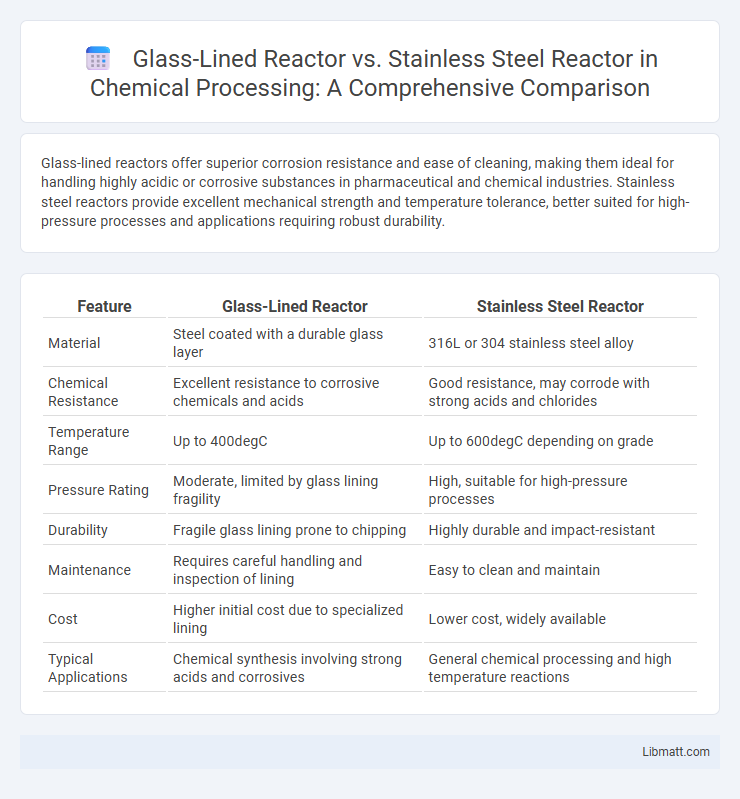
Glass-lined reactors offer superior corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for handling highly acidic or corrosive substances in pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Stainless steel reactors provide excellent mechanical strength and temperature tolerance, better suited for high-pressure processes and applications requiring robust durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass-Lined Reactor | Stainless Steel Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel coated with a durable glass layer | 316L or 304 stainless steel alloy |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals and acids | Good resistance, may corrode with strong acids and chlorides |
| Temperature Range | Up to 400degC | Up to 600degC depending on grade |
| Pressure Rating | Moderate, limited by glass lining fragility | High, suitable for high-pressure processes |
| Durability | Fragile glass lining prone to chipping | Highly durable and impact-resistant |
| Maintenance | Requires careful handling and inspection of lining | Easy to clean and maintain |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to specialized lining | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Applications | Chemical synthesis involving strong acids and corrosives | General chemical processing and high temperature reactions |
Introduction to Glass-Lined and Stainless Steel Reactors
Glass-lined reactors offer superior chemical resistance and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for handling corrosive substances in pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Stainless steel reactors provide excellent mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature processes. Your choice depends on the specific chemical compatibility and operational requirements of your application.
Material Composition and Structure
Glass-lined reactors consist of a carbon steel or stainless steel vessel coated internally with a durable, corrosion-resistant glass layer, providing excellent chemical inertness and resistance to aggressive substances. Stainless steel reactors are fabricated entirely from stainless steel alloys like 304 or 316 grades, offering superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity but less chemical resistance compared to glass lining. The glass lining in reactors forms a non-porous, smooth surface that prevents contamination and corrosion, whereas stainless steel's metallic surface is susceptible to certain acids and requires surface passivation for enhanced durability.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Glass-lined reactors exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel reactors, making them ideal for handling highly acidic or alkaline chemicals. The glass lining forms a non-reactive, inert barrier that prevents metal corrosion and contamination, ensuring product purity and extending equipment lifespan. Stainless steel reactors may suffer from pitting and crevice corrosion under aggressive chemical conditions, limiting their durability in harsh environments.
Thermal and Mechanical Properties
Glass-lined reactors offer superior corrosion resistance and smooth surface characteristics, ensuring chemical inertness and preventing contamination, while stainless steel reactors provide higher mechanical strength and better thermal conductivity for efficient heat transfer. Glass lining excels in handling highly corrosive media at moderate temperatures, but stainless steel reactors withstand higher pressure and temperature conditions due to their robust mechanical properties. You should consider thermal conductivity and durability requirements when choosing between glass-lined and stainless steel reactors for your specific chemical processes.
Chemical Compatibility and Applications
Glass-lined reactors offer superior chemical compatibility with highly corrosive substances such as strong acids, alkalis, and oxidizing agents, making them ideal for pharmaceutical and specialty chemical manufacturing. Stainless steel reactors provide excellent mechanical strength and are suitable for a wide range of moderate chemical processes, including food processing and petrochemical production. Your choice depends on the specific chemical resistance required and the nature of the reaction environment.
Cleaning and Maintenance Considerations
Glass-lined reactors offer superior chemical resistance and smooth surfaces that reduce residue buildup, making cleaning easier and minimizing contamination risk during Your production cycles. Stainless steel reactors require more intensive cleaning protocols due to potential corrosion and surface roughness, which can trap residues and increase maintenance frequency. Choosing the appropriate reactor depends on Your process materials and cleaning efficiency requirements to ensure optimal operational longevity.
Cost Analysis and Life Cycle
Glass-lined reactors typically incur higher initial costs due to specialized coating and fabrication processes, whereas stainless steel reactors are generally more economical upfront. Over the life cycle, glass-lined reactors offer superior corrosion resistance and longer maintenance intervals, reducing downtime and replacement expenses. Stainless steel reactors may require more frequent repairs or lining replacements, increasing total operational costs despite lower initial investment.
Safety Features and Performance
Glass-lined reactors offer superior chemical resistance, preventing corrosion and reducing contamination risks in handling aggressive substances, thereby enhancing operational safety. Stainless steel reactors provide excellent mechanical strength and durability, suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature processes but require careful monitoring to avoid corrosion in harsh chemical environments. Performance-wise, glass-lined reactors maintain product purity and simplify cleaning, while stainless steel reactors excel in heat transfer efficiency and structural integrity for demanding industrial applications.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Glass-lined reactors are ideal for the pharmaceutical and chemical industries due to their superior corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, making them suitable for handling aggressive acids and sensitive compounds. Stainless steel reactors excel in food processing and petrochemical applications where high pressure and temperature conditions require robust mechanical strength and durability. Your choice depends on the specific chemical compatibility, operating environment, and contamination control needs of your industry.
Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Process
Glass-lined reactors offer superior corrosion resistance and chemical inertness, making them ideal for highly acidic or corrosive processes, while stainless steel reactors provide excellent mechanical strength and thermal conductivity for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Your choice depends on the specific chemical compatibility, operating conditions, and maintenance requirements of your process to ensure efficiency and longevity. Evaluating factors such as temperature range, pressure, and reactant reactivity will guide you in selecting the optimal reactor material for your production needs.
glass-lined reactor vs stainless steel reactor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com