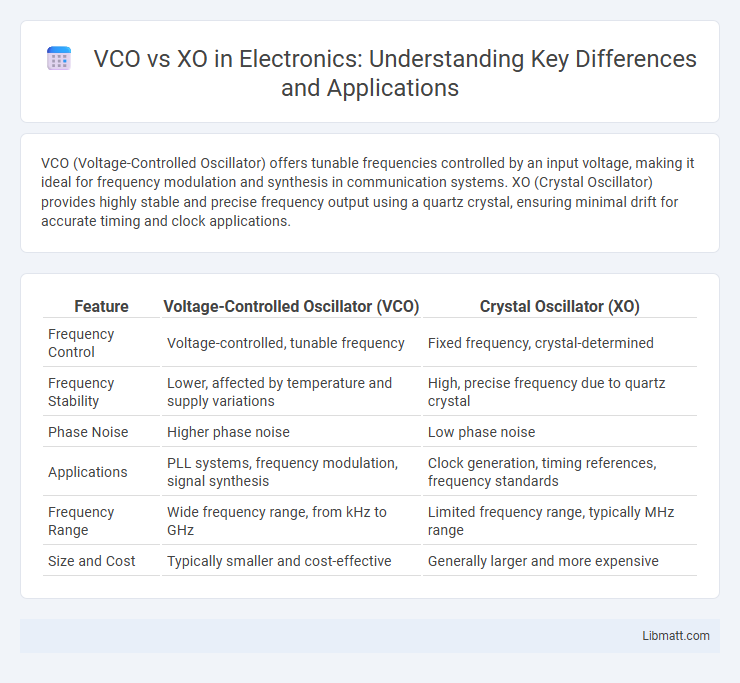
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator) offers tunable frequencies controlled by an input voltage, making it ideal for frequency modulation and synthesis in communication systems. XO (Crystal Oscillator) provides highly stable and precise frequency output using a quartz crystal, ensuring minimal drift for accurate timing and clock applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) | Crystal Oscillator (XO) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Control | Voltage-controlled, tunable frequency | Fixed frequency, crystal-determined |
| Frequency Stability | Lower, affected by temperature and supply variations | High, precise frequency due to quartz crystal |
| Phase Noise | Higher phase noise | Low phase noise |
| Applications | PLL systems, frequency modulation, signal synthesis | Clock generation, timing references, frequency standards |
| Frequency Range | Wide frequency range, from kHz to GHz | Limited frequency range, typically MHz range |
| Size and Cost | Typically smaller and cost-effective | Generally larger and more expensive |
Introduction to VCO and XO
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator) and XO (Crystal Oscillator) are essential components in electronic frequency generation, with VCOs offering adjustable frequency output controlled by input voltage, making them suitable for applications needing frequency modulation or tuning. XOs provide highly stable and precise oscillation frequencies based on the mechanical resonance of a quartz crystal, often used in timing circuits and communication systems requiring minimal frequency drift. Your choice between VCO and XO depends on the need for frequency stability versus tunability in your electronic design.
What is a Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO)?
A Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose output frequency varies based on an input control voltage, commonly used in frequency synthesis and modulation applications. Unlike a fixed crystal oscillator (XO), a VCO provides adjustable frequency outputs, enabling dynamic tuning in radios, PLL circuits, and communication devices. Your designs benefit from VCOs by achieving flexible frequency control within a wide operational range, essential for modern signal processing systems.
What is a Crystal Oscillator (XO)?
A Crystal Oscillator (XO) is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal to generate a precise frequency signal, essential for accurate timing in electronic devices. The quartz crystal's stable oscillation frequency ensures minimal drift over temperature and time, making XOs ideal for applications requiring high frequency stability such as clocks, radios, and communication systems. Your choice of an XO guarantees consistent performance where timing precision is critical compared to a Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) that offers tunability but less frequency stability.
Key Differences Between VCO and XO
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator) frequency is adjustable based on input voltage, enabling dynamic tuning for applications like phase-locked loops and frequency synthesis. XO (Crystal Oscillator) employs quartz crystal to maintain a highly stable and precise frequency, ideal for clock generation and timing in digital circuits. Key differences include frequency stability, tuning range, and application suitability, with VCOs offering flexibility and XOs providing superior accuracy.
Frequency Stability: VCO vs XO
Crystal oscillators (XO) provide superior frequency stability compared to voltage-controlled oscillators (VCO) due to their reliance on the mechanical resonance of a quartz crystal, which minimizes frequency drift over temperature and time. VCOs offer tunable frequency capabilities but are more susceptible to variations caused by voltage changes, temperature fluctuations, and device aging. In precision timing and communication systems, the XO's stability ensures consistent performance, whereas VCOs are preferred in applications requiring dynamic frequency adjustments despite lower stability.
Applications of VCOs
Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) are widely used in communication systems for frequency modulation and signal generation, enabling precise tuning in phase-locked loops (PLLs). They serve as essential components in wireless transmitters, radar systems, and frequency synthesizers due to their ability to vary output frequency based on input voltage. VCOs also play a critical role in clock generation and timing circuits within microprocessors and digital systems.
Applications of XOs
XOs (crystal oscillators) are widely used in applications requiring highly stable and precise frequency references, such as communication systems, microprocessors, and GPS devices. Their superior frequency accuracy and low phase noise make them essential in timing circuits for embedded systems and network infrastructure. XOs are preferred in scenarios demanding consistent signal integrity over a wide temperature range and long-term reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VCO
Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) offer the advantage of easy frequency tuning via voltage input, making them ideal for applications like phase-locked loops and frequency modulation. Their compact size and lower power consumption provide design flexibility, but they can suffer from higher phase noise and less frequency stability compared to Crystal Oscillators (XOs). If your system demands fine frequency control and adaptability over absolute precision, a VCO may be the better choice despite its susceptibility to temperature variations and signal jitter.
Advantages and Disadvantages of XO
An XO (crystal oscillator) provides superior frequency stability and low phase noise due to its precision quartz crystal, making it ideal for high-accuracy applications like communication systems and GPS devices. However, XOs tend to have a fixed frequency output and limited tuning range, reducing flexibility compared to VCOs (voltage-controlled oscillators), which offer wide tuning capabilities at the expense of slightly higher phase noise and less stability. The choice of XO is favored when consistent, reliable frequency is critical, despite its higher cost and size compared to VCO alternatives.
Choosing the Right Oscillator: VCO or XO?
Choosing the right oscillator depends on the specific application requirements such as frequency stability and tuning capabilities. Voltage-Controlled Oscillators (VCOs) offer flexible frequency adjustment through voltage input, ideal for frequency modulation and agile signal generation. Crystal Oscillators (XOs) provide superior frequency stability and low phase noise, making them the preferred choice for precision timing and reference clock applications.
VCO vs XO Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com