Polymer cement offers excellent adhesion and durability for various construction applications, making it ideal for reinforcing structures and waterproofing. Resin cement provides superior bond strength and chemical resistance, ensuring your dental restorations or precision assemblies remain securely fixed over time.
Table of Comparison
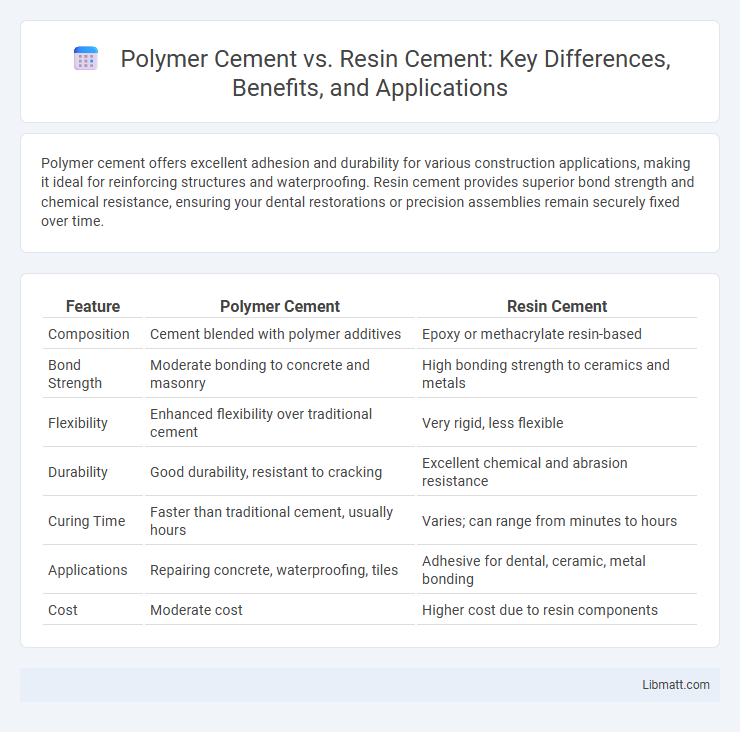
| Feature | Polymer Cement | Resin Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement blended with polymer additives | Epoxy or methacrylate resin-based |
| Bond Strength | Moderate bonding to concrete and masonry | High bonding strength to ceramics and metals |
| Flexibility | Enhanced flexibility over traditional cement | Very rigid, less flexible |
| Durability | Good durability, resistant to cracking | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Curing Time | Faster than traditional cement, usually hours | Varies; can range from minutes to hours |
| Applications | Repairing concrete, waterproofing, tiles | Adhesive for dental, ceramic, metal bonding |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to resin components |
Introduction to Polymer Cement and Resin Cement
Polymer cement is a composite material combining cement with polymers to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and durability in construction applications. Resin cement, made from synthetic resins such as epoxy or methacrylate, offers superior bonding strength, chemical resistance, and aesthetic versatility for both dental and industrial uses. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with polymer cement favored for structural repairs and resin cement preferred for precision bonding and high-performance finishes.
Composition and Chemical Structure
Polymer cement consists primarily of a blend of cementitious materials and synthetic polymers, enhancing flexibility and adhesion through a network of polymer chains interspersed within the cement matrix. Resin cement is formulated from methacrylate or epoxy resins, offering a dense, cross-linked polymer structure that provides superior bond strength and chemical resistance. Understanding the differences in chemical composition directly impacts your choice for durability and application-specific performance in construction or restoration projects.
Key Differences Between Polymer Cement and Resin Cement
Polymer cement differs from resin cement primarily in composition and application, with polymer cement combining cementitious materials and polymers for enhanced flexibility and durability, ideal for construction and repair works. Resin cement consists mainly of synthetic resins, providing superior adhesive strength and resistance to chemical and moisture degradation, often used in dental and industrial applications. The choice between polymer cement and resin cement depends on factors such as bonding requirements, environmental exposure, and mechanical stresses involved.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymer cement exhibits high compressive strength and excellent resistance to environmental factors, making it durable in harsh conditions such as freeze-thaw cycles and chemical exposure. Resin cement offers superior tensile strength and adhesion properties, providing enhanced bonding with various substrates and reducing the risk of cracking or debonding over time. Both materials ensure durability, but resin cement is preferred for applications requiring strong adhesion and flexibility, while polymer cement excels in structural reinforcement under compressive loads.
Bonding Mechanisms and Adhesion
Polymer cement relies on mechanical interlocking and chemical bonding through polymerization to create strong adhesion to substrates, whereas resin cement uses methacrylate-based resins that chemically bond to tooth structures via adhesive monomers. The adhesion of polymer cement depends largely on surface roughness and micromechanical retention, while resin cement offers superior bond strength through hybrid layer formation and resin infiltration into dentin collagen fibers. Your choice of cement should consider these bonding mechanisms to ensure optimal durability and longevity in restorative dental procedures.
Application Areas in Construction and Dentistry
Polymer cement is widely used in construction for applications such as concrete repair, tile adhesives, and waterproofing due to its excellent bonding and flexibility properties. Resin cement is primarily utilized in dentistry for bonding crowns, bridges, inlays, and orthodontic appliances because of its superior adhesive strength and esthetic versatility. Both materials offer distinct benefits tailored to their specific application needs in structural durability and dental precision.
Setting Time and Curing Processes
Polymer cement typically has a faster setting time, often curing within 1 to 2 hours depending on environmental conditions, which makes it suitable for quicker construction projects. Resin cement, on the other hand, requires a longer curing period that can range from several hours up to several days due to its chemical composition and polymerization process. The curing process of resin cement involves a chemical reaction triggered by mixing or light activation, leading to a stronger and more durable bond, whereas polymer cement cures primarily through hydration and evaporation.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polymer cement exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations due to its durable polymer matrix, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Resin cement offers excellent chemical resistance and strong adhesion, but can degrade under prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture without proper protective coatings. Your choice between polymer cement and resin cement should consider the specific environmental stresses of the application to ensure longevity and performance.
Cost and Availability
Polymer cement generally offers lower cost and wider availability compared to resin cement, making it a budget-friendly choice for many construction projects. Resin cement, while more expensive, provides superior durability and chemical resistance, often justifying the higher investment for specialized applications. Your decision depends on balancing upfront cost with long-term performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Cement: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right cement involves evaluating factors such as bonding strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance. Polymer cement offers enhanced adhesion and crack resistance suitable for dynamic structures, while resin cement provides superior chemical durability and aesthetics for precise applications like dental restorations. Consider project requirements, exposure conditions, and material compatibility to select the optimal cement type for long-lasting performance.
Polymer cement vs Resin cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com