Green cement reduces carbon emissions by incorporating industrial waste and alternative materials, making it more environmentally friendly than conventional cement. Your construction projects benefit from enhanced sustainability without compromising strength or durability compared to traditional cement options.
Table of Comparison
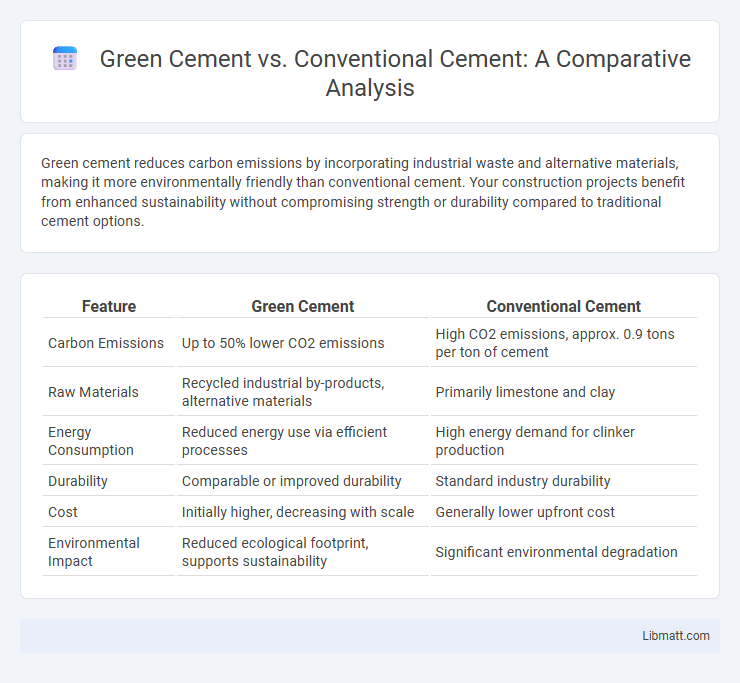
| Feature | Green Cement | Conventional Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Up to 50% lower CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions, approx. 0.9 tons per ton of cement |
| Raw Materials | Recycled industrial by-products, alternative materials | Primarily limestone and clay |
| Energy Consumption | Reduced energy use via efficient processes | High energy demand for clinker production |
| Durability | Comparable or improved durability | Standard industry durability |
| Cost | Initially higher, decreasing with scale | Generally lower upfront cost |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced ecological footprint, supports sustainability | Significant environmental degradation |
Introduction to Green Cement and Conventional Cement
Green cement is an eco-friendly alternative to conventional cement, designed to reduce carbon emissions and environmental impact during production by incorporating sustainable materials such as industrial byproducts and recycled aggregates. Conventional cement, primarily composed of clinker, limestone, and gypsum, is energy-intensive to produce and contributes significantly to global CO2 emissions, accounting for approximately 8% of worldwide carbon dioxide release. Advances in green cement aim to maintain structural integrity and durability while promoting sustainability in the construction industry.
Key Differences Between Green Cement and Conventional Cement
Green cement significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing industrial waste materials like fly ash or slag as partial substitutes for clinker, whereas conventional cement relies heavily on limestone calcination, producing higher CO2 levels. Your choice between green cement and conventional cement impacts environmental sustainability, as green cement promotes energy efficiency and reduced resource depletion. Performance-wise, green cement often offers similar strength and durability to conventional cement, making it a viable eco-friendly alternative in construction projects.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green cement significantly reduces carbon dioxide emissions by utilizing alternative materials such as fly ash, slag, and recycled industrial waste, leading to lower energy consumption during production compared to conventional Portland cement. Conventional cement manufacturing accounts for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions due to high-temperature kiln processes and limestone calcination. By incorporating sustainable raw materials and innovative production techniques, green cement minimizes environmental impacts, including lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced depletion of non-renewable resources.
Composition and Raw Materials Used
Green cement primarily uses supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash, slag, and natural pozzolans, replacing a significant portion of traditional clinker, which reduces carbon emissions. Conventional cement relies heavily on limestone and clay, calcined at high temperatures to produce clinker, resulting in higher energy consumption and CO2 output. Your choice of green cement supports sustainable construction by utilizing industrial by-products and eco-friendly raw materials.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint
Green cement significantly reduces energy consumption by utilizing alternative raw materials and lower-temperature curing processes compared to conventional cement, which typically requires high thermal energy during clinker production. The carbon footprint of green cement is markedly lower due to decreased reliance on fossil fuels and incorporation of industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, resulting in reduced CO2 emissions. This sustainability advantage positions green cement as a key material in reducing the environmental impact of construction projects globally.
Performance and Durability
Green cement offers comparable or superior performance and durability to conventional cement due to its reduced carbon footprint and innovative materials like fly ash or slag that enhance strength and resistance to chemical attack. Your construction projects benefit from green cement's improved long-term durability, which minimizes cracking and extends structural lifespan under harsh environmental conditions. This makes green cement a sustainable alternative without compromising the mechanical properties essential for high-quality concrete applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Green cement often incurs higher initial costs due to sustainable raw materials and energy-efficient production methods, but its use can lead to long-term economic benefits through lower carbon taxes and potential government subsidies. Conventional cement remains more affordable upfront, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale, yet its environmental externalities may increase future regulatory expenses. Evaluating your project's lifecycle costs and local policy incentives is crucial for determining the economic feasibility between green and conventional cement options.
Market Trends and Adoption Rates
Green cement is rapidly gaining market share due to rising environmental regulations and increasing demand for sustainable construction materials, with global adoption rates expected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% through 2030. Conventional cement, though still dominant, faces declining growth as industries prioritize reducing carbon emissions and meeting net-zero targets. Regions like Europe and North America lead in green cement adoption, driven by government incentives and corporate sustainability commitments.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementation
Green cement faces challenges such as higher production costs and limited availability of raw materials compared to conventional cement, which relies heavily on clinker and fossil fuels. Regulatory hurdles, lack of standardized industry guidelines, and resistance to change within construction sectors further impede widespread adoption. Moreover, performance inconsistencies and uncertainty regarding long-term durability create barriers for green cement integration in large-scale infrastructure projects.
Future Outlook and Innovations in Cement Industry
Green cement technology is rapidly advancing, with innovations such as carbon capture integration and alternative raw materials reducing CO2 emissions by up to 70% compared to conventional cement. The future outlook highlights increased adoption of geopolymer cements and alkali-activated binders, promoting sustainability and lower environmental impact in construction. Your choice of cement can significantly influence carbon footprint reduction as the industry moves towards greener, more efficient production methods.
Green cement vs Conventional cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com