable concrete with minimal water addition.
Effects on Strength and Durability
Water reducers enhance concrete strength by reducing water content without compromising workability, resulting in a denser matrix with improved durability against freeze-thaw cycles and chemical attacks. Superplasticizers provide a more significant reduction in water-to-cement ratio, leading to higher early and ultimate strength by producing high-performance concrete with superior flowability and reduced porosity. The improved particle dispersion from superplasticizers further extends durability, making them ideal for critical infrastructure exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Applications in Modern Construction
Water reducers and superplasticizers play critical roles in modern construction by enhancing concrete performance and workability. Water reducers are commonly used in general concrete applications to improve strength and reduce water content, while superplasticizers are essential for high-performance concrete requiring superior fluidity and flow without added water. Understanding the specific needs of your project ensures the appropriate admixture selection for optimal structural integrity and durability.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Admixture
Water reducers enhance concrete workability and strength by reducing water content up to 15%, promoting better hydration and durability but may require longer setting times and have limited slump retention. Superplasticizers significantly increase fluidity with water reduction up to 30%, enabling high-strength, self-consolidating concrete applications while potentially causing rapid slump loss and increased sensitivity to mix variations. Selecting between water reducers and superplasticizers depends on project-specific demands for workability, setting time, and strength, balancing performance benefits against cost and compatibility constraints.
Selecting the Right Admixture for Your Project
Choosing between water reducers and superplasticizers depends on the specific requirements of your concrete project, including desired workability, strength, and setting time. Water reducers improve concrete flow with a moderate reduction in water content, enhancing strength and durability for standard applications, while superplasticizers provide a high-range water reduction, enabling high-strength and high-performance concrete with excellent workability. Understanding project demands and consulting product datasheets ensures the optimal admixture selection to achieve targeted structural performance and cost efficiency.
Water Reducer vs Superplasticizer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com