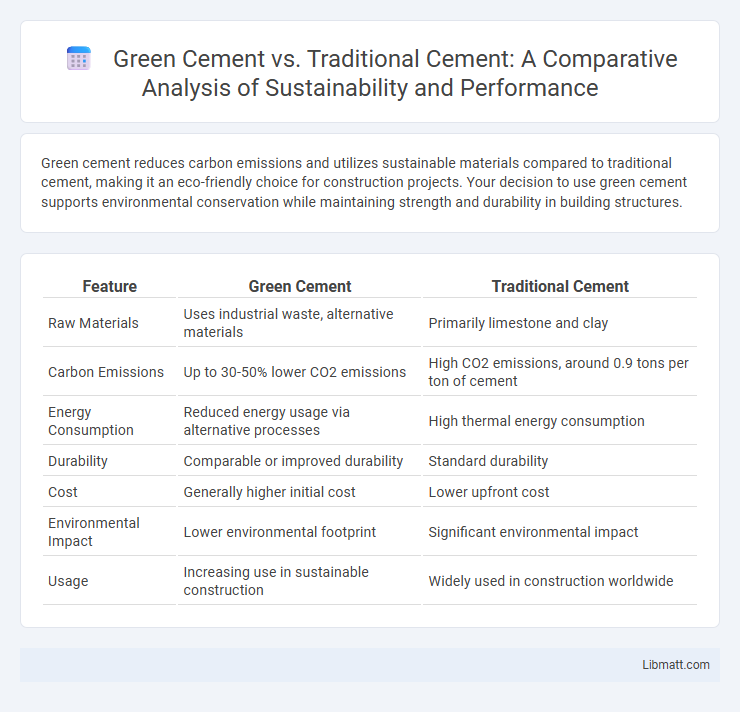
Green cement reduces carbon emissions and utilizes sustainable materials compared to traditional cement, making it an eco-friendly choice for construction projects. Your decision to use green cement supports environmental conservation while maintaining strength and durability in building structures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Cement | Traditional Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Uses industrial waste, alternative materials | Primarily limestone and clay |
| Carbon Emissions | Up to 30-50% lower CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions, around 0.9 tons per ton of cement |
| Energy Consumption | Reduced energy usage via alternative processes | High thermal energy consumption |
| Durability | Comparable or improved durability | Standard durability |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower environmental footprint | Significant environmental impact |
| Usage | Increasing use in sustainable construction | Widely used in construction worldwide |
Understanding Green Cement: An Overview
Green cement is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional cement, produced with lower carbon emissions and incorporating industrial by-products such as fly ash and slag. Its formulation reduces reliance on clinker, the most carbon-intensive component in conventional cement, thereby minimizing environmental impact. Green cement maintains comparable strength and durability while promoting sustainability in construction projects.
What Defines Traditional Cement?
Traditional cement is primarily composed of clinker produced by heating limestone and clay at high temperatures, with Portland cement being the most common type. It releases significant amounts of CO2 during production, contributing approximately 8% of global carbon emissions. Its strength, durability, and widespread availability make it the standard material in construction despite environmental concerns.
Raw Materials Comparison: Green vs Traditional Cement
Green cement utilizes industrial by-products like fly ash and slag as raw materials, significantly reducing the reliance on conventional limestone and clay found in traditional cement production. This substitution lowers carbon emissions and conserves natural resources by decreasing the need for extensive quarrying. Your choice of green cement supports sustainable practices while maintaining comparable strength and durability to traditional cement options.
Manufacturing Processes: Sustainability and Efficiency
Green cement manufacturing utilizes alternative raw materials like industrial byproducts and low-carbon binders, significantly reducing CO2 emissions compared to traditional cement processes that rely heavily on limestone calcination. The sustainability of green cement is enhanced by energy-efficient technologies such as waste heat recovery and lower temperature kiln operations, which optimize resource use and decrease environmental impact. Your choice of green cement supports a cleaner production cycle that promotes circular economy principles while maintaining comparable performance and durability.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Analysis
Green cement significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to traditional cement by utilizing alternative raw materials and energy-efficient processes that lower CO2 emissions by up to 30-50%. Traditional cement production involves the calcination of limestone, releasing approximately 0.9 tons of CO2 per ton of cement produced, contributing substantially to global greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing green cement for Your construction projects helps minimize environmental impact while supporting sustainable development goals.
Performance and Durability Differences
Green cement exhibits comparable or enhanced performance and durability compared to traditional cement due to its lower carbon footprint and use of supplementary materials like fly ash or slag. Studies show green cement's improved resistance to chemical attacks, reduced permeability, and enhanced long-term strength development. Traditional cement typically has faster initial setting times, but green cement's sustainable additives contribute to superior durability in aggressive environments.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Long-term Savings
Green cement typically has a higher upfront cost compared to traditional cement due to the use of eco-friendly materials and advanced manufacturing processes. However, long-term savings are realized through reduced energy consumption, lower carbon taxes, and improved durability that decreases maintenance expenses. Economic evaluations highlight that green cement becomes more cost-effective over the lifecycle of construction projects by mitigating environmental impact and enhancing structural longevity.
Adoption Challenges and Market Trends
Green cement faces adoption challenges such as higher production costs, limited availability of raw materials like fly ash and slag, and a lack of standardized regulations. Market trends indicate increasing demand driven by environmental regulations, growing awareness of carbon footprint reduction, and innovations in low-carbon technologies among construction firms. Regional disparities exist, with Europe and Asia leading adoption due to stricter emission targets, while emerging markets show slower uptake due to cost sensitivity and infrastructure constraints.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Green cement complies with evolving regulatory standards such as the ASTM C1157 and European EN 197-1 that emphasize reduced carbon footprints and sustainable materials. Certifications like LEED and Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) validate the eco-friendly properties of green cement, promoting its use in sustainable construction projects. Traditional cement primarily meets established strength and durability codes but generally lacks specific environmental certifications that highlight greenhouse gas reductions.
Future Outlook: The Role of Green Cement in Construction
Green cement is poised to transform the construction industry by significantly reducing carbon emissions, a key factor as global regulations tighten around sustainability. Advances in materials science enable green cement to achieve comparable strength and durability to traditional Portland cement while utilizing industrial byproducts and alternative binders. Adoption of green cement supports eco-friendly building practices and aligns with the rising demand for low-carbon infrastructure development worldwide.
Green Cement vs Traditional Cement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com