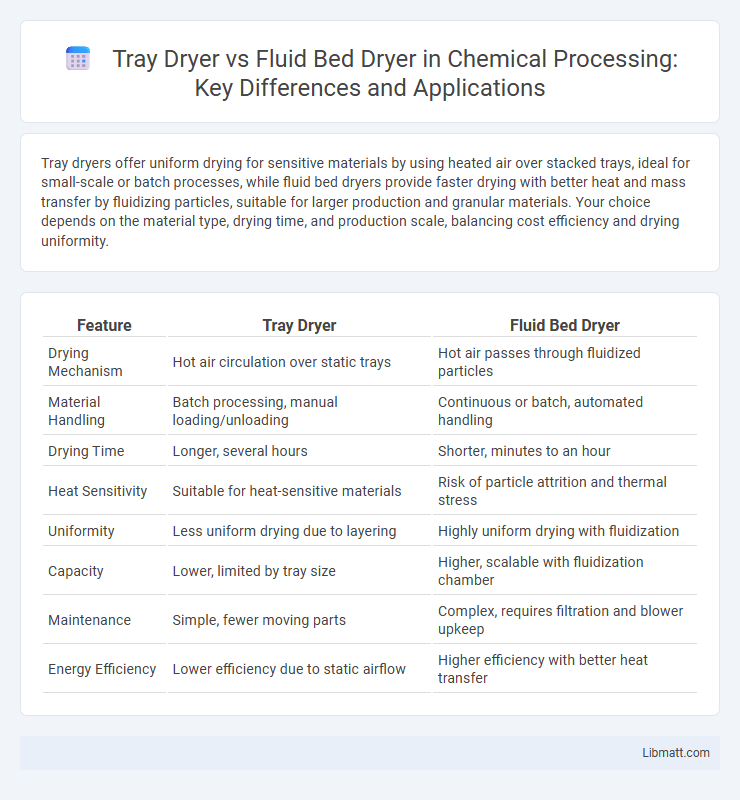
Tray dryers offer uniform drying for sensitive materials by using heated air over stacked trays, ideal for small-scale or batch processes, while fluid bed dryers provide faster drying with better heat and mass transfer by fluidizing particles, suitable for larger production and granular materials. Your choice depends on the material type, drying time, and production scale, balancing cost efficiency and drying uniformity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tray Dryer | Fluid Bed Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Mechanism | Hot air circulation over static trays | Hot air passes through fluidized particles |
| Material Handling | Batch processing, manual loading/unloading | Continuous or batch, automated handling |
| Drying Time | Longer, several hours | Shorter, minutes to an hour |
| Heat Sensitivity | Suitable for heat-sensitive materials | Risk of particle attrition and thermal stress |
| Uniformity | Less uniform drying due to layering | Highly uniform drying with fluidization |
| Capacity | Lower, limited by tray size | Higher, scalable with fluidization chamber |
| Maintenance | Simple, fewer moving parts | Complex, requires filtration and blower upkeep |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to static airflow | Higher efficiency with better heat transfer |
Introduction to Tray Dryers and Fluid Bed Dryers
Tray dryers utilize stacked trays to dry materials by hot air circulation, offering uniform drying for heat-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and food. Fluid bed dryers suspend particles in a hot air stream, enhancing drying speed and efficiency for granular and pelletized materials often used in chemical and food industries. Both dryers play crucial roles in industrial drying processes, with tray dryers excelling in batch drying and fluid bed dryers preferred for continuous operations.
Principle of Operation: Tray Dryer vs Fluid Bed Dryer
Tray dryers operate by circulating hot air over stationary trays stacked with materials, relying on conduction and convection to remove moisture through gradual drying. Fluid bed dryers suspend particles in a heated air stream, promoting rapid drying via enhanced contact and uniform heat distribution. Your choice depends on material sensitivity and drying speed, with fluid bed dryers offering faster processing for granular products.
Key Applications in Various Industries
Tray dryers are widely used in the pharmaceutical and food industries for drying heat-sensitive materials, herbs, and powders with precise temperature control. Fluid bed dryers excel in chemical and agricultural sectors by efficiently drying granules, pellets, and seeds through rapid hot air circulation, enhancing drying uniformity and throughput. Your choice depends on the material type and drying speed required, as tray dryers suit batch processing while fluid bed dryers support continuous operation.
Design and Construction Differences
Tray dryers consist of stacked trays enclosed in a heated chamber, featuring simple construction with limited airflow control, primarily designed for batch drying of uniform products. Fluid bed dryers utilize a perforated bed through which hot air is fluidized to suspend and dry particles continuously, enabling efficient heat and mass transfer with uniform drying and rapid processing. The design of fluid bed dryers incorporates advanced airflow systems and vibration mechanisms, contrasting with the static, tray-based arrangement of tray dryers.
Drying Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Tray dryers provide uniform drying suitable for small batches but often require longer processing times due to limited heat transfer efficiency. Fluid bed dryers enhance drying efficiency by promoting excellent air-solid contact, resulting in faster moisture removal and improved drying uniformity. The fluid bed dryer generally outperforms the tray dryer in throughput and energy utilization, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Tray dryers typically consume more energy due to longer drying times and lower heat transfer efficiency, resulting in higher operational costs compared to fluid bed dryers. Fluid bed dryers enhance energy efficiency by promoting uniform heat distribution and faster drying rates, reducing energy consumption and overall process costs. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between initial investment and long-term energy savings for optimal cost efficiency.
Product Quality and Uniformity Outcomes
Tray dryers provide consistent drying with moderate airflow, resulting in uniform moisture reduction but may cause uneven heat distribution in thick layers. Fluid bed dryers offer superior product quality by suspending particles in a hot air stream, ensuring rapid and homogenous drying with minimal hotspots. The choice depends on desired uniformity levels, as fluid bed dryers generally achieve better product consistency and lower moisture variance.
Scalability and Space Requirements
Tray dryers offer a compact design suitable for small to medium-scale drying operations, making them ideal when space is limited but batch processing is required. Fluid bed dryers provide superior scalability for large-scale industrial production with efficient drying rates, though they typically demand more floor space and complex infrastructure. Your choice depends on the balance between available space and the scale of drying needed for optimal operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Tray dryers require regular cleaning to prevent product contamination and efficient heat transfer, with maintenance focused on tray integrity and chamber sealing, while fluid bed dryers demand more routine inspection of air filters, blowers, and vibration systems for optimal performance. Operationally, tray dryers offer simple temperature control but slower drying times, whereas fluid bed dryers provide uniform drying with faster processing but involve more complex system calibration and higher energy consumption. Your choice depends on balancing ease of maintenance against desired drying efficiency and throughput.
Choosing the Right Dryer: Factors to Consider
Selecting between a tray dryer and a fluid bed dryer depends on factors such as product type, drying time, and heat sensitivity. Tray dryers are ideal for batch drying of heat-sensitive materials with uniform drying requirements, offering controlled temperature and moisture removal. Fluid bed dryers excel in rapid drying of granular or particulate products, providing excellent mixing and consistent drying in continuous operations.
Tray dryer vs fluid bed dryer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com