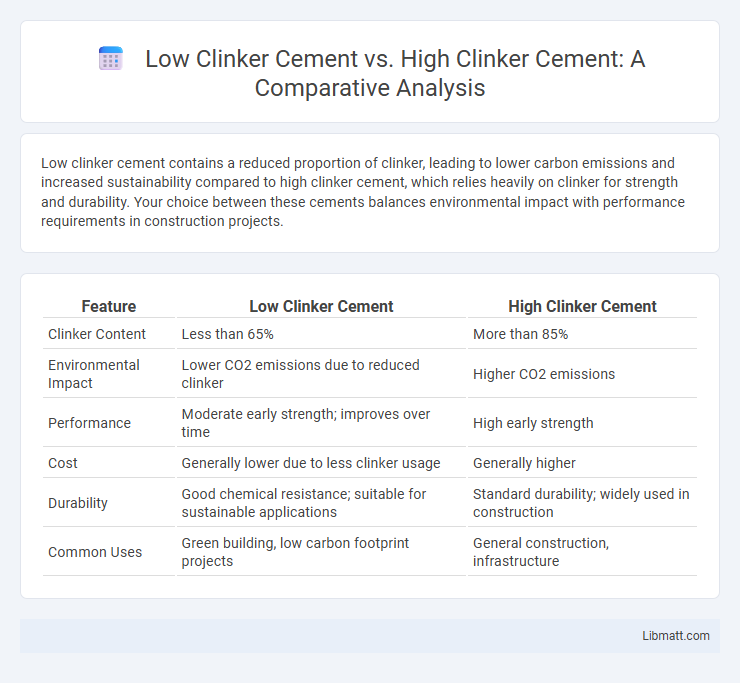
Low clinker cement contains a reduced proportion of clinker, leading to lower carbon emissions and increased sustainability compared to high clinker cement, which relies heavily on clinker for strength and durability. Your choice between these cements balances environmental impact with performance requirements in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low Clinker Cement | High Clinker Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Clinker Content | Less than 65% | More than 85% |
| Environmental Impact | Lower CO2 emissions due to reduced clinker | Higher CO2 emissions |
| Performance | Moderate early strength; improves over time | High early strength |
| Cost | Generally lower due to less clinker usage | Generally higher |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance; suitable for sustainable applications | Standard durability; widely used in construction |
| Common Uses | Green building, low carbon footprint projects | General construction, infrastructure |
Introduction to Clinker in Cement Production
Clinker, the primary component in cement production, forms by heating limestone and clay at high temperatures to create nodules essential for cement strength. Low clinker cement contains a reduced proportion of clinker, incorporating supplementary materials like fly ash or slag to improve sustainability and reduce carbon emissions. High clinker cement relies heavily on clinker content, ensuring higher strength but contributing more to environmental impact due to increased calcination and fuel consumption.
Defining Low Clinker Cement
Low clinker cement is characterized by a reduced proportion of clinker, typically less than 60%, replaced with supplementary cementitious materials such as fly ash, slag, or limestone. This formulation lowers CO2 emissions and enhances sustainability compared to high clinker cement, which contains over 90% clinker, resulting in higher energy consumption and environmental impact. Low clinker cement offers improved durability and reduced heat of hydration, making it suitable for eco-friendly construction projects.
Understanding High Clinker Cement
High Clinker Cement contains a higher percentage of clinker, typically around 95%, which results in faster hardening and higher early strength compared to Low Clinker Cement. This type of cement is ideal for construction projects requiring quick setting times and durable structures, especially in environments exposed to chemical attacks. You should choose High Clinker Cement when superior strength and rapid development of concrete properties are critical for your building needs.
Key Differences Between Low and High Clinker Cement
Low clinker cement contains a reduced proportion of clinker, typically below 65%, resulting in lower CO2 emissions and enhanced sustainability compared to high clinker cement, which has clinker content often exceeding 95%. High clinker cement offers higher early strength and faster setting times, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid strength development, whereas low clinker variants prioritize durability and environmental benefits through supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag. The key differences center on clinker percentage, environmental impact, strength development, and cost efficiency, influencing their selection based on project requirements and ecological considerations.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
Low clinker cement reduces carbon dioxide emissions significantly by lowering the amount of clinker, the most energy-intensive component, in its composition, enhancing sustainability in construction projects. High clinker cement generates higher emissions due to increased calcination and fossil fuel consumption during clinker production, contributing more to environmental pollution. You can improve your project's environmental footprint by choosing low clinker cement, which supports reduced greenhouse gas emissions and promotes sustainable building practices.
Performance and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Low clinker cement exhibits enhanced durability and reduced heat of hydration compared to high clinker cement, making it ideal for large-scale concrete projects and environments prone to thermal cracking. High clinker cement delivers superior early strength and rapid setting times, which benefit construction schedules requiring quick load-bearing capacity. Your choice between these cements should balance performance needs with environmental considerations, as low clinker cement also offers lower carbon emissions during production.
Cost Implications of Low vs High Clinker Cement
Low clinker cement generally offers lower production costs due to reduced energy consumption and decreased raw material expenses, which can directly benefit your project budget. High clinker cement, while typically stronger and faster-setting, involves higher production costs and carbon emissions, translating into increased overall price. Evaluating the balance between cost savings and performance requirements is essential when choosing between low and high clinker cement for construction projects.
Applications and Suitability in Construction
Low clinker cement is ideal for large-scale infrastructure projects requiring sustainability and reduced carbon emissions, such as dams and bridges, due to its lower heat of hydration and enhanced durability. High clinker cement, with its higher strength and faster setting properties, is suitable for high-performance applications like highways, precast concrete, and structural elements requiring rapid load-bearing capacity. Selection depends on the balance between environmental impact, mechanical properties, and project-specific performance criteria.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Low clinker cement typically meets environmental regulatory standards by producing lower CO2 emissions during manufacturing, aligning with green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM. High clinker cement must comply with traditional construction codes and standards such as ASTM C150 or EN 197-1, focusing on strength and durability requirements. Your project's certification goals will influence the choice between low clinker cement for sustainability compliance or high clinker cement for conventional regulatory acceptance.
Future Trends in Cement Manufacturing
Low Clinker Cement, characterized by a reduced clinker content and higher supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), is gaining traction due to its lower carbon footprint compared to traditional High Clinker Cement. Future trends in cement manufacturing emphasize sustainability, leading to increased adoption of low clinker blends to meet stricter environmental regulations and reduce CO2 emissions. Your choice of cement will likely shift toward low clinker options as the industry innovates with alternative binders and energy-efficient production technologies.
Low Clinker Cement vs High Clinker Cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com