Refractory bricks offer superior structural stability and precise shaping for high-temperature applications, while castables provide versatile installation and seamless joints through their moldable, monolithic form. Your choice depends on the specific thermal and mechanical demands of your project, balancing durability with ease of application.
Table of Comparison
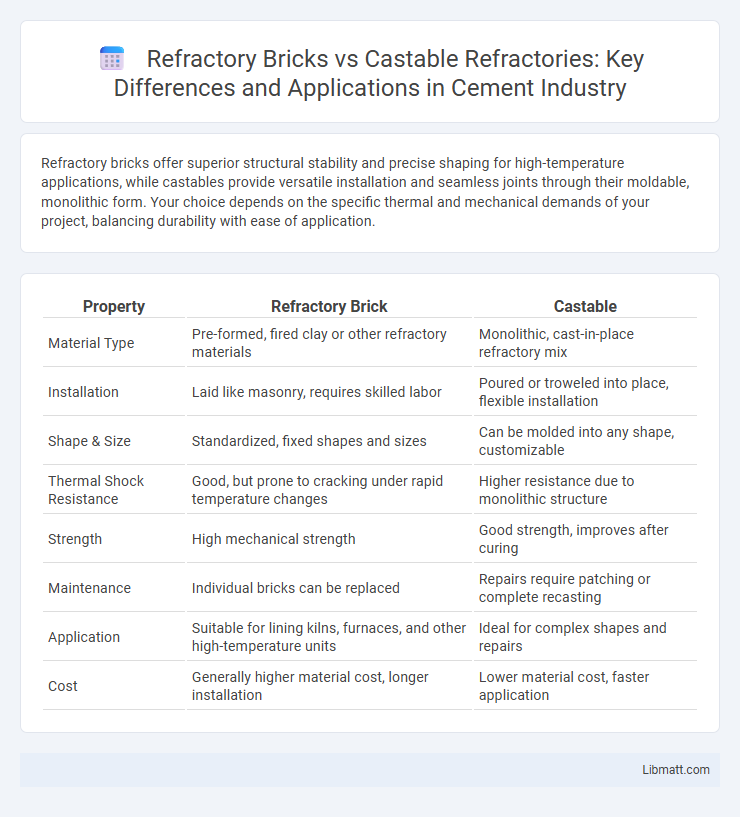
| Property | Refractory Brick | Castable |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Pre-formed, fired clay or other refractory materials | Monolithic, cast-in-place refractory mix |
| Installation | Laid like masonry, requires skilled labor | Poured or troweled into place, flexible installation |
| Shape & Size | Standardized, fixed shapes and sizes | Can be molded into any shape, customizable |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good, but prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes | Higher resistance due to monolithic structure |
| Strength | High mechanical strength | Good strength, improves after curing |
| Maintenance | Individual bricks can be replaced | Repairs require patching or complete recasting |
| Application | Suitable for lining kilns, furnaces, and other high-temperature units | Ideal for complex shapes and repairs |
| Cost | Generally higher material cost, longer installation | Lower material cost, faster application |
Introduction to Refractory Brick and Castable
Refractory bricks, also known as firebricks, are pre-formed ceramic blocks designed to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, commonly used in furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces. Castable refractories, composed of a mix of aggregates, binders, and additives, are moldable materials that harden in place, offering flexibility for custom shapes and repairs in high-temperature environments. Your choice between refractory bricks and castables depends on the specific thermal resistance, installation method, and structural requirements of your project.
Key Differences Between Refractory Brick and Castable
Refractory brick consists of pre-shaped, fired blocks designed for specific thermal and mechanical properties, offering precise dimensions and easy installation in kilns and furnaces. Castable refractory is a moldable, unshaped material that sets in place and provides greater flexibility for complex shapes and repairs, allowing you to customize linings without joint weaknesses. Key differences include installation methods, heat resistance, mechanical strength, and adaptability to irregular surfaces, which determine the optimal choice for your high-temperature applications.
Composition and Material Properties
Refractory bricks are made primarily from pre-formed alumina, silica, or fireclay materials that undergo high-temperature firing to achieve durability and thermal stability, offering excellent resistance to abrasion and corrosion. Castable refractories consist of a blend of refractory aggregates, binders like calcium aluminate cement, and additives that cure in place to form a monolithic, seamless structure with strong thermal shock resistance and customizable shapes. The key material differences influence their application, with bricks providing consistent density and mechanical strength while castables offer flexibility in installation and repair, adapting to complex geometries and thermal expansion requirements.
Installation Methods: Bricks vs Castables
Refractory bricks require precise stacking and mortar application during installation, ensuring uniform joints and structural integrity for thermal resistance. Castable refractories, poured as a slurry into molds or forms, conform to complex shapes and harden in place, reducing installation time and labor. Your choice impacts installation efficiency and the longevity of high-temperature linings in furnaces or kilns.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Refractory bricks offer superior thermal performance due to their dense structure and low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-temperature applications requiring long-term heat resistance. Castables provide flexibility in shaping and installation but generally exhibit higher thermal conductivity and lower heat resistance compared to refractory bricks. Thermal stability of refractory bricks typically exceeds 1500degC, whereas castables are effective up to around 1400degC, influencing material selection based on operational temperature demands.
Durability and Service Life Comparison
Refractory bricks offer superior durability due to their dense, pre-fired composition that provides consistent thermal resistance and mechanical strength, resulting in a longer service life in high-temperature environments. Castable refractories, while more versatile and easier to shape in situ, may exhibit lower durability under extreme thermal cycling and mechanical stress, potentially reducing their service longevity. Selecting between refractory brick and castable often depends on specific operational demands, with bricks favored for long-term, high-stress applications requiring extended service life.
Application Areas for Refractory Brick
Refractory bricks are extensively used in high-temperature applications such as furnace linings, kilns, and fireplaces where structural strength and thermal stability are critical. These bricks provide excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for steelmaking, glass production, and petrochemical industries. Their precise shapes and sizes also facilitate easy installation in complex structural designs requiring durability under extreme heat conditions.
Application Areas for Refractory Castable
Refractory castables are extensively used in steelmaking furnaces, cement kilns, and petrochemical reactors thanks to their excellent thermal shock resistance and ease of installation. These materials provide reliable lining solutions in high-temperature environments such as power plants, incinerators, and glass melting furnaces, ensuring durability under extreme operating conditions. Their versatility allows for customized formulations tailored to specific thermal and mechanical requirements across various industrial sectors.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Refractory bricks generally have a higher initial cost due to manufacturing and installation complexity, but offer durability and lower maintenance expenses over time. Castable refractories provide cost-effective flexibility for irregular shapes and quicker installation, reducing labor costs but may require more frequent upkeep. Your budgeting should weigh upfront expenses against long-term performance and maintenance to determine the optimal choice for specific industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right refractory material involves evaluating thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Refractory bricks offer precise shapes and higher durability for structural applications, whereas castables provide flexibility in complex geometries and faster installation times. Cost-effectiveness, maintenance requirements, and specific operational temperatures are critical factors influencing the choice between refractory bricks and castable materials.
Refractory Brick vs Castable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com