Pneumatic conveying uses air pressure or vacuum to move bulk materials through pipelines, offering a clean, dust-free solution ideal for fragile or fine powders. Mechanical conveying relies on equipment like belts, screws, or conveyors to transport materials, providing efficient handling for heavier, coarser products over shorter distances.
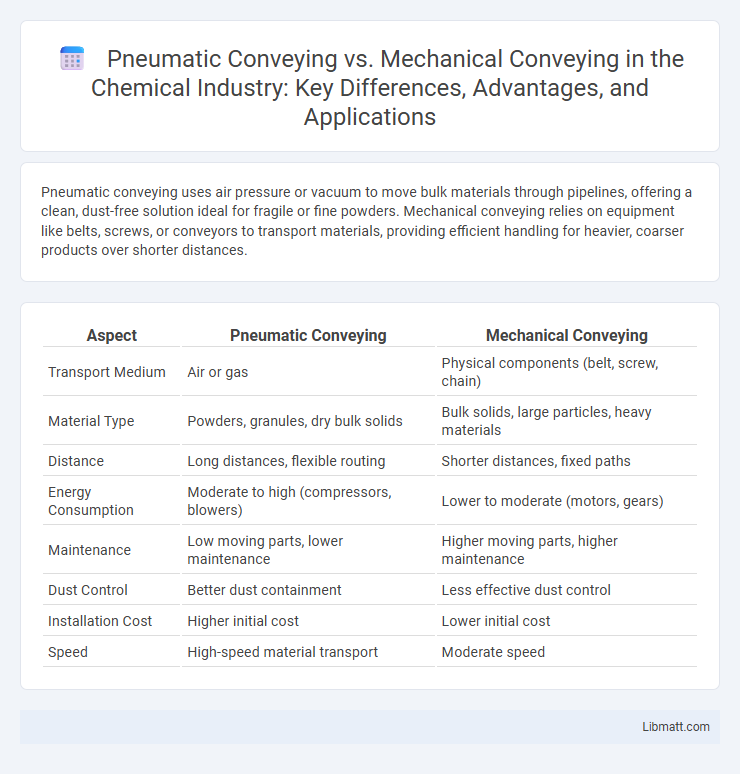
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pneumatic Conveying | Mechanical Conveying |
|---|---|---|
| Transport Medium | Air or gas | Physical components (belt, screw, chain) |
| Material Type | Powders, granules, dry bulk solids | Bulk solids, large particles, heavy materials |
| Distance | Long distances, flexible routing | Shorter distances, fixed paths |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate to high (compressors, blowers) | Lower to moderate (motors, gears) |
| Maintenance | Low moving parts, lower maintenance | Higher moving parts, higher maintenance |
| Dust Control | Better dust containment | Less effective dust control |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Speed | High-speed material transport | Moderate speed |
Introduction to Material Conveying Systems
Material conveying systems include pneumatic and mechanical conveying, each suited for specific applications and materials. Pneumatic conveying uses air pressure or vacuum to transport powders and granules through pipelines, offering flexibility and enclosed operation to reduce contamination. Mechanical conveying employs belts, screws, or chains to move bulk solids with high efficiency for heavier or abrasive materials, ensuring reliable handling in various industries.
Overview of Pneumatic Conveying
Pneumatic conveying systems transport bulk materials through pipelines using a controlled flow of air or gas, offering high flexibility and enclosed handling to reduce contamination. These systems are ideal for powders, granules, and other lightweight materials, enabling efficient transfer over long distances with minimal product degradation. Pneumatic conveying outperforms mechanical methods in terms of dust control and maintenance requirements, especially in sensitive industrial applications.
Overview of Mechanical Conveying
Mechanical conveying utilizes equipment such as belts, screw conveyors, and bucket elevators to transport bulk materials through physical force, offering high capacity and energy efficiency for heavy and abrasive substances. This method provides precise control over material flow and minimizes product degradation, making it ideal for handling fragile or dense materials. Mechanical conveyors are widely used in industries like mining, agriculture, and manufacturing where continuous, reliable bulk transport is essential.
Key Differences Between Pneumatic and Mechanical Conveying
Pneumatic conveying transports bulk materials using air or gas flow, making it ideal for lightweight or abrasive particles, while mechanical conveying relies on physical components like belts, chains, or screw conveyors to move materials. Pneumatic systems offer flexibility in layout and reduced contamination risk, whereas mechanical conveying provides higher capacity and is better suited for heavy, dense materials. Understanding these key differences helps you select the most efficient conveying method tailored to your material handling needs.
Material Compatibility and Limitations
Pneumatic conveying suits fine, abrasive, or fragile materials by using airflow to transport them gently through pipelines, minimizing damage and contamination. Mechanical conveying is ideal for bulkier, heavier, or heat-sensitive materials, relying on belts, screws, or chains, but it may cause degradation or segregation in delicate substances. Understanding these material compatibility differences helps you select the most efficient and safe conveying method for your specific application.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Pneumatic conveying systems typically consume more energy due to the need for air compressors to transport materials through pipelines, increasing overall operating costs compared to mechanical conveying. Mechanical conveying, such as belt or screw conveyors, operates with lower power requirements and minimal air pressure, leading to enhanced energy efficiency and reduced maintenance expenses. Companies often select mechanical conveying to optimize cost-effectiveness and reduce energy consumption in bulk material handling applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Pneumatic conveying systems require complex installation with airtight pipelines and specialized compressors to ensure efficient material flow, often demanding more frequent maintenance to prevent blockages and wear in components like filters and blowers. Mechanical conveying involves straightforward installation using belts, rollers, or screws, resulting in easier routine maintenance focused on lubrication, belt alignment, and replacing worn parts, which typically reduces downtime. Your choice hinges on balancing the initial setup complexity and ongoing maintenance effort suited to your operational needs.
Dust Control and Environmental Considerations
Pneumatic conveying systems excel in dust control by operating in a sealed environment, minimizing particulate emissions and reducing workplace contamination. Mechanical conveying methods often generate more dust due to open transfer points, requiring additional dust suppression measures to meet environmental regulations. Effective dust containment in pneumatic systems supports compliance with air quality standards and enhances operator safety.
System Flexibility and Scalability
Pneumatic conveying systems offer superior flexibility and scalability by easily adapting to varied plant layouts and enabling quick rerouting of materials through pipelines with minimal space requirements. Mechanical conveying systems, such as belt or screw conveyors, often face limitations in layout modifications due to fixed equipment positions and larger spatial footprints. The choice between pneumatic and mechanical conveying depends on production demands, with pneumatic systems providing better scalability for handling diverse materials and fluctuating volumes efficiently.
Choosing the Right Conveying System for Your Application
Selecting the right conveying system depends on material characteristics, distance, and system efficiency requirements. Pneumatic conveying suits fine, abrasive, or fragile materials needing dust control and flexible layouts, offering high-speed transport through pressurized air or vacuum. Mechanical conveying excels with bulky, heavy, or abrasive products, providing energy-efficient, low-maintenance solutions like belt and screw conveyors ideal for short distances and large volumes.
pneumatic conveying vs mechanical conveying Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com