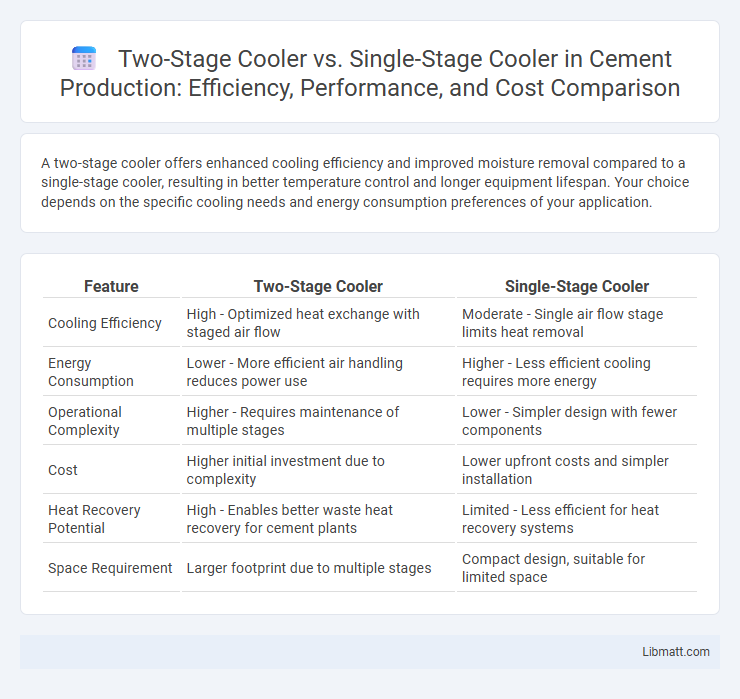
A two-stage cooler offers enhanced cooling efficiency and improved moisture removal compared to a single-stage cooler, resulting in better temperature control and longer equipment lifespan. Your choice depends on the specific cooling needs and energy consumption preferences of your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Two-Stage Cooler | Single-Stage Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Efficiency | High - Optimized heat exchange with staged air flow | Moderate - Single air flow stage limits heat removal |
| Energy Consumption | Lower - More efficient air handling reduces power use | Higher - Less efficient cooling requires more energy |
| Operational Complexity | Higher - Requires maintenance of multiple stages | Lower - Simpler design with fewer components |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to complexity | Lower upfront costs and simpler installation |
| Heat Recovery Potential | High - Enables better waste heat recovery for cement plants | Limited - Less efficient for heat recovery systems |
| Space Requirement | Larger footprint due to multiple stages | Compact design, suitable for limited space |
Introduction to Industrial Coolers
Industrial coolers play a crucial role in managing temperature control for various manufacturing processes, with two-stage and single-stage coolers being the primary options you might encounter. Single-stage coolers operate using a single compression cycle, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness for moderate cooling demands. Two-stage coolers employ two compression cycles, providing enhanced efficiency and greater cooling capacity ideal for more intensive industrial applications.
How Single-Stage Coolers Work
Single-stage coolers operate using a single compressor that cycles on and off to maintain the desired temperature, delivering consistent cooling by compressing refrigerant to lower air temperature. This simple design offers reliable performance and energy efficiency for moderate climate conditions or smaller spaces. Your cooling needs may be adequately met by single-stage coolers due to their straightforward mechanism and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Two-Stage Coolers
Two-stage coolers operate with two levels of cooling capacity, allowing the system to run at a lower horsepower during mild weather and switch to full power in extreme heat, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort. These coolers maintain a more consistent temperature and humidity level compared to single-stage coolers, which operate at only one fixed speed. You benefit from improved indoor air quality and reduced energy bills with a two-stage cooler's advanced technology.
Key Differences Between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Coolers
Single-stage coolers operate with one compressor speed, cycling on and off to maintain temperature, which can lead to more temperature fluctuations and higher energy consumption. Two-stage coolers use a compressor with two speed settings, running at a lower speed for most of the time to provide consistent cooling and improved energy efficiency. Your choice depends on the need for precise temperature control and long-term energy savings, with two-stage coolers offering better performance in these aspects.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Two-stage coolers operate at variable speeds, allowing them to adjust cooling output and consume less energy during mild weather compared to single-stage coolers, which run at full capacity whenever on. This modulation leads to improved energy efficiency, reducing electricity bills and lowering your carbon footprint. Single-stage coolers, while less expensive upfront, often result in higher energy consumption due to their constant full-speed operation.
Cooling Performance and Temperature Range
Two-stage coolers provide superior cooling performance by cycling between high and low compressor speeds, enabling precise temperature control and improved efficiency in a broader temperature range. Single-stage coolers operate at a fixed compressor speed, which limits temperature consistency and energy efficiency, especially in extreme heat conditions. This makes two-stage units ideal for environments requiring stable temperatures between 55degF and 70degF, while single-stage coolers typically maintain a narrower range around 65degF to 75degF.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
A two-stage cooler typically incurs a higher initial investment due to its complex design and enhanced cooling efficiency compared to a single-stage cooler, which offers a more affordable upfront cost. Maintenance expenses for two-stage coolers can be higher, as their dual compressor system requires specialized parts and skilled labor, while single-stage coolers generally have lower maintenance costs due to simpler mechanics. Evaluating long-term operational savings against upfront and maintenance costs is crucial for cost-effective cooling system decisions.
Application Suitability for Each Cooler
Two-stage coolers are ideal for environments with extreme temperature fluctuations, such as commercial refrigeration in food storage and industrial processes requiring precise cooling control. Single-stage coolers suit moderate climates and applications like residential air conditioning or small-scale commercial use where temperature consistency demands are lower. Choosing between them depends on factors like cooling capacity, energy efficiency needs, and operational complexity based on the application's specific thermal load.
Pros and Cons of Two-Stage Coolers
Two-stage coolers offer increased efficiency by operating at two different capacities, which reduces energy consumption and maintains more consistent indoor temperatures compared to single-stage coolers. Their ability to run at a lower speed for the majority of the time also results in quieter performance and improved humidity control, enhancing overall comfort. However, two-stage coolers typically have higher upfront costs and more complex maintenance requirements due to their advanced technology.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Cooling System
For optimal cooling efficiency and energy savings, a two-stage cooler is ideal for larger spaces or environments with fluctuating temperatures due to its ability to modulate cooling output. Single-stage coolers are cost-effective and simpler, best suited for smaller, consistent-temperature areas. Evaluate space size, climate variability, and budget to select the most appropriate cooling system.
Two-Stage Cooler vs Single-Stage Cooler Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com