Ionic exchange effectively removes dissolved ions and hardness from water by replacing unwanted minerals with sodium or potassium ions, making it ideal for softening. Reverse osmosis uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter out a broad range of contaminants, including dissolved solids, bacteria, and chemicals, providing comprehensive purification for your water needs.
Table of Comparison
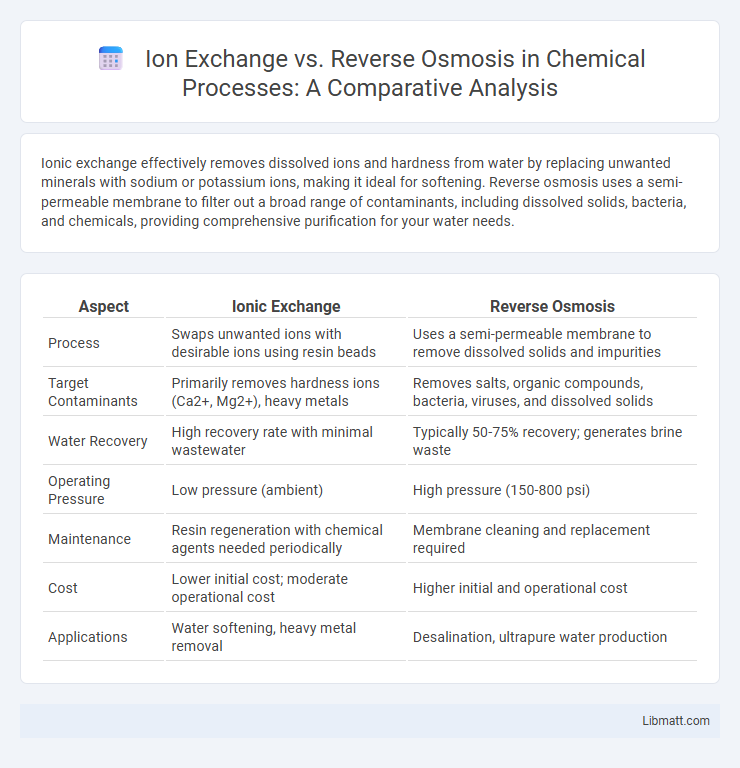
| Aspect | Ionic Exchange | Reverse Osmosis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Swaps unwanted ions with desirable ions using resin beads | Uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved solids and impurities |
| Target Contaminants | Primarily removes hardness ions (Ca2+, Mg2+), heavy metals | Removes salts, organic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and dissolved solids |
| Water Recovery | High recovery rate with minimal wastewater | Typically 50-75% recovery; generates brine waste |
| Operating Pressure | Low pressure (ambient) | High pressure (150-800 psi) |
| Maintenance | Resin regeneration with chemical agents needed periodically | Membrane cleaning and replacement required |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; moderate operational cost | Higher initial and operational cost |
| Applications | Water softening, heavy metal removal | Desalination, ultrapure water production |
Introduction to Water Purification Methods
Ionic exchange and reverse osmosis are two advanced water purification methods that effectively remove contaminants from your water supply. Ionic exchange uses resin beads to swap harmful ions like calcium and magnesium with more desirable ions, improving water softness and taste. Reverse osmosis employs a semi-permeable membrane to eliminate up to 99% of dissolved solids, bacteria, and pollutants, offering comprehensive purification for safer drinking water.
What is Ion Exchange?
Ion exchange is a water purification process that removes undesirable ions by exchanging them with more acceptable ions using resin beads. Commonly used to soften hard water, ion exchange effectively reduces calcium, magnesium, and heavy metals by replacing them with sodium or potassium ions. This method enhances water quality for industrial, residential, and commercial applications by preventing scale buildup and improving taste.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that removes contaminants by forcing water through a semipermeable membrane, effectively filtering out dissolved salts, bacteria, and organic molecules. Unlike ion exchange, which swaps harmful ions for less harmful ones, reverse osmosis physically blocks impurities, producing high-purity water. This method is widely used in desalination, drinking water treatment, and industrial applications due to its efficiency in reducing total dissolved solids (TDS).
How Ion Exchange Works
Ion exchange operates by swapping undesirable ions in water with more acceptable ions using resin beads, effectively removing contaminants like calcium, magnesium, and heavy metals. The process involves cation and anion exchange resins, which target positively and negatively charged ions, respectively, ensuring softer, purified water. This method is particularly efficient for water softening and selective ion removal compared to the membrane filtration in reverse osmosis.
How Reverse Osmosis Works
Reverse osmosis works by forcing water through a semipermeable membrane that blocks contaminants, including salts, bacteria, and organic molecules, allowing only clean water to pass. This process removes up to 99% of dissolved solids, significantly improving water purity compared to ionic exchange, which primarily targets specific ions. You benefit from reverse osmosis with highly purified water suitable for drinking, cooking, and sensitive equipment.
Key Differences between Ion Exchange and Reverse Osmosis
Ion exchange and reverse osmosis differ primarily in their mechanisms for water purification; ion exchange removes dissolved ions by exchanging undesirable ions with harmless ones, while reverse osmosis forces water through a semipermeable membrane to remove a broader range of contaminants including salts, bacteria, and organic molecules. Ion exchange systems are typically more effective for softening hard water and removing specific ions such as calcium and magnesium, whereas reverse osmosis systems provide more comprehensive filtration, addressing total dissolved solids and microbial impurities. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right water treatment method based on your water quality needs and desired purity level.
Efficiency and Effectiveness Comparison
Ionic exchange effectively removes specific ions like calcium and magnesium, making it ideal for water softening and certain targeted contaminant removal. Reverse osmosis provides higher overall purification efficiency by filtering out a broader range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, and microorganisms, resulting in more comprehensive water treatment. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize selective ion removal or extensive contaminant reduction for optimal water quality.
Applications and Use Cases
Ion exchange is commonly used in water softening, industrial wastewater treatment, and purification of pharmaceuticals by selectively removing ions such as calcium, magnesium, and heavy metals. Reverse osmosis serves a vital role in seawater desalination, producing ultrapure water for drinking, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing by filtering out dissolved salts and organic molecules. Both technologies are essential in environmental management, with ion exchange addressing specific ion removal and reverse osmosis providing broad-spectrum filtration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Ion exchange offers efficient removal of water hardness and specific contaminants like heavy metals, while being cost-effective and easy to maintain; however, it requires frequent resin regeneration and may add sodium to the water. Reverse osmosis delivers superior purification by filtering out a wide range of impurities including salts, bacteria, and viruses, ensuring high water quality but involves higher energy consumption and water wastage. Your choice depends on water quality needs, budget, and maintenance preferences, balancing the trade-offs between operational cost and filtration effectiveness.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Choosing the right water purification system depends on your specific water quality and usage requirements. Ion exchange effectively removes hardness and heavy metals, making it ideal for softening and improving taste, while reverse osmosis excels at eliminating a broader range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, bacteria, and organic compounds. Consider your water source and desired purity level to select the system that best meets your needs and ensures safe, clean water for your home or business.
ionic exchange vs reverse osmosis Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com