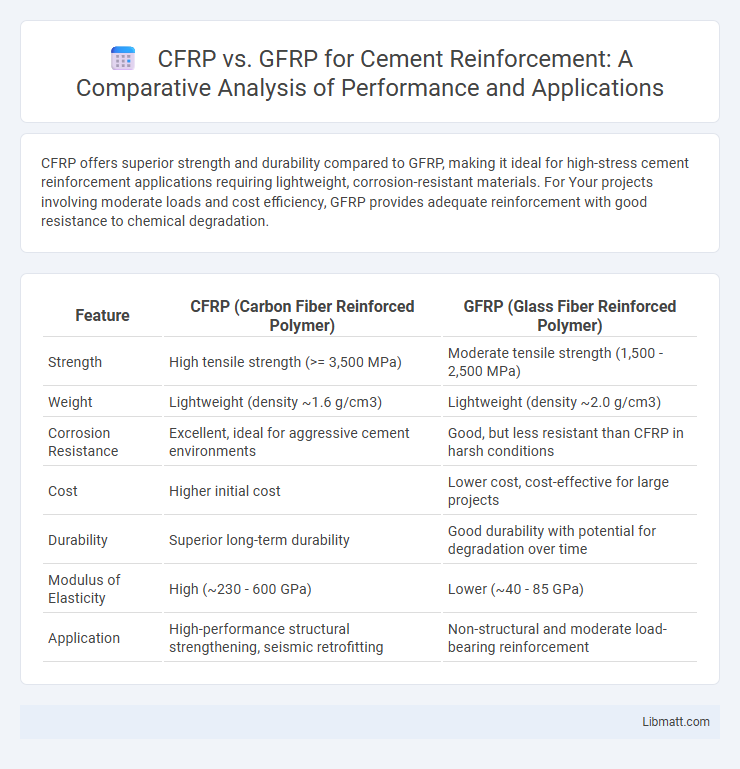
CFRP offers superior strength and durability compared to GFRP, making it ideal for high-stress cement reinforcement applications requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials. For Your projects involving moderate loads and cost efficiency, GFRP provides adequate reinforcement with good resistance to chemical degradation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) | GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile strength (>= 3,500 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (1,500 - 2,500 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight (density ~1.6 g/cm3) | Lightweight (density ~2.0 g/cm3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, ideal for aggressive cement environments | Good, but less resistant than CFRP in harsh conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, cost-effective for large projects |
| Durability | Superior long-term durability | Good durability with potential for degradation over time |
| Modulus of Elasticity | High (~230 - 600 GPa) | Lower (~40 - 85 GPa) |
| Application | High-performance structural strengthening, seismic retrofitting | Non-structural and moderate load-bearing reinforcement |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Polymers in Cement
Fiber Reinforced Polymers (FRPs) such as Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP) and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers (GFRP) are increasingly used to enhance the strength and durability of cement-based structures. CFRP offers superior tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance reinforcing applications in concrete repair and retrofitting. GFRP, while more cost-effective, provides excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength, suitable for less demanding structural reinforcement or where economic considerations are prioritized.
What is CFRP?
CFRP, or Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer, is a composite material consisting of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance compared to traditional materials. It provides enhanced tensile strength and stiffness, making it highly effective for reinforcing cement structures where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. Your cement reinforcement projects benefit from CFRP's ability to improve structural performance while reducing maintenance costs over time.
What is GFRP?
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) consists of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering high tensile strength and corrosion resistance for cement reinforcement applications. GFRP is lightweight, non-conductive, and provides excellent durability against chemical exposure in concrete structures. Compared to Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP), GFRP is more cost-effective but has lower stiffness and strength properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: CFRP vs GFRP
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer), making it more effective for cement reinforcement in structures requiring high load-bearing capacity. While GFRP provides better impact resistance and is generally more cost-effective, CFRP's higher modulus of elasticity ensures enhanced durability and reduced deformation under stress. Your choice depends on balancing mechanical performance needs with budget constraints and specific application requirements.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) in cement reinforcement applications, due to its high chemical inertness and resistance to alkaline environments common in concrete. While GFRP provides good corrosion resistance, it is more susceptible to degradation from moisture ingress and chemical attacks over time, which may reduce its service life in aggressive environments. The enhanced durability of CFRP translates into longer-lasting structural reinforcement with lower maintenance costs and improved structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: CFRP vs GFRP
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) typically costs significantly more than Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) due to the higher price of carbon fibers and more complex manufacturing processes. GFRP offers a more cost-effective solution for cement reinforcement in large-scale applications, with material costs often 30-50% lower than CFRP. Despite the higher initial expense, CFRP provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability, which can justify the investment in projects requiring enhanced performance and longer service life.
Installation and Workability
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and better resistance to corrosion, making installation in cement reinforcement more durable but requires careful handling due to its brittleness. GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) provides easier workability and flexibility during installation, allowing faster application with fewer specialized tools, though it may be less durable in harsh chemical environments. Your choice depends on balancing installation efficiency with long-term performance requirements in cement reinforcement projects.
Performance in Different Environmental Conditions
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) exhibits superior durability and mechanical strength in harsh environmental conditions such as high humidity, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures, maintaining its structural integrity longer than GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer). GFRP tends to be more susceptible to moisture absorption and alkaline environments, which can lead to reduced tensile strength and accelerated degradation over time when used in cement reinforcement. The enhanced corrosion resistance of CFRP makes it more suitable for applications demanding long-term reliability in aggressive environments.
Common Applications in Cement Reinforcement
CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) and GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) are widely used in cement reinforcement for enhancing structural performance. CFRP is preferred for high-strength, corrosion-resistant applications such as bridge decks and seismic retrofitting due to its superior tensile strength and stiffness. GFRP is commonly employed in non-corrosive environments like parking garages, water tanks, and architectural panels, providing cost-effective reinforcement with good durability.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Choosing between CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) and GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) for cement reinforcement depends on factors such as tensile strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. CFRP offers superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring long-term durability, while GFRP provides a more economical solution with good resistance to alkaline environments. Consider your project's load requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to determine which composite fiber best suits your cement reinforcement needs.
CFRP vs GFRP for Cement Reinforcement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com