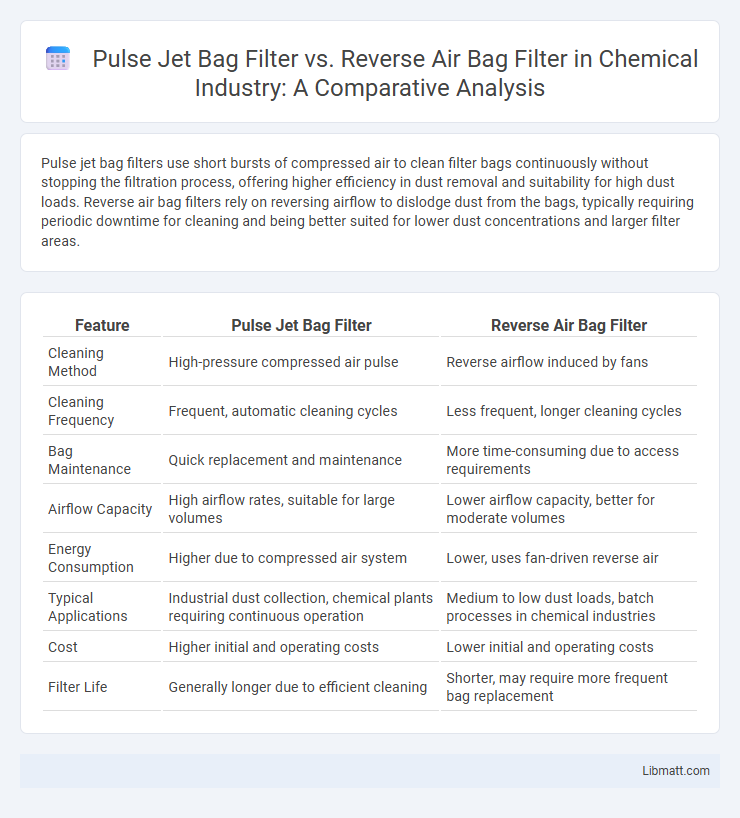
Pulse jet bag filters use short bursts of compressed air to clean filter bags continuously without stopping the filtration process, offering higher efficiency in dust removal and suitability for high dust loads. Reverse air bag filters rely on reversing airflow to dislodge dust from the bags, typically requiring periodic downtime for cleaning and being better suited for lower dust concentrations and larger filter areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pulse Jet Bag Filter | Reverse Air Bag Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning Method | High-pressure compressed air pulse | Reverse airflow induced by fans |
| Cleaning Frequency | Frequent, automatic cleaning cycles | Less frequent, longer cleaning cycles |
| Bag Maintenance | Quick replacement and maintenance | More time-consuming due to access requirements |
| Airflow Capacity | High airflow rates, suitable for large volumes | Lower airflow capacity, better for moderate volumes |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to compressed air system | Lower, uses fan-driven reverse air |
| Typical Applications | Industrial dust collection, chemical plants requiring continuous operation | Medium to low dust loads, batch processes in chemical industries |
| Cost | Higher initial and operating costs | Lower initial and operating costs |
| Filter Life | Generally longer due to efficient cleaning | Shorter, may require more frequent bag replacement |
Introduction to Bag Filtration Systems
Pulse jet bag filters use short bursts of compressed air to clean the bags while operating continuously, providing high efficiency in dust collection and maintaining steady airflow. Reverse air bag filters rely on a slower, reverse airflow to clean the bags intermittently, often requiring downtime for the cleaning cycle and suitable for larger particles. Your choice between the two depends on factors like dust load, particle size, and the need for continuous operation.
Pulse Jet Bag Filter: Overview and Working Principle
Pulse jet bag filters operate using a high-pressure pulse of compressed air that rapidly cleans the filter bags by dislodging accumulated dust and particles. This self-cleaning mechanism ensures continuous filtration without the need for shutdown, making it highly efficient for industrial air pollution control. Your system benefits from maintaining optimal airflow and reducing downtime with this reliable cleaning process.
Reverse Air Bag Filter: Overview and Working Principle
Reverse air bag filters operate by directing air in the opposite flow to dislodge dust particles collected on the filter bags, utilizing a blower or fan to reverse airflow within the filter compartments. This method allows continuous filtration by cleaning one compartment at a time while others remain in operation, enhancing operational efficiency. The cleaning cycle involves a gradual, low-pressure airflow that loosens dust without causing excessive wear on the fabric filter bags.
Key Differences Between Pulse Jet and Reverse Air Bag Filters
Pulse jet bag filters utilize short bursts of compressed air to clean filter bags while maintaining continuous operation, enhancing filtration efficiency and reducing downtime. Reverse air bag filters employ a slower air flow in the opposite direction to gently dislodge dust, making them suitable for low to moderate dust loads but with periodic shutdowns required. Your choice depends on factors like dust type, plant design, and maintenance preferences, as pulse jet systems excel in high-capacity, continuous processes, whereas reverse air systems are favored for gentler cleaning and energy savings.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Pulse jet bag filters deliver high filtration efficiency by rapidly cleaning filter bags with short bursts of compressed air, maintaining consistent pressure drop and enabling continuous operation. Reverse air bag filters operate with slower, less intense cleaning cycles using reverse airflow, resulting in lower energy consumption but reduced filtration performance and efficiency. Pulse jet systems are preferred in industries requiring high dust load handling and tight emission controls due to their superior dust cake removal and extended filter life.
Maintenance Requirements and Operational Costs
Pulse jet bag filters require less maintenance due to their continuous cleaning process, which reduces downtime and extends filter life. Your operational costs are typically lower compared to reverse air bag filters, as pulse jet systems use less compressed air and need fewer manual interventions. Reverse air bag filters demand longer cleaning cycles and more frequent maintenance, leading to higher labor and energy expenses.
Space and Installation Considerations
Pulse jet bag filters require less installation space due to their compact design and vertical airflow, making them ideal for facilities with limited floor area. Reverse air bag filters need more room because of their horizontal airflow and larger housing necessary for the airflow reversal system. Installation complexity is higher for reverse air systems due to additional ductwork and access for cleaning, whereas pulse jet designs offer simpler, modular installation and easier maintenance.
Typical Applications and Industries
Pulse jet bag filters are widely used in industries with high dust loads and continuous operation requirements, such as cement manufacturing, chemical processing, and power plants, due to their efficient cleaning mechanism and ability to handle variable airflows. Reverse air bag filters find typical applications in industries like grain processing, woodworking, and pharmaceuticals, where lower energy consumption and gentle cleaning of delicate filter media are prioritized. Both technologies serve critical roles in controlling particulate emissions across diverse manufacturing and processing sectors.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Compliance
Pulse jet bag filters offer superior environmental impact control by maintaining higher filtration efficiency and continuous operation, reducing particulate emissions under stringent regulatory standards such as EPA and EU directives. Reverse air bag filters, while effective in dust collection, operate intermittently and may allow higher fugitive emissions, posing challenges in meeting increasingly strict air quality regulations. Compliance with environmental laws often favors pulse jet systems due to their enhanced dust containment, lower pressure drops, and reduced energy consumption, contributing to sustainable industrial processes.
Choosing the Right Bag Filter for Your Needs
Pulse jet bag filters offer high cleaning efficiency and continuous operation by using short bursts of compressed air to dislodge dust, ideal for applications with heavy dust loads and tight space constraints. Reverse air bag filters use a slower, gentler cleaning process suitable for lower dust concentrations and environments where noise and air usage must be minimized. Selecting the right bag filter depends on factors such as dust type, plant layout, maintenance capabilities, and overall operational requirements to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
pulse jet bag filter vs reverse air bag filter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com