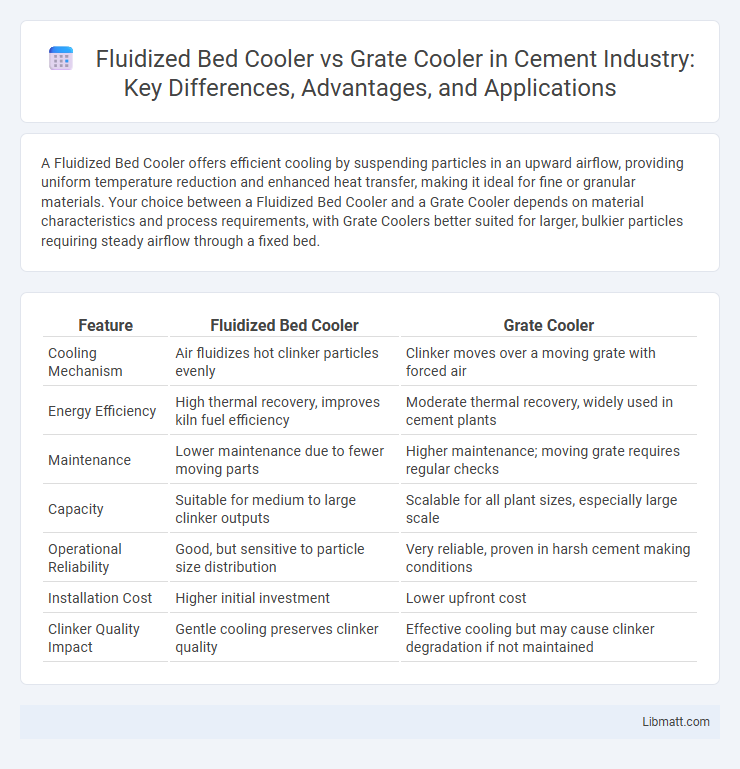
A Fluidized Bed Cooler offers efficient cooling by suspending particles in an upward airflow, providing uniform temperature reduction and enhanced heat transfer, making it ideal for fine or granular materials. Your choice between a Fluidized Bed Cooler and a Grate Cooler depends on material characteristics and process requirements, with Grate Coolers better suited for larger, bulkier particles requiring steady airflow through a fixed bed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fluidized Bed Cooler | Grate Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Mechanism | Air fluidizes hot clinker particles evenly | Clinker moves over a moving grate with forced air |
| Energy Efficiency | High thermal recovery, improves kiln fuel efficiency | Moderate thermal recovery, widely used in cement plants |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance; moving grate requires regular checks |
| Capacity | Suitable for medium to large clinker outputs | Scalable for all plant sizes, especially large scale |
| Operational Reliability | Good, but sensitive to particle size distribution | Very reliable, proven in harsh cement making conditions |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Clinker Quality Impact | Gentle cooling preserves clinker quality | Effective cooling but may cause clinker degradation if not maintained |
Introduction to Cooler Technologies in Cement Production
Fluidized bed coolers and grate coolers are essential technologies in cement production for rapidly cooling clinker while recovering heat for energy efficiency. Fluidized bed coolers utilize a bed of fine particles fluidized by air to achieve uniform cooling and improved thermal exchange, enhancing clinker quality and reducing energy consumption. Grate coolers, on the other hand, use a moving grate to transport hot clinker while air passes from below, providing robust cooling and high durability for large-scale cement plants.
What is a Fluidized Bed Cooler?
A Fluidized Bed Cooler is an industrial cooling device used primarily in cement production to rapidly reduce the temperature of clinker by passing air through a bed of hot particles, creating a fluidized state that enhances heat transfer. This cooler improves energy efficiency by recovering heat for preheating combustion air, and offers uniform cooling with minimal mechanical wear compared to traditional grate coolers. Its design ensures effective temperature control and increased output quality in high-temperature material handling processes.
What is a Grate Cooler?
A Grate Cooler is an industrial cooling device primarily used in cement plants to rapidly cool hot clinker by passing it over a series of moving grate plates with air flowing underneath. It offers efficient heat recovery and a compact design, making it suitable for continuous clinker cooling processes. Your choice between a Grate Cooler and a Fluidized Bed Cooler depends on factors like clinker temperature, energy efficiency goals, and maintenance requirements.
Working Principles: Fluidized Bed vs Grate Cooler
Fluidized bed coolers operate by passing air through a bed of hot material, causing particles to become suspended and promoting efficient heat exchange. Grate coolers function by moving material on a perforated grate while air flows through from below, allowing staged cooling. Understanding these working principles helps you select the right cooler for optimizing thermal management in industrial processes.
Heat Recovery Efficiency Comparison
Fluidized bed coolers achieve higher heat recovery efficiency by providing uniform cooling and enhanced heat transfer through fluidization of particles, resulting in temperatures as low as 80-100degC in discharged material. Grate coolers typically exhibit lower efficiency due to uneven cooling caused by solid bed movement, with exhaust gases often reaching around 150degC, which limits heat recovery potential. Optimizing fluidized bed coolers can recover up to 70-80% of heat energy, surpassing the 50-60% range commonly observed in grate cooler systems.
Energy Consumption and Operational Costs
Fluidized bed coolers typically consume less energy due to efficient heat transfer and lower air volume requirements compared to grate coolers, resulting in reduced operational costs. Grate coolers have higher mechanical complexity and frequent maintenance needs, increasing downtime and repair expenses. Optimizing cooler selection based on specific plant capacity and fuel type can significantly impact overall energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Fluidized Bed Coolers require less frequent maintenance due to their uniform cooling and reduced mechanical wear, enhancing overall durability. Grate Coolers demand regular inspections and part replacements, especially for grate plates exposed to high thermal and mechanical stress. You can achieve longer operational lifespan with a Fluidized Bed Cooler by minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Fluidized bed coolers reduce environmental impact by providing more efficient heat exchange, leading to lower energy consumption and decreased greenhouse gas emissions compared to grate coolers. Grate coolers tend to generate higher particulate emissions and require more frequent maintenance to control dust and pollution. Your choice between the two should consider the fluidized bed cooler's advantage in minimizing air pollution and promoting sustainable operations.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Fluidized bed coolers excel in industries requiring uniform cooling of granular materials like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing due to their efficient heat transfer and gentle handling. Grate coolers suit heavy-duty applications such as cement and minerals, where robust construction handles large, coarse materials and high temperatures effectively. Your choice depends on specific process requirements, including material properties and cooling capacity needed.
Choosing the Right Cooler: Key Considerations
Choosing the right cooler, such as a Fluidized Bed Cooler versus a Grate Cooler, depends on factors like product temperature, cooling efficiency, and dust handling capabilities. Fluidized Bed Coolers excel in uniform cooling and energy efficiency for fine particles, while Grate Coolers offer robust performance for coarse materials and better dust containment. Your selection should consider material characteristics, operational environment, and maintenance requirements to optimize cooling performance and cost-effectiveness.
Fluidized Bed Cooler vs Grate Cooler Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com