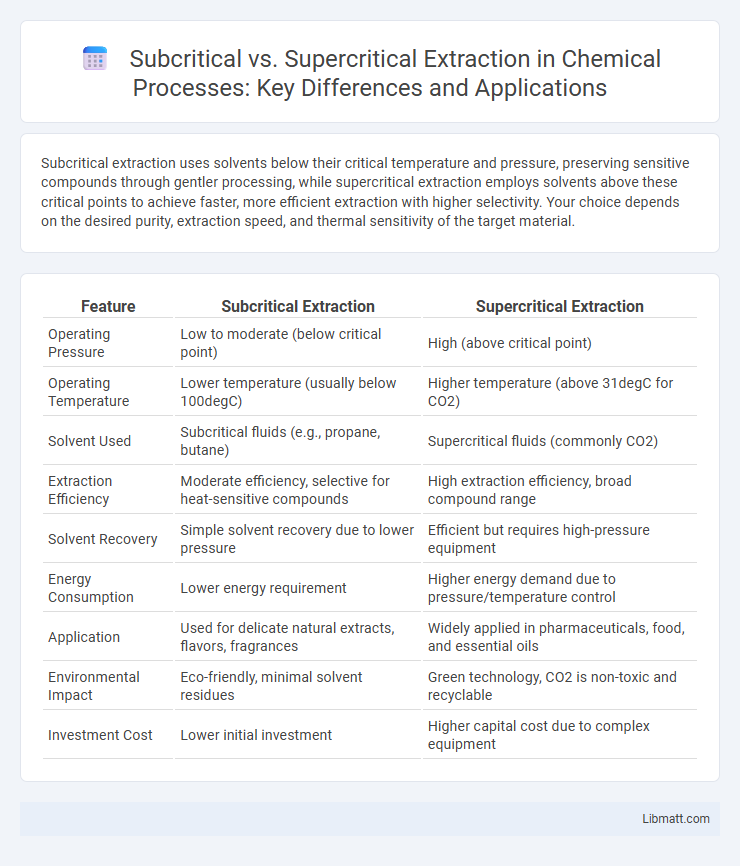
Subcritical extraction uses solvents below their critical temperature and pressure, preserving sensitive compounds through gentler processing, while supercritical extraction employs solvents above these critical points to achieve faster, more efficient extraction with higher selectivity. Your choice depends on the desired purity, extraction speed, and thermal sensitivity of the target material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Subcritical Extraction | Supercritical Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure | Low to moderate (below critical point) | High (above critical point) |
| Operating Temperature | Lower temperature (usually below 100degC) | Higher temperature (above 31degC for CO2) |
| Solvent Used | Subcritical fluids (e.g., propane, butane) | Supercritical fluids (commonly CO2) |
| Extraction Efficiency | Moderate efficiency, selective for heat-sensitive compounds | High extraction efficiency, broad compound range |
| Solvent Recovery | Simple solvent recovery due to lower pressure | Efficient but requires high-pressure equipment |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy requirement | Higher energy demand due to pressure/temperature control |
| Application | Used for delicate natural extracts, flavors, fragrances | Widely applied in pharmaceuticals, food, and essential oils |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, minimal solvent residues | Green technology, CO2 is non-toxic and recyclable |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher capital cost due to complex equipment |
Introduction to Extraction Techniques
Subcritical extraction utilizes solvents at temperatures below their critical point to selectively dissolve target compounds, preserving thermolabile substances and optimizing flavor profiles. Supercritical extraction employs fluids above their critical temperature and pressure, enhancing solvent diffusivity and penetration, enabling efficient recovery of bioactive compounds with minimal solvent residue. Both techniques offer tunable parameters that maximize extraction yields and purity for pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and food industries.
Defining Subcritical Extraction
Subcritical extraction utilizes solvents at temperatures and pressures below their critical point, allowing selective compound extraction with minimal thermal degradation. Commonly employed solvents include CO2, which remains in a liquid state under subcritical conditions, ensuring efficient recovery of thermally sensitive bioactive compounds. This method is especially beneficial in extracting flavors, fragrances, and herbal constituents, preserving their integrity compared to the more intensive supercritical extraction process.
Explaining Supercritical Extraction
Supercritical extraction utilizes a fluid above its critical temperature and pressure, combining gas-like diffusion properties with liquid-like solvating power to efficiently separate target compounds from complex matrices. This method offers precise control over selectivity and solubility, often using supercritical CO2 for its non-toxic, tunable, and environmentally friendly characteristics. Your extraction process benefits from higher purity and reduced solvent residues compared to subcritical extraction, which operates below the critical point with less efficient mass transfer.
Key Differences in Mechanisms
Subcritical extraction uses solvents at temperatures and pressures below their critical point, preserving heat-sensitive compounds through gentle dissolution, whereas supercritical extraction operates above critical temperature and pressure, utilizing supercritical fluids with unique diffusivity and solvating power to penetrate matrices efficiently. The mechanism of subcritical extraction relies heavily on liquid solvent properties, while supercritical extraction combines gas-like diffusion and liquid-like solvation for enhanced extraction efficiency. Your choice between these methods depends on the target compound's stability and extraction speed requirements.
Solvent Types and Their Roles
Subcritical extraction utilizes solvents such as propane or butane at temperatures and pressures below their critical points, enabling selective extraction of target compounds with minimal degradation. Supercritical extraction predominantly uses supercritical carbon dioxide, valued for its tunable solvent power and non-toxic, environmentally friendly properties, facilitating efficient separation of bioactive constituents. The solvent type in each method critically influences extraction selectivity, yield, and preservation of thermolabile compounds.
Efficiency and Yield Comparison
Subcritical extraction operates at lower temperatures and pressures, preserving sensitive compounds and delivering high-quality extracts with moderate efficiency. Supercritical extraction, using supercritical CO2, achieves higher yields and faster extraction due to superior solvent properties and deeper matrix penetration. Your choice depends on balancing extract quality against extraction speed and overall yield requirements.
Applications Across Industries
Subcritical extraction is widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries for extracting delicate compounds like flavors, fragrances, and bioactive substances due to its lower temperature and pressure conditions, preserving product integrity. Supercritical extraction finds extensive applications in the environmental, chemical, and nutraceutical sectors, enabling efficient extraction of essential oils, cannabinoids, and pollutants with superior solvent power and selectivity at elevated pressures and temperatures. Both techniques enhance sustainability and product purity, tailoring solvent properties to specific industrial needs.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Subcritical extraction uses lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption and minimizing the risk of explosion compared to supercritical extraction, which operates at higher pressures and can pose increased safety hazards. Environmentally, subcritical methods often utilize safer solvents like CO2 or hydrocarbons with less environmental impact, whereas supercritical extraction requires careful handling of pressurized gases to prevent leaks and accidents. Choosing subcritical extraction can enhance your process safety and lower environmental footprint while maintaining effective extraction performance.
Cost and Equipment Implications
Subcritical extraction generally involves lower operational costs due to reduced pressure and temperature requirements, leading to less expensive and simpler equipment compared to supercritical extraction systems. Supercritical extraction demands high-pressure vessels and advanced control units, significantly increasing initial capital investment and maintenance expenses. Companies must weigh these cost and equipment implications against desired extraction efficiency and product quality when selecting between the two methods.
Choosing the Best Extraction Method
Choosing the best extraction method depends on the compound's sensitivity and desired purity; subcritical extraction operates at lower temperatures and pressures, preserving heat-sensitive compounds but often with longer extraction times and lower yields. Supercritical extraction uses CO2 at high pressure and temperature, achieving higher efficiency and selectivity for non-polar compounds, making it ideal for extracting essential oils, cannabinoids, and flavors. Process scalability, environmental impact, and solvent recovery capabilities also play critical roles in determining the optimal extraction technique for industrial applications.
subcritical extraction vs supercritical extraction Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com