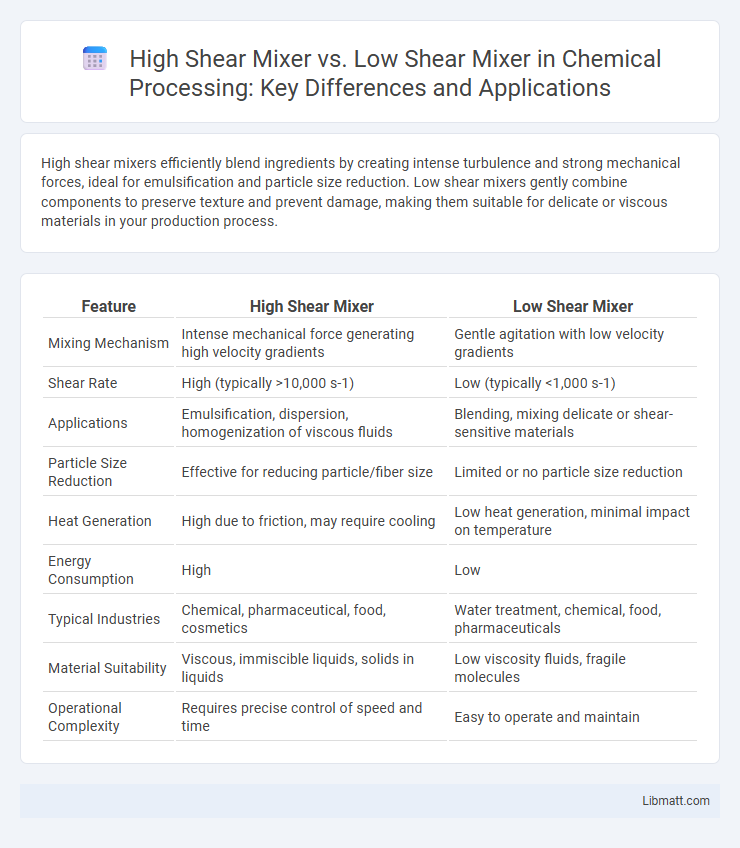
High shear mixers efficiently blend ingredients by creating intense turbulence and strong mechanical forces, ideal for emulsification and particle size reduction. Low shear mixers gently combine components to preserve texture and prevent damage, making them suitable for delicate or viscous materials in your production process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Shear Mixer | Low Shear Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing Mechanism | Intense mechanical force generating high velocity gradients | Gentle agitation with low velocity gradients |
| Shear Rate | High (typically >10,000 s-1) | Low (typically <1,000 s-1) |
| Applications | Emulsification, dispersion, homogenization of viscous fluids | Blending, mixing delicate or shear-sensitive materials |
| Particle Size Reduction | Effective for reducing particle/fiber size | Limited or no particle size reduction |
| Heat Generation | High due to friction, may require cooling | Low heat generation, minimal impact on temperature |
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Typical Industries | Chemical, pharmaceutical, food, cosmetics | Water treatment, chemical, food, pharmaceuticals |
| Material Suitability | Viscous, immiscible liquids, solids in liquids | Low viscosity fluids, fragile molecules |
| Operational Complexity | Requires precise control of speed and time | Easy to operate and maintain |
Overview of High Shear and Low Shear Mixers
High shear mixers operate at high rotational speeds to generate intense mechanical energy, efficiently breaking down particles and dispersing ingredients in emulsions and suspensions. Low shear mixers function with gentle agitation, preserving the structural integrity of delicate materials and preventing over-processing in applications like blending viscous liquids or suspensions. Selection depends on product formulation requirements, as high shear mixers excel in creating fine emulsions, while low shear mixers are ideal for uniform mixing without damaging sensitive components.
Key Operational Differences
High shear mixers generate intense mechanical forces using rapidly rotating blades, promoting rapid emulsification, dispersion, and particle size reduction, ideal for viscous and complex formulations. Low shear mixers operate at slower speeds, creating gentle agitation suitable for blending delicate ingredients without altering their structure or causing foam formation. The operational distinction lies in shear rate and mixing intensity, impacting processing time, energy consumption, and suitability for specific applications like pharmaceutical emulsions or food batter preparation.
Applications of High Shear Mixers
High shear mixers are essential in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries for emulsifying, homogenizing, and dispersing viscous materials and powders into liquids. They efficiently reduce particle size and improve product texture and stability in applications such as creams, lotions, sauces, and adhesives. High shear mixers excel at handling tough mixing tasks that require intense mechanical force to achieve uniform consistency and prevent sedimentation.
Applications of Low Shear Mixers
Low shear mixers are ideal for delicate applications such as emulsifying, blending, and dispersing fragile ingredients in industries like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing. They preserve product integrity by minimizing air incorporation and shear-induced damage, ensuring consistent texture and quality in sensitive formulations. These mixers excel in homogenizing viscous liquids and suspensions without compromising stability or molecular structure.
Advantages of High Shear Mixing
High shear mixers provide rapid and efficient particle size reduction, resulting in finer emulsions and improved product uniformity. Their ability to generate intense shear forces enhances mixing speed and promotes better dispersion of ingredients in challenging formulations. This makes high shear mixers ideal for industries requiring consistent texture and stability, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing.
Benefits of Low Shear Mixing
Low shear mixing preserves the integrity of delicate ingredients by minimizing damage from intense agitation, making it ideal for sensitive emulsions, suspensions, and biological materials. This gentle mixing approach enhances product stability, uniformity, and texture, reducing risks of over-processing or ingredient breakdown. Your formulations will benefit from improved consistency and extended shelf life, especially in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food applications where ingredient sensitivity is crucial.
Energy Consumption Comparison
High shear mixers generally consume more energy than low shear mixers due to their intense rotor-stator mechanisms creating rapid fluid motion and turbulence. Low shear mixers operate at slower speeds with less mechanical force, resulting in significantly lower power usage and reduced energy costs. Energy consumption differences are critical for industries aiming to optimize processing efficiency and operational expenses.
Mixing Efficiency and Homogeneity
High shear mixers deliver superior mixing efficiency by rapidly breaking down particles and ensuring uniform dispersion, ideal for processes requiring fine emulsions or suspensions. Low shear mixers operate at gentler speeds, preserving ingredient integrity but often resulting in longer mixing times and less homogeneity in complex mixtures. Choosing the right mixer for your process depends on balancing the need for thorough blending with the sensitivity of your materials to shear forces.
Equipment Cost Analysis
High shear mixers generally entail higher equipment costs due to their complex design and powerful motor requirements, making them suitable for precise emulsification or homogenization tasks. Low shear mixers offer a cost-effective alternative, with simpler construction and lower maintenance expenses, ideal for gentle blending or suspensions. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints against processing needs and product specifications.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Application
High shear mixers are ideal for applications requiring rapid emulsification, particle size reduction, and uniform blending, especially in pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries. Low shear mixers excel in gently blending delicate materials without compromising texture or structural integrity, making them suitable for viscous liquids and sensitive ingredients. Selecting the right mixer depends on factors such as material viscosity, desired mixing speed, and product sensitivity to shear forces.
High shear mixer vs low shear mixer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com