Pin headers provide a series of male connectors that fit into sockets offering female connections, enabling modular component assembly and easy circuit expansion. Choosing the right combination ensures reliable electrical connections and simplifies maintenance in your electronic projects.
Table of Comparison
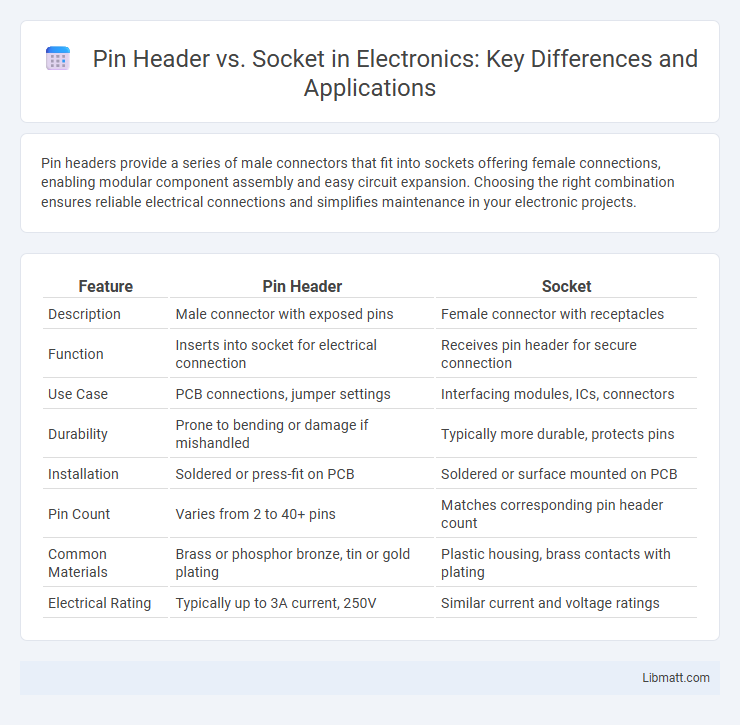
| Feature | Pin Header | Socket |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Male connector with exposed pins | Female connector with receptacles |
| Function | Inserts into socket for electrical connection | Receives pin header for secure connection |
| Use Case | PCB connections, jumper settings | Interfacing modules, ICs, connectors |
| Durability | Prone to bending or damage if mishandled | Typically more durable, protects pins |
| Installation | Soldered or press-fit on PCB | Soldered or surface mounted on PCB |
| Pin Count | Varies from 2 to 40+ pins | Matches corresponding pin header count |
| Common Materials | Brass or phosphor bronze, tin or gold plating | Plastic housing, brass contacts with plating |
| Electrical Rating | Typically up to 3A current, 250V | Similar current and voltage ratings |
Introduction to Pin Headers and Sockets
Pin headers and sockets serve as essential connectors in electronic circuits, enabling secure and detachable electrical connections between components or modules. Pin headers consist of rows of metal pins mounted on a plastic base, designed to be inserted into matching sockets or directly soldered onto PCBs. Sockets are receptacles with corresponding holes or clips that receive pin headers, facilitating easy assembly, maintenance, and replacement of electronic parts.
What is a Pin Header?
A pin header is a row or grid of metal pins molded into a plastic base, used to connect electronic components or boards by inserting into matching sockets or connectors. This component delivers reliable electrical connections in various electronics, including microcontroller boards, sensors, and PCBs. Understanding the function of a pin header helps you design and troubleshoot circuit assemblies effectively.
What is a Socket?
A socket is a type of electrical connector designed to receive and securely hold a pin header, facilitating reliable electrical connections between circuit boards or components. It features a hollow or receptacle structure that ensures precise alignment and easy insertion or removal of pins without soldering. Sockets are essential in modular electronics, enabling quick assembly, maintenance, and component replacement.
Key Differences Between Pin Headers and Sockets
Pin headers consist of rigid metal pins arranged in a grid or row, serving as connectors for circuit boards, while sockets provide receptacles that securely hold these pins in place. The primary difference lies in their function, with pin headers offering protruding connections and sockets ensuring stable, removable interfaces. Your choice depends on whether you need a fixed connection or a component that allows easy disconnection and replacement.
Common Applications of Pin Headers
Pin headers are commonly used in printed circuit boards (PCBs) for connecting various electronic components, including microcontrollers, sensors, and modules, facilitating easy prototyping and modular assembly. These connectors provide reliable, compact, and cost-effective solutions for interfacing cables, jumper wires, or daughter boards. Your projects benefit from pin headers' versatility in applications such as Arduino shields, Raspberry Pi HATs, and embedded systems requiring frequent board-to-board or component-to-board connections.
Common Uses of Sockets
Sockets are commonly used in electronics to provide a secure and reliable connection between components such as integrated circuits (ICs) and printed circuit boards (PCBs). They facilitate easy replacement and maintenance by allowing components to be inserted or removed without soldering, which is critical in prototyping and modular systems. Sockets are also widely employed in computer hardware for connecting CPUs, memory modules, and peripheral devices, ensuring stable electrical contact and minimizing wear on the components.
Advantages of Pin Headers
Pin headers offer superior mechanical stability and durability, making them ideal for high-vibration environments and ensuring reliable long-term connections. Their simple design allows for easy soldering and flexible customization in varying pin counts and pitches, enhancing compatibility across diverse electronic applications. Pin headers also provide cost-effective assembly without compromising electrical performance, which benefits both prototyping and mass production processes.
Benefits of Using Sockets
Sockets offer secure, reliable connections that simplify maintenance and upgrades by allowing easy component replacement without soldering. They protect your circuit board from damage caused by frequent insertions and removals, enhancing the longevity of your electronic devices. Using sockets improves flexibility in prototyping and reduces downtime in production environments.
Pin Header vs Socket: Which to Choose?
Pin headers provide a fixed, durable interface ideal for permanent or semi-permanent connections in electronics projects, while sockets offer flexibility and ease of replacement without soldering, making them suitable for modular designs. You should choose pin headers for robust, compact setups where reliability is critical, and sockets when frequent component swapping or testing is essential. Evaluating your project's maintenance needs and connection stability will guide your decision between pin headers and sockets.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Connector
Selecting the right connector between pin headers and sockets depends on application requirements such as durability, ease of assembly, and signal integrity. Pin headers offer reliable soldered connections ideal for permanent setups, while sockets provide flexibility for frequent replacement or testing. Optimal connector choice enhances overall system performance and maintenance efficiency in electronic designs.
Pin Header vs Socket Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com