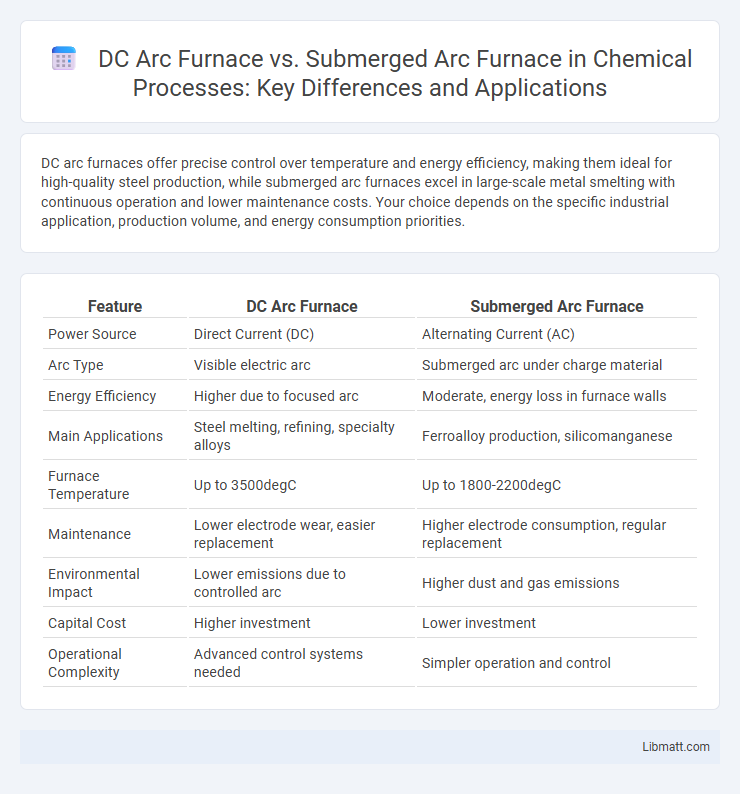
DC arc furnaces offer precise control over temperature and energy efficiency, making them ideal for high-quality steel production, while submerged arc furnaces excel in large-scale metal smelting with continuous operation and lower maintenance costs. Your choice depends on the specific industrial application, production volume, and energy consumption priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DC Arc Furnace | Submerged Arc Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Direct Current (DC) | Alternating Current (AC) |
| Arc Type | Visible electric arc | Submerged arc under charge material |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher due to focused arc | Moderate, energy loss in furnace walls |
| Main Applications | Steel melting, refining, specialty alloys | Ferroalloy production, silicomanganese |
| Furnace Temperature | Up to 3500degC | Up to 1800-2200degC |
| Maintenance | Lower electrode wear, easier replacement | Higher electrode consumption, regular replacement |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions due to controlled arc | Higher dust and gas emissions |
| Capital Cost | Higher investment | Lower investment |
| Operational Complexity | Advanced control systems needed | Simpler operation and control |
Overview of DC Arc Furnace and Submerged Arc Furnace
DC Arc Furnace utilizes direct current to generate an electric arc between graphite electrodes and the scrap metal, allowing efficient melting with reduced energy consumption and lower noise levels. Submerged Arc Furnace operates by inserting electrodes deep into the raw materials, where an electric arc forms beneath the surface, enabling high-temperature processing for large-scale production of ferroalloys and metal recovery. Your choice between these furnaces depends on factors like energy efficiency, production scale, and specific metallurgical requirements.
Principle of Operation: DC Arc vs Submerged Arc
DC arc furnaces operate by establishing an electric arc directly between the electrode and the metal bath, resulting in concentrated heat and efficient energy transfer. In contrast, submerged arc furnaces generate heat through electric arcs beneath the charge layer, where the electrodes are submerged in the material, promoting uniform smelting and reducing heat loss. Understanding these principles allows you to select the most suitable furnace type for specific metallurgical processes, optimizing performance and energy consumption.
Key Technological Differences
DC arc furnaces use direct current between graphite electrodes and the metal, producing stable arcs and precise temperature control, while submerged arc furnaces operate with alternating current submerged in the charge material, leading to high energy efficiency and reduced emissions. DC arc furnaces offer faster melting rates and improved energy efficiency with better electrode consumption, whereas submerged arc furnaces are preferred for large-scale smelting with greater throughput and lower operational costs. Your choice depends on specific production needs, including scale, energy consumption, and material type.
Advantages of DC Arc Furnace
DC arc furnaces offer superior energy efficiency compared to submerged arc furnaces, significantly reducing electricity consumption. You benefit from precise control over the arc length and temperature, leading to improved process stability and higher-quality steel production. Reduced electrode consumption and lower maintenance costs further enhance the overall cost-effectiveness of DC arc furnace technology.
Advantages of Submerged Arc Furnace
Submerged arc furnaces offer higher energy efficiency due to direct contact between electrodes and the charge, enabling better heat transfer and reduced heat losses. They support continuous operation with stable temperature control, leading to increased productivity and lower operational costs compared to DC arc furnaces. The improved process stability also results in consistent product quality, especially in ferroalloy production and smelting applications.
Applications and Material Suitability
DC arc furnaces excel in processing high-quality steel and specialty alloys due to their precise temperature control and lower energy consumption, making them ideal for smaller batches and recycled scrap metals. Submerged arc furnaces are better suited for large-scale metallurgical processes, including ferroalloy production and smelting of ores, thanks to their ability to handle higher volumes and operate continuously. Your choice between these furnaces should consider the specific material characteristics and production scale to maximize efficiency and output quality.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
DC arc furnaces offer higher energy efficiency compared to submerged arc furnaces by minimizing power losses through a direct current supply, resulting in lower electrical consumption per ton of output. Submerged arc furnaces typically experience greater heat loss and require more energy to maintain operational temperatures due to their alternating current systems. Your choice between these technologies will impact operational costs significantly, with DC arc furnaces providing superior energy savings in long-term industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
DC arc furnaces generate lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to submerged arc furnaces due to their higher energy efficiency and better control of the electric arc, resulting in reduced overall carbon footprint. Submerged arc furnaces tend to produce more dust and particulate matter emissions, requiring extensive filtration systems to comply with environmental regulations. Your choice between these technologies can significantly influence emission control strategies and environmental compliance efforts within metallurgical industries.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance
DC arc furnaces generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced electrode technology and direct current power systems, while submerged arc furnaces benefit from lower capital expenses with simpler AC power configurations. Maintenance for DC arc furnaces demands specialized electrode replacement and sophisticated cooling systems, increasing operational expenses, whereas submerged arc furnaces require frequent refractory lining repairs and electrode consumption monitoring, leading to varied ongoing maintenance budgets. Overall, submerged arc furnaces tend to offer lower maintenance costs but higher energy consumption, contrasting with DC arc furnaces' reduced energy use and increased upkeep investments.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Furnace
Selecting between a DC arc furnace and a submerged arc furnace depends on factors such as energy efficiency, production scale, and raw material type. DC arc furnaces offer better energy consumption for smaller, precise melting operations, while submerged arc furnaces excel in large-scale smelting with higher throughput and lower electrode wear. Considerations like capital cost, operational flexibility, and environmental impact guide optimal furnace choice for specific metallurgical applications.
DC arc furnace vs submerged arc furnace Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com