Cement setting time refers to the period required for cement paste to transition from a fluid state to a solid state, while hardening time denotes the duration needed for the cement to gain strength and durability after setting. Understanding the difference between these times ensures Your construction projects achieve optimal structural integrity and longevity.
Table of Comparison
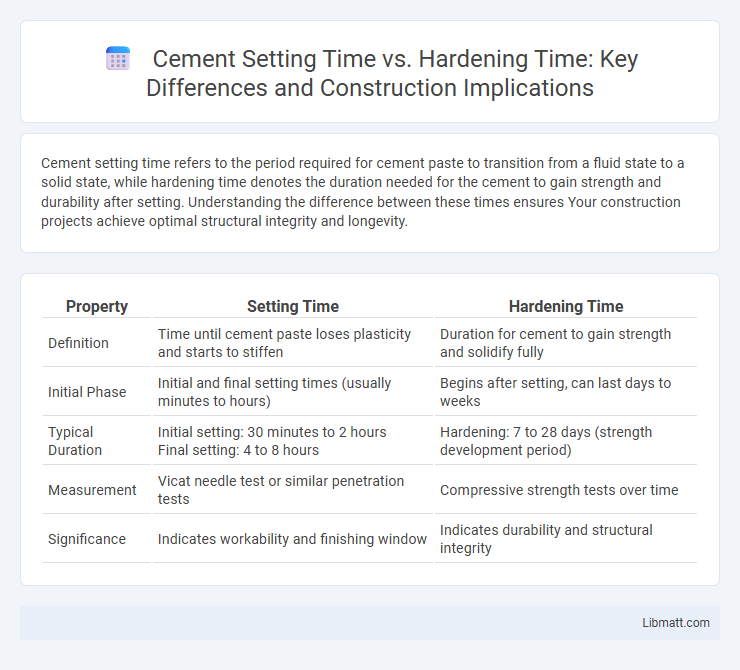
| Property | Setting Time | Hardening Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time until cement paste loses plasticity and starts to stiffen | Duration for cement to gain strength and solidify fully |
| Initial Phase | Initial and final setting times (usually minutes to hours) | Begins after setting, can last days to weeks |
| Typical Duration | Initial setting: 30 minutes to 2 hours Final setting: 4 to 8 hours |
Hardening: 7 to 28 days (strength development period) |
| Measurement | Vicat needle test or similar penetration tests | Compressive strength tests over time |
| Significance | Indicates workability and finishing window | Indicates durability and structural integrity |
Introduction to Cement Setting and Hardening
Cement setting time refers to the duration it takes for cement to begin losing its plasticity and start solidifying, typically categorized into initial and final setting times. Hardening time denotes the period over which the cement gains strength and rigidity, evolving from a plastic to a hardened state capable of bearing loads. Understanding the difference between setting and hardening is crucial for optimizing your construction schedule and ensuring effective curing practices for durable structures.
Defining Cement Setting Time
Cement setting time refers to the duration required for cement to transform from a fluid or plastic state to a solid state, enabling it to resist deformation. Initial setting time marks the beginning of the solidification process, while final setting time indicates when the cement completely loses plasticity. Setting time is crucial for scheduling construction activities and ensuring proper workability of concrete mixtures.
Understanding Cement Hardening Time
Cement setting time refers to the period required for the cement paste to lose its plasticity and gain initial rigidity, crucial for molding and shaping before hardening begins. Hardening time, on the other hand, encompasses the longer process during which the cement gains strength and durability through a chemical reaction called hydration. Understanding cement hardening time helps you optimize curing practices to achieve desired structural performance and longevity in your construction projects.
Key Differences Between Setting and Hardening
Setting time of cement refers to the duration it takes for the cement paste to transition from a fluid to a rigid state, typically categorized into initial and final setting times measured in minutes. Hardening time involves the period during which the cement develops strength and gains durability, often spanning days to weeks and quantified through compressive strength tests. Key differences lie in their roles: setting defines workability and mold retention, whereas hardening determines long-term structural integrity and load-bearing capacity.
Factors Influencing Setting Time
Cement setting time is primarily influenced by factors such as temperature, water-to-cement ratio, and cement composition, with higher temperatures accelerating setting and lower water content reducing it. The presence of admixtures like accelerators or retarders significantly modifies the rate at which cement transitions from plastic to solid state. Particle size distribution and fineness of the cement particles also play crucial roles, with finer particles typically resulting in faster setting times.
Factors Affecting Hardening Time
Hardening time of cement is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, water-cement ratio, and the presence of chemical admixtures, which alter hydration rates and microstructure development. Unlike setting time, which marks the initial stiffening of cement paste, hardening time relates to strength gain and durability, directly impacted by curing conditions and cement composition. Understanding these variables helps optimize your concrete mix for desired performance and structural integrity.
Importance of Setting and Hardening in Construction
Setting time determines when cement transitions from a fluid to a solid state, allowing initial workability crucial for shaping and molding in construction. Hardening time reflects the period cement gains strength and durability, impacting the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of your construction project. Understanding both processes ensures optimal scheduling and quality control, preventing premature loads or delays.
Methods to Measure Setting and Hardening Times
The setting time of cement can be measured using the Vicat apparatus, which determines the initial and final setting by assessing the penetration resistance of a cement paste. Hardening time, on the other hand, is typically evaluated through compressive strength tests at various intervals, reflecting the cement's progress in gaining rigidity and durability. Understanding these methods helps you accurately monitor the curing process to ensure optimal construction performance.
Common Issues Related to Setting and Hardening
Cement setting time and hardening time are critical factors impacting construction quality, with common issues including premature setting causing insufficient workability and delayed hardening leading to structural weakness. Moisture level, temperature, and improper mix proportions often disrupt the balance between setting and hardening, resulting in cracks or reduced strength. You must monitor these parameters closely to ensure optimal curing and durability of concrete structures.
Practical Tips to Optimize Cement Setting and Hardening
To optimize cement setting and hardening time, ensure precise water-to-cement ratios, as excess water prolongs setting while insufficient water impedes hardening. Maintain consistent ambient temperature and humidity levels, since cooler temperatures slow the chemical reactions crucial for both setting and strength gain. Your concrete mix will achieve optimal performance by incorporating admixtures like accelerators or retarders tailored to project timelines and environmental conditions.
Cement setting time vs Hardening time Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com