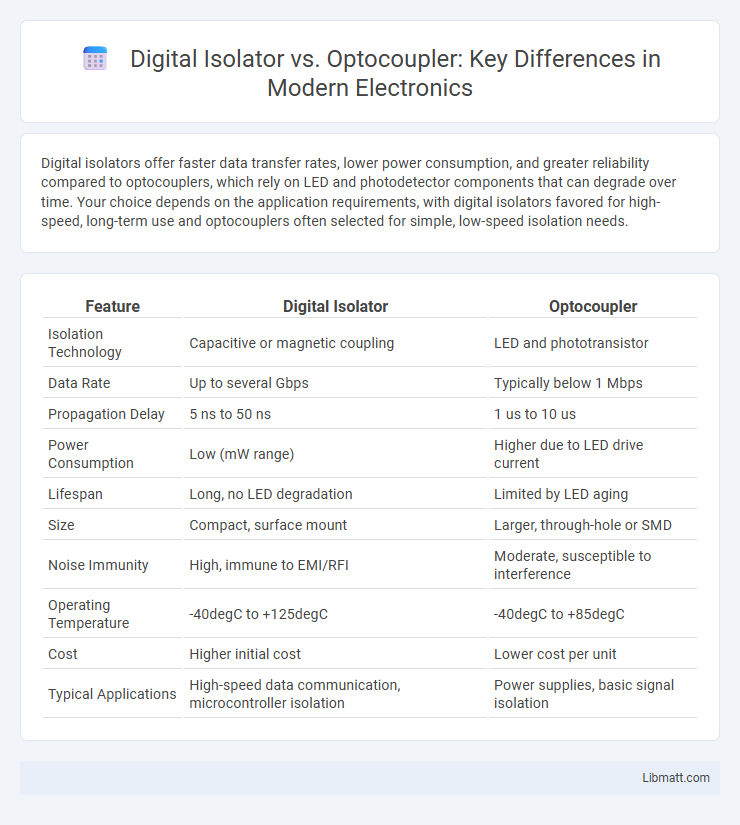
Digital isolators offer faster data transfer rates, lower power consumption, and greater reliability compared to optocouplers, which rely on LED and photodetector components that can degrade over time. Your choice depends on the application requirements, with digital isolators favored for high-speed, long-term use and optocouplers often selected for simple, low-speed isolation needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Isolator | Optocoupler |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation Technology | Capacitive or magnetic coupling | LED and phototransistor |
| Data Rate | Up to several Gbps | Typically below 1 Mbps |
| Propagation Delay | 5 ns to 50 ns | 1 us to 10 us |
| Power Consumption | Low (mW range) | Higher due to LED drive current |
| Lifespan | Long, no LED degradation | Limited by LED aging |
| Size | Compact, surface mount | Larger, through-hole or SMD |
| Noise Immunity | High, immune to EMI/RFI | Moderate, susceptible to interference |
| Operating Temperature | -40degC to +125degC | -40degC to +85degC |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost per unit |
| Typical Applications | High-speed data communication, microcontroller isolation | Power supplies, basic signal isolation |
Introduction to Signal Isolation Technologies
Signal isolation technologies are essential for protecting electronic circuits from high voltages and noise by electrically separating different system sections while enabling data transfer. Digital isolators use capacitive or magnetic coupling to transmit signals without physical contacts, offering faster data rates, lower power consumption, and longer lifespan compared to optocouplers. Optocouplers rely on LED and photodetector pairs to achieve isolation but tend to have slower response times, limited bandwidth, and age-related performance degradation.
What is a Digital Isolator?
A digital isolator is a semiconductor device that provides electrical isolation and signal transmission using capacitive or magnetic coupling, enabling high-speed data transfer without direct electrical connection. It replaces traditional optocouplers by offering smaller size, higher reliability, longer lifespan, and better performance in terms of propagation delay and signal integrity. Digital isolators are commonly used in industrial automation, medical equipment, and communication systems to ensure signal isolation and noise immunity.
What is an Optocoupler?
An optocoupler is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits using light, typically consisting of an LED and a phototransistor. It provides galvanic isolation to protect sensitive components from high voltages and noise, making it ideal for communication between different voltage domains. Your choice between a digital isolator and an optocoupler depends on factors like speed, size, and power consumption, with optocouplers generally favored for simpler, lower-speed applications.
Working Principles of Digital Isolators
Digital isolators use semiconductor-based isolation methods like capacitive, magnetic, or radio-frequency coupling to transmit digital signals across an isolation barrier, ensuring signal integrity and high data rates. Unlike optocouplers, which rely on light transmission and photodetectors, digital isolators offer faster switching speeds, lower power consumption, and enhanced reliability without degradation over time. Your choice benefits from improved noise immunity and precise signal transmission in applications requiring galvanic isolation.
Working Principles of Optocouplers
Optocouplers operate using light to electrically isolate input and output signals, where an LED converts electrical input into light that is detected by a phototransistor or photodiode on the output side. This optical coupling provides high voltage isolation and reduces noise interference, crucial in protecting sensitive components in your circuits. Compared to digital isolators that use capacitive or magnetic coupling, optocouplers rely on optical signals for isolation and signal transmission.
Key Differences: Digital Isolator vs Optocoupler
Digital isolators leverage semiconductor technology to provide faster data transmission speeds and higher noise immunity compared to optocouplers, which rely on LED and photodetector components for isolation. Optocouplers typically exhibit slower response times and limited bandwidth but offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for low-speed applications. Your choice depends on the required isolation performance, signal speed, and system reliability in environments with electromagnetic interference.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Noise Immunity, and Reliability
Digital isolators outperform optocouplers in speed, offering data rates up to several hundred Mbps compared to optocouplers' typical maximum of 10 Mbps, making them ideal for high-speed communication. In terms of noise immunity, digital isolators utilize capacitive or magnetic coupling technology, providing superior resilience to EMI and signal degradation, whereas optocouplers rely on optical signals that can be more susceptible to noise and aging effects. Reliability favors digital isolators as they have longer lifespans, no LED wear-out, and stable performance over temperature variations, contrasting with optocouplers which suffer from LED degradation and reduced efficiency over time.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Digital isolators consume significantly less power compared to optocouplers due to their semiconductor-based design, which enables faster signal transmission with minimal energy loss. Optocouplers rely on LED and phototransistor components, resulting in higher power usage and slower response times. Choosing a digital isolator can improve your system's efficiency by reducing power consumption and enhancing overall performance.
Application Scenarios for Each Technology
Digital isolators excel in applications requiring high-speed data transmission and low power consumption, such as industrial automation, data communication interfaces, and precision measurement systems. Optocouplers are preferred in environments with high voltage isolation needs and electromagnetic interference, commonly found in switching power supplies, motor control circuits, and medical equipment. The choice depends on required isolation voltage, signal speed, and noise immunity specific to each application scenario.
Choosing the Right Isolation Device for Your Project
Digital isolators offer faster data transmission, lower power consumption, and longer lifespan compared to optocouplers, making them ideal for high-speed and precision applications. Optocouplers provide cost-effective galvanic isolation with excellent noise immunity, suitable for simple or low-frequency signal isolation tasks. Evaluating your project's speed requirements, signal integrity, and environmental factors ensures you select the most efficient isolation device tailored to your needs.
Digital isolator vs Optocoupler Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com