Coaxial cable offers reliable shielding against electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for long-distance signal transmission in television and internet applications, while twinaxial cable features two inner conductors within a single shield for enhanced high-speed data transfer in short-range connections like data centers. Understanding the differences in their construction and performance helps you choose the right cable for your specific networking or communication needs.
Table of Comparison
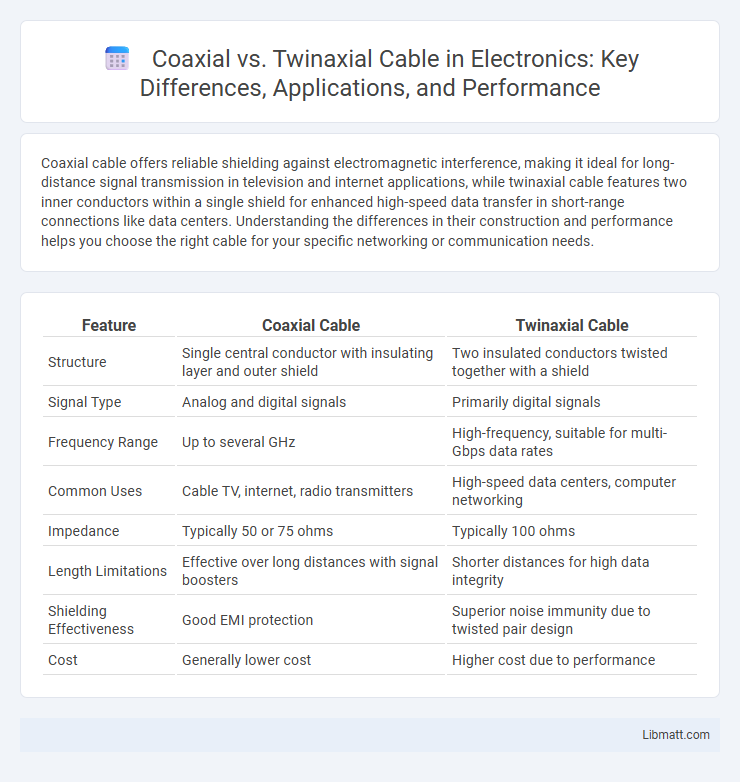
| Feature | Coaxial Cable | Twinaxial Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single central conductor with insulating layer and outer shield | Two insulated conductors twisted together with a shield |
| Signal Type | Analog and digital signals | Primarily digital signals |
| Frequency Range | Up to several GHz | High-frequency, suitable for multi-Gbps data rates |
| Common Uses | Cable TV, internet, radio transmitters | High-speed data centers, computer networking |
| Impedance | Typically 50 or 75 ohms | Typically 100 ohms |
| Length Limitations | Effective over long distances with signal boosters | Shorter distances for high data integrity |
| Shielding Effectiveness | Good EMI protection | Superior noise immunity due to twisted pair design |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to performance |
Introduction to Coaxial and Twinaxial Cables
Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, and outer jacket, designed for high-frequency signal transmission with minimal interference. Twinaxial cables feature two insulated conductors enclosed within a shield, often used for short-distance, high-speed data connections like server and storage interfaces. Both cable types offer noise immunity but differ in structure, applications, and signal transmission capabilities.
Structure and Design Differences
Coaxial cables feature a single central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer jacket, designed to minimize electromagnetic interference and signal loss. Twinaxial cables consist of two tightly twisted conductors enclosed within a shared shield and outer jacket, offering improved noise immunity and better performance in high-speed data transmission. Your choice depends on specific application requirements, such as distance, frequency, and environmental interference.
Signal Transmission Capabilities
Coaxial cable offers robust signal transmission with excellent resistance to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for cable TV and broadband internet. Twinaxial cable supports high-speed data transmission over shorter distances, often used in data centers for connecting servers and switches. Your choice depends on distance and speed requirements, with coaxial preferred for longer runs and twinaxial excelling in low-latency, high-frequency environments.
Bandwidth and Data Rate Comparison
Coaxial cables typically support bandwidths up to 1 GHz, enabling data rates around 10 Gbps in modern implementations, while twinaxial cables excel in shorter distances with higher data rates, often reaching 100 Gbps due to their lower latency and reduced electromagnetic interference. Your choice between coaxial and twinaxial cables hinges on the required bandwidth and distance, with twinaxial being optimal for high-speed data center environments. Twinaxial cables provide superior performance in high-frequency signals, making them ideal for ultra-fast data transmission in network infrastructure.
Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
Coaxial cable provides strong electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding through its single central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and a metallic shield, effectively blocking external noise. Twinaxial cable uses two inner conductors twisted together with an overall shield, offering excellent EMI rejection and reduced crosstalk, especially beneficial in high-speed data transmissions. Your choice depends on the application's sensitivity to interference and the required data transfer distance.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Coaxial cables are predominantly used in cable television distribution, internet connections, and RF signal transmission due to their high-frequency performance and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Twinaxial cables find common applications in high-speed data communication within data centers, especially for short-range connections like server linking and storage area networks, benefiting from reduced crosstalk and latency. Both cable types serve specific niches: coaxial for analog and digital video signals, twinaxial for advanced digital data transmission in enterprise environments.
Installation and Flexibility
Coaxial cables offer greater installation flexibility due to their single central conductor and durable shielding, making them easier to route through tight spaces and around corners. Twinaxial cables, with their dual-conductor design, provide superior noise immunity but are generally bulkier and less flexible, requiring careful handling during installation to avoid signal degradation. Both cable types demand appropriate connectors and proper grounding to maintain optimal performance in various networking environments.
Cost Considerations
Coaxial cables generally offer a lower cost option for short to medium-distance data transmission compared to twinaxial cables, which tend to be more expensive due to their enhanced shielding and higher performance capabilities. Your choice should factor in the total cost of ownership, including installation complexity and maintenance expenses, as twinaxial cables may reduce interference and improve signal integrity in demanding environments. Budgeting for higher upfront costs with twinaxial cables can result in long-term savings through improved reliability and reduced downtime.
Performance in High-Speed Networks
Coaxial cables provide reliable performance with moderate bandwidth suitable for older high-speed networks, but suffer from higher signal attenuation over long distances compared to twinaxial cables. Twinaxial cables excel in high-speed data transmission environments, offering superior noise immunity and lower latency, making them ideal for modern data centers and short-range high-frequency applications. Their enhanced shielding and reduced electromagnetic interference support faster transmission rates up to tens of gigabits per second.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
Choosing between coaxial and twinaxial cable depends on your specific networking requirements, including distance, bandwidth, and interference tolerance. Coaxial cable excels in longer cable runs with moderate bandwidth and better shielding against electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for cable TV and broadband internet. Twinaxial cable offers higher data rates with shorter reach, ideal for data centers and server connections where low latency and high-speed transmission are critical.
Coaxial vs Twinaxial cable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com