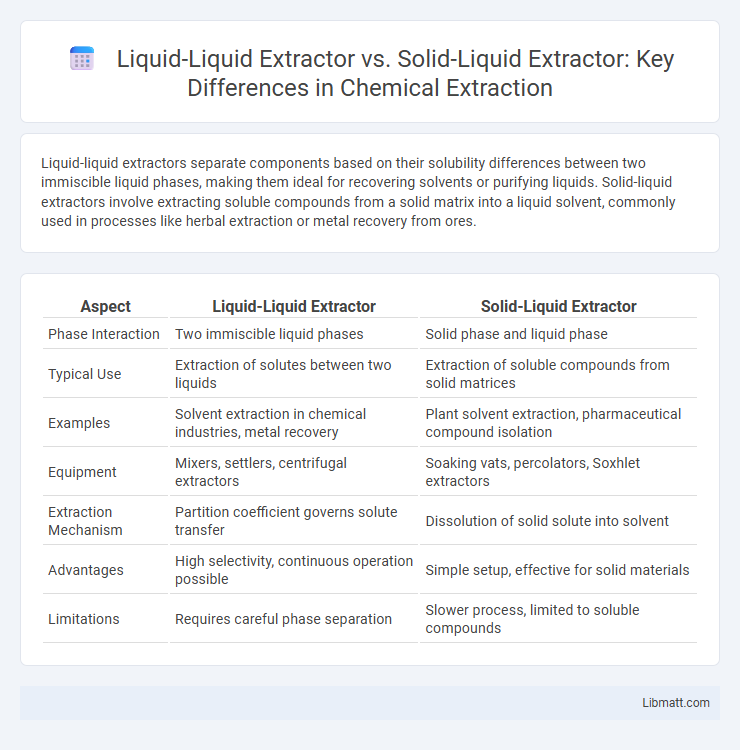
Liquid-liquid extractors separate components based on their solubility differences between two immiscible liquid phases, making them ideal for recovering solvents or purifying liquids. Solid-liquid extractors involve extracting soluble compounds from a solid matrix into a liquid solvent, commonly used in processes like herbal extraction or metal recovery from ores.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Liquid-Liquid Extractor | Solid-Liquid Extractor |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Interaction | Two immiscible liquid phases | Solid phase and liquid phase |
| Typical Use | Extraction of solutes between two liquids | Extraction of soluble compounds from solid matrices |
| Examples | Solvent extraction in chemical industries, metal recovery | Plant solvent extraction, pharmaceutical compound isolation |
| Equipment | Mixers, settlers, centrifugal extractors | Soaking vats, percolators, Soxhlet extractors |
| Extraction Mechanism | Partition coefficient governs solute transfer | Dissolution of solid solute into solvent |
| Advantages | High selectivity, continuous operation possible | Simple setup, effective for solid materials |
| Limitations | Requires careful phase separation | Slower process, limited to soluble compounds |
Introduction to Liquid-Liquid and Solid-Liquid Extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction involves separating compounds based on their different solubilities in two immiscible liquid phases, commonly used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries for separating organic and aqueous layers. Solid-liquid extraction refers to the process of isolating soluble components from a solid matrix by contacting it with a suitable solvent, frequently applied in food processing, herbal extraction, and environmental analysis. Both techniques leverage differences in solubility but differ by their phase interactions, equipment design, and target applications.
Fundamental Principles of Extraction Methods
Liquid-liquid extractors operate on the principle of partitioning solutes between two immiscible liquid phases based on their relative solubilities, exploiting differences in distribution coefficients to achieve separation. Solid-liquid extractors rely on solvent diffusion and solubilization to remove target compounds from solid matrices, emphasizing contact efficiency and solvent penetration within the solid particles. Your choice between these methods depends on the nature of the feed material and the specific separation challenge posed by the solute's physical and chemical properties.
Overview of Liquid-Liquid Extractors
Liquid-liquid extractors separate compounds based on solubility differences between two immiscible liquid phases, often used in chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries. These extractors efficiently transfer solutes from one liquid to another, optimizing purity and yield by controlling phase contact time and mixing intensity. Your choice between liquid-liquid and solid-liquid extraction depends on the physical state of the feed and desired separation efficiency.
Overview of Solid-Liquid Extractors
Solid-liquid extractors separate desired compounds by dissolving solids into a liquid solvent, commonly used in pharmaceutical and food industries for extracting bioactive ingredients from plant materials. These extractors rely on factors like solvent type, particle size, temperature, and agitation to optimize extraction efficiency, with equipment ranging from batch tanks to continuous extractors such as percolators and rotary extractors. Compared to liquid-liquid extractors, solid-liquid systems handle heterogeneous mixtures and require careful control of solid-liquid mass transfer dynamics for efficient separation.
Key Differences Between Liquid-Liquid and Solid-Liquid Extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction involves separating compounds based on their solubility in two immiscible liquids, typically an aqueous phase and an organic solvent, whereas solid-liquid extraction extracts solutes from a solid matrix using a liquid solvent. Liquid-liquid extraction is commonly used for purifying liquids and separating non-polar and polar substances, while solid-liquid extraction is essential for recovering compounds such as oils, flavors, and pharmaceuticals from solids. The efficiency of liquid-liquid extraction depends on factors like partition coefficient and phase ratio, whereas solid-liquid extraction relies on solvent penetration, agitation, and temperature.
Applications in Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Liquid-liquid extractors are extensively used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries for separating compounds based on their solubility differences in immiscible liquids, such as purifying antibiotics and extracting bioactive compounds. Solid-liquid extractors excel in processes like solid phase extraction during drug formulation and purification of natural products, where target compounds are dissolved from a solid matrix into a solvent. Both extraction techniques are critical for optimizing product purity and yield in pharmaceuticals and chemical syntheses.
Advantages and Limitations of Liquid-Liquid Extractors
Liquid-liquid extractors offer high selectivity and efficient phase contact, enabling effective separation of soluble components between immiscible liquid phases, which enhances your extraction yield in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. However, these extractors face limitations such as solvent contamination, emulsion formation, and higher operational costs compared to solid-liquid extractors that primarily deal with solids and solvents, often requiring less complex equipment. While liquid-liquid extractors excel in separating liquid mixtures, they can be less suitable for handling solid materials or mixtures with negligible liquid phases.
Pros and Cons of Solid-Liquid Extractors
Solid-liquid extractors offer precise separation of soluble solids from solid matrices, making them ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries due to their ability to handle high solid content efficiently. Their main advantages include simplified operation, lower energy consumption, and suitability for heat-sensitive materials, but they may face limitations like slower extraction rates and potential incomplete extraction compared to liquid-liquid extractors. You should consider the specific application and material properties to decide if the trade-offs in extraction speed and completeness are acceptable for your process needs.
Efficiency Factors in Extraction Processes
Liquid-liquid extractors offer higher efficiency in separating components with different solubilities due to enhanced mass transfer between immiscible liquid phases, making them ideal for extracting heat-sensitive compounds. Solid-liquid extractors rely on solvent penetration and diffusion into solid matrices, where particle size, solvent type, and agitation significantly influence extraction rates and yield. Your choice depends on the physical state of the materials and the desired extraction speed, with liquid-liquid extraction generally providing faster and more selective recovery.
Choosing the Right Extraction Method for Your Application
Selecting between liquid-liquid and solid-liquid extractors depends on the physical state and solubility of the target compounds; liquid-liquid extraction excels in separating components based on differential solubility in immiscible solvents, ideal for liquid mixtures. Solid-liquid extraction is suited for isolating compounds from solid matrices by dissolving target analytes into a suitable solvent, making it essential for plant, soil, or solid waste processing. Evaluate factors like sample nature, desired purity, and solvent compatibility to optimize extraction efficiency and yield for your specific application.
Liquid-liquid extractor vs solid-liquid extractor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com