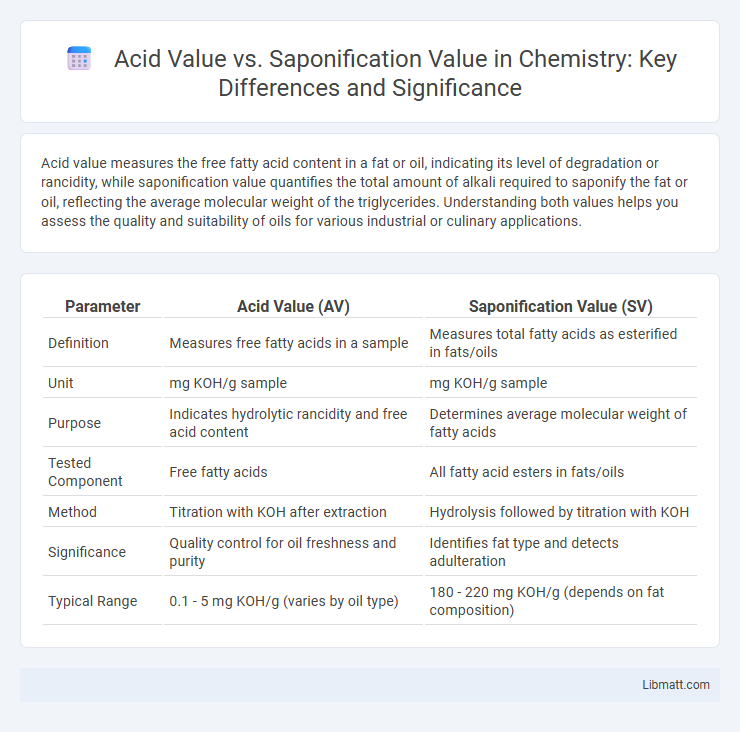
Acid value measures the free fatty acid content in a fat or oil, indicating its level of degradation or rancidity, while saponification value quantifies the total amount of alkali required to saponify the fat or oil, reflecting the average molecular weight of the triglycerides. Understanding both values helps you assess the quality and suitability of oils for various industrial or culinary applications.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Acid Value (AV) | Saponification Value (SV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures free fatty acids in a sample | Measures total fatty acids as esterified in fats/oils |
| Unit | mg KOH/g sample | mg KOH/g sample |
| Purpose | Indicates hydrolytic rancidity and free acid content | Determines average molecular weight of fatty acids |
| Tested Component | Free fatty acids | All fatty acid esters in fats/oils |
| Method | Titration with KOH after extraction | Hydrolysis followed by titration with KOH |
| Significance | Quality control for oil freshness and purity | Identifies fat type and detects adulteration |
| Typical Range | 0.1 - 5 mg KOH/g (varies by oil type) | 180 - 220 mg KOH/g (depends on fat composition) |
Introduction to Acid Value and Saponification Value
Acid value measures the amount of free fatty acids in a fat or oil, indicating its degree of hydrolysis and potential rancidity. Saponification value quantifies the total amount of potassium hydroxide needed to saponify a fat or oil sample, reflecting the average molecular weight of the fatty acids present. These values are critical for assessing the quality and suitability of oils in industries such as cosmetics, food, and soap manufacturing.
Defining Acid Value: Meaning and Importance
Acid value measures the amount of free fatty acids present in fats or oils, indicating the degree of hydrolysis or spoilage. It plays a crucial role in assessing the quality and stability of edible oils, lubricants, and biodiesel by revealing their acidity level. Understanding acid value helps manufacturers ensure product safety, optimize processing conditions, and maintain desired shelf life.
Understanding Saponification Value: Concept and Significance
Saponification value measures the amount of alkali needed to completely saponify a fat or oil, reflecting its average molecular weight and fatty acid chain length. This value is crucial in determining the quality and suitability of oils for soap making and other industrial applications, as it helps you understand the fat's chemical properties. Unlike the acid value, which indicates free fatty acid content, saponification value provides insight into the entire fat composition and potential yield of soap.
Chemical Principles Behind Acid Value and Saponification Value
Acid value measures the free fatty acids present in a fat or oil by quantifying the amount of potassium hydroxide (KOH) required to neutralize these acids, indicating hydrolytic rancidity and quality degradation. Saponification value represents the total amount of KOH necessary to completely saponify the triglycerides and free fatty acids in a sample, reflecting the average molecular weight and chain length of the lipids. Both values rely on titration with standardized alkali but differ in chemical focus: acid value targets free acids, while saponification value assesses total ester content.
Key Differences Between Acid Value and Saponification Value
Acid value measures the free fatty acid content in fats or oils, indicating the degree of hydrolysis, while saponification value quantifies the total amount of alkali required to saponify both free and bound fatty acids in a fat or oil sample. Acid value is crucial for assessing oil quality and rancidity, whereas saponification value helps determine the average molecular weight of fatty acids and the type of fat. Understanding these differences is essential for quality control in industries like soap manufacturing, food production, and biodiesel processing.
Factors Affecting Acid and Saponification Values
The acid value is influenced by factors such as the degree of hydrolysis, storage conditions, and the presence of free fatty acids, which indicate the extent of fat deterioration. Saponification value depends on the average molecular weight of the fatty acids and the length of the carbon chains in the triglycerides, revealing information about the oil or fat composition. Understanding these variables helps you assess the quality and purity of fats and oils accurately.
Methods for Measuring Acid and Saponification Values
Acid value is measured by titrating the free fatty acids in an oil or fat sample with a standardized alkali solution, typically using phenolphthalein as an indicator to determine the point at which neutralization occurs. Saponification value is determined by refluxing the sample with a known excess of potassium hydroxide, then titrating the remaining alkali with a standard acid to calculate the amount of alkali consumed in soap formation. Understanding these methods helps Your lab accurately assess oil quality and purity through precise chemical analysis.
Applications in Industry: Oils, Fats, and Soap Manufacturing
Acid value and saponification value are critical parameters in the oils, fats, and soap manufacturing industries, as they determine the quality, purity, and usability of raw materials and finished products. Acid value measures free fatty acid content, indicating oil degradation and suitability for food or cosmetic applications, while saponification value reflects the average molecular weight of fatty acids, essential for formulating soaps with proper hardness and cleansing properties. Understanding these values ensures your production processes yield consistent, high-quality products compliant with industry standards.
Interpreting Results: Quality Control Implications
Acid value indicates the free fatty acid content, revealing the degree of lipid hydrolysis and rancidity, while saponification value measures the average molecular weight of fatty acids in fats and oils. High acid values suggest poor quality or degraded oil, affecting your product's stability and sensory attributes. Saponification value helps ensure consistency in formulation by confirming the fat's fatty acid profile, critical for quality control in manufacturing processes.
Summary: Choosing the Right Value for Your Analysis
Acid value measures the free fatty acid content in a fat or oil, indicating its purity and degree of hydrolysis, while saponification value quantifies the total fatty acid content by measuring the amount of alkali required to saponify the fat. Selecting between acid value and saponification value depends on whether your analysis aims to assess oil quality, detect rancidity, or determine average molecular weight of triglycerides. Understanding these values ensures accurate evaluation of your sample's composition and suitability for intended applications.
Acid value vs saponification value Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com