RS422 supports point-to-point and multi-drop communication with higher data rates over longer distances, making it ideal for reliable, noise-resistant serial data transmission. RS485 enhances network flexibility by allowing multiple devices to share a single communication line using differential signaling, which improves your system's robustness in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
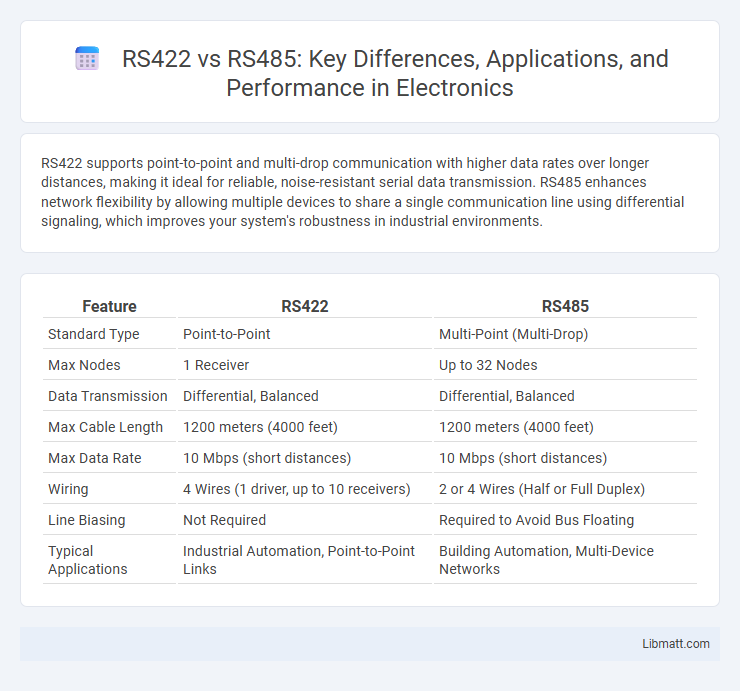
| Feature | RS422 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Type | Point-to-Point | Multi-Point (Multi-Drop) |
| Max Nodes | 1 Receiver | Up to 32 Nodes |
| Data Transmission | Differential, Balanced | Differential, Balanced |
| Max Cable Length | 1200 meters (4000 feet) | 1200 meters (4000 feet) |
| Max Data Rate | 10 Mbps (short distances) | 10 Mbps (short distances) |
| Wiring | 4 Wires (1 driver, up to 10 receivers) | 2 or 4 Wires (Half or Full Duplex) |
| Line Biasing | Not Required | Required to Avoid Bus Floating |
| Typical Applications | Industrial Automation, Point-to-Point Links | Building Automation, Multi-Device Networks |
Overview of RS422 and RS485
RS422 and RS485 are serial communication standards widely used in industrial and automation systems for reliable data transmission over long distances. RS422 supports unidirectional, point-to-point or multi-drop configurations with differential signaling, allowing data transfer rates up to 10 Mbps and distances up to 1,200 meters. RS485 enhances this by enabling bidirectional, multi-point communication on a single twisted pair, supporting up to 32 devices on the bus and making it ideal for complex networked environments.
Key Differences Between RS422 and RS485
RS422 supports point-to-point or multi-drop configurations with up to 10 receivers on one transmitter, operating over a single-ended differential pair for each signal, ensuring high noise immunity and data rates up to 10 Mbps over 1,200 meters. RS485, designed for multipoint networks, allows up to 32 devices on a single differential pair, enabling bidirectional communication with half-duplex or full-duplex modes and offering robust performance in industrial environments with data rates up to 35 Mbps over shorter distances. The primary difference lies in RS422's unidirectional communication suited for longer cable lengths, while RS485 provides flexible multipoint interconnection with improved bus arbitration for complex network topologies.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
RS422 and RS485 differ primarily in their electrical characteristics, impacting signal transmission and network architecture. RS422 supports unidirectional communication using differential signaling with a single driver and up to 10 receivers over distances up to 1,200 meters, while RS485 enables bidirectional communication with multiple drivers and receivers on a multidrop bus, accommodating up to 32 devices and similar cable lengths. Your choice depends on application requirements for network topology, noise immunity, and data direction control.
Data Transmission Modes
RS422 supports full-duplex communication by using separate pairs of wires for sending and receiving data, enabling simultaneous two-way transmission. RS485 operates primarily in half-duplex mode, utilizing a single twisted pair for both transmitting and receiving data, which reduces wiring complexity and cost. Understanding your system's data transmission requirements will help you choose between RS422's higher performance in bidirectional communication and RS485's efficiency in multi-point networks.
Network Topology and Wiring
RS422 supports point-to-point or multi-drop network topologies, allowing up to 10 receivers on a single transmitter, with differential twisted-pair wiring to minimize noise. RS485 enables true multipoint communication with up to 32 drivers and 32 receivers on the same bus, using a balanced differential line ideal for long distances and noisy industrial environments. Your choice depends on the required network scale and complexity, with RS485 being more flexible for larger, bus-based networks.
Communication Distance and Speed
RS422 supports communication distances up to 1,200 meters at lower speeds, typically 100 kbps, while RS485 can achieve similar distances but offers higher speeds up to 10 Mbps over shorter distances. RS485's differential signaling allows for robust communication in electrically noisy environments and supports multi-point networks with up to 32 devices on a single bus, enhancing its versatility for industrial applications. Choosing between RS422 and RS485 depends on the specific requirements for data rate and network topology in a given system design.
Supported Devices and Network Capacity
RS422 supports up to 10 receivers on a single transmitter, making it suitable for point-to-multipoint configurations with limited devices. RS485 expands network capacity significantly, allowing up to 32 devices to communicate on a single bus, facilitating multi-point and complex industrial networks. The differential signaling in both standards ensures robust data transmission over long distances, but RS485's enhanced device support and network scalability make it the preferred choice for extensive monitoring and control systems.
Noise Immunity and Reliability
RS422 offers superior noise immunity through differential signaling, which reduces electromagnetic interference over long cable runs, making it highly reliable in industrial environments. RS485 enhances this by supporting multi-point connections and higher noise resistance, ideal for complex network topologies. Understanding these differences ensures your communication system maintains optimal performance and minimizes data corruption.
Common Applications of RS422 and RS485
RS422 is commonly used in point-to-point communication systems such as industrial automation and CNC machines due to its support for high data rates and long cable lengths. RS485 finds widespread application in multi-drop networks like building automation, MODBUS communication, and elevator control systems because of its ability to support up to 32 devices on a single bus. Both standards excel in noisy industrial environments, with RS485 often preferred for its robustness in complex network topologies.
Choosing Between RS422 and RS485
RS485 supports multi-point communication with up to 32 devices on a single bus, making it ideal for complex industrial networks, while RS422 is typically limited to point-to-point or multi-drop configurations with fewer devices. RS485 offers better noise immunity and longer cable lengths, supporting distances up to 1200 meters, whereas RS422 typically maxes out around 4000 feet but with fewer connected nodes. Your choice should depend on the network size, device count, and required communication distance, with RS485 favored for scalability and RS422 for simpler, dedicated connections.
RS422 vs RS485 Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com