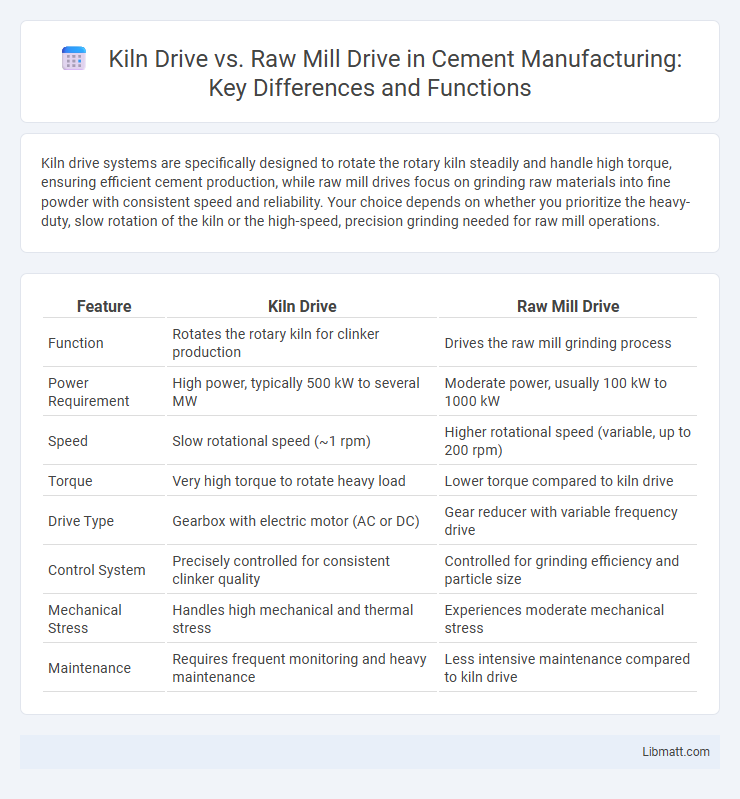
Kiln drive systems are specifically designed to rotate the rotary kiln steadily and handle high torque, ensuring efficient cement production, while raw mill drives focus on grinding raw materials into fine powder with consistent speed and reliability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the heavy-duty, slow rotation of the kiln or the high-speed, precision grinding needed for raw mill operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kiln Drive | Raw Mill Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Rotates the rotary kiln for clinker production | Drives the raw mill grinding process |
| Power Requirement | High power, typically 500 kW to several MW | Moderate power, usually 100 kW to 1000 kW |
| Speed | Slow rotational speed (~1 rpm) | Higher rotational speed (variable, up to 200 rpm) |
| Torque | Very high torque to rotate heavy load | Lower torque compared to kiln drive |
| Drive Type | Gearbox with electric motor (AC or DC) | Gear reducer with variable frequency drive |
| Control System | Precisely controlled for consistent clinker quality | Controlled for grinding efficiency and particle size |
| Mechanical Stress | Handles high mechanical and thermal stress | Experiences moderate mechanical stress |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent monitoring and heavy maintenance | Less intensive maintenance compared to kiln drive |
Introduction to Kiln Drive and Raw Mill Drive
Kiln Drive and Raw Mill Drive are essential components in cement manufacturing, with the Kiln Drive powering the rotary kiln to facilitate the high-temperature processing of raw materials. Raw Mill Drive operates the raw mill, grinding raw materials into fine powder for kiln feed. Understanding their roles helps optimize your plant's efficiency and maintain consistent production quality.
Core Functions: Kiln Drive vs Raw Mill Drive
Kiln drives primarily regulate the rotation of the rotary kiln, ensuring consistent heating for efficient clinker production in cement manufacturing. Raw mill drives control the grinding process of raw materials, optimizing particle size for proper chemical reactions during clinker formation. Both systems rely on robust motor and gearbox assemblies but serve distinct roles in maintaining production quality and energy efficiency.
Key Components and Configurations
Kiln Drive systems typically include components such as a high-torque gear reducer, pinion, large diameter girth gear, and heavy-duty bearings designed to handle variable loads and high temperatures. Raw Mill Drive setups consist of a motor, gearbox, couplings, and a raw mill roller that operate under consistent load conditions and require precise speed control for uniform grinding. The kiln drive configuration emphasizes durability and torque transmission, while the raw mill drive focuses on fine adjustments and maintaining stable operation.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Kiln Drive systems typically consume higher energy due to the need to maintain continuous rotation of heavy rotary kilns at temperatures up to 1450degC, requiring robust motors and drives designed for high torque and durability. Raw Mill Drives operate at lower speeds with lower torque requirements, leading to relatively lower energy consumption and improved efficiency in grinding raw materials before kiln processing. Optimizing drive selection and implementing variable frequency drives (VFDs) in both systems significantly enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Operational Challenges and Solutions
Kiln Drive systems often face challenges such as high torque variations, thermal expansion effects, and alignment issues, requiring robust couplings and frequent maintenance to ensure reliability. Raw Mill Drives encounter operational difficulties including abrasive dust, heavy load fluctuations, and variable speed requirements, which demand specialized dust-proof seals, vibration monitoring, and advanced control systems. Implementing condition monitoring technologies and employing adaptive control strategies effectively mitigate downtime and enhance performance in both drive applications.
Maintenance Requirements and Best Practices
Kiln drive systems require frequent inspection and lubrication of gears and bearings to prevent overheating and misalignment, with emphasis on regular monitoring of coupling and pinion wear. Raw mill drives demand vigilant maintenance of heavy-duty gearboxes, ensuring proper oil level and contamination control to avoid premature failure under high torque loads. Best practices for both include scheduled downtime for thorough inspections, use of condition monitoring tools like vibration analysis, and adherence to manufacturer-recommended service intervals.
Performance Comparison and Optimization
Kiln Drive delivers high torque and steady rotation essential for clinker production, while Raw Mill Drive emphasizes variable speed control for efficient grinding of raw materials. Optimizing performance involves selecting the right motor technology and gear system to match each drive's load profile, ensuring energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. You can improve overall plant productivity by integrating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance tailored to the specific demands of Kiln and Raw Mill Drives.
Technological Innovations in Drive Systems
Kiln Drive and Raw Mill Drive have seen significant technological innovations, with advanced variable frequency drives (VFDs) enhancing energy efficiency and precise speed control in large-scale industrial applications. Kiln Drive systems integrate smart sensors and predictive maintenance algorithms to optimize thermal processing, reducing downtime and operational costs. Your facility benefits from these innovations by achieving smoother operation and longer component lifespan, boosting overall production reliability.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Kiln Drive and Raw Mill Drive systems adhere to stringent industry standards such as ISO 9001 and IEC guidelines to ensure operational safety and efficiency in cement manufacturing. Compliance with these standards mandates regular inspection, torque monitoring, and vibration analysis to prevent equipment failure and maintain optimal performance. Both drives must also meet environmental regulations on energy consumption and emissions, reinforcing sustainable industrial practices.
Future Trends in Cement Plant Drive Systems
Kiln Drive and Raw Mill Drive systems in cement plants are evolving with a focus on energy efficiency and automation, driven by advancements in variable frequency drives (VFDs) and predictive maintenance technologies. Future trends highlight the integration of smart sensors and AI-based control systems to optimize torque and reduce power consumption, enhancing operational reliability. Your cement plant's drive system can benefit significantly from these innovations by improving process stability and lowering overall maintenance costs.
Kiln Drive vs Raw Mill Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com