Synchronous communication occurs in real-time, such as phone calls or video meetings, allowing immediate feedback and dynamic interaction. Asynchronous communication, like emails or messaging apps, enables you to respond at your convenience, enhancing flexibility and thoughtful exchanges.
Table of Comparison
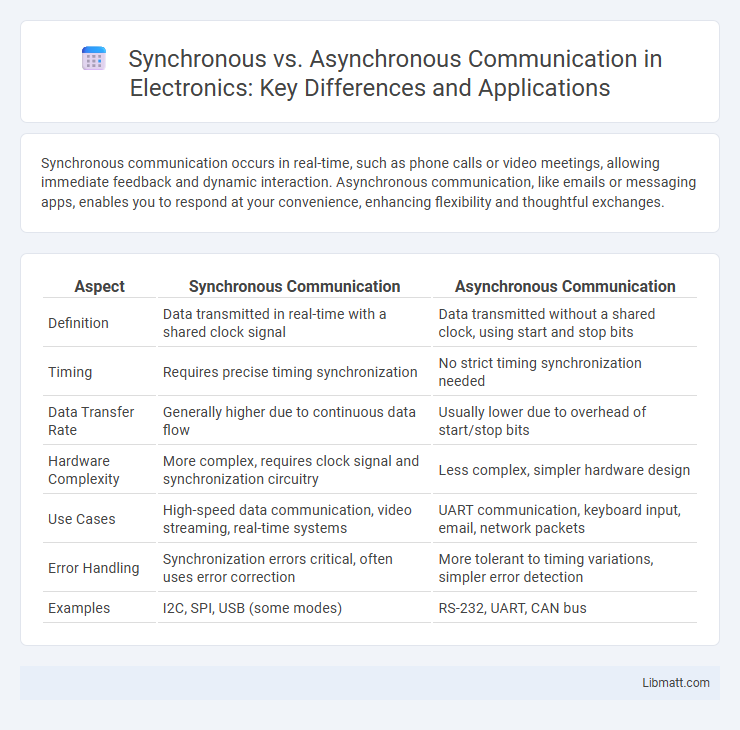
| Aspect | Synchronous Communication | Asynchronous Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data transmitted in real-time with a shared clock signal | Data transmitted without a shared clock, using start and stop bits |
| Timing | Requires precise timing synchronization | No strict timing synchronization needed |
| Data Transfer Rate | Generally higher due to continuous data flow | Usually lower due to overhead of start/stop bits |
| Hardware Complexity | More complex, requires clock signal and synchronization circuitry | Less complex, simpler hardware design |
| Use Cases | High-speed data communication, video streaming, real-time systems | UART communication, keyboard input, email, network packets |
| Error Handling | Synchronization errors critical, often uses error correction | More tolerant to timing variations, simpler error detection |
| Examples | I2C, SPI, USB (some modes) | RS-232, UART, CAN bus |
Introduction to Synchronous and Asynchronous Communication
Synchronous communication occurs in real-time, enabling immediate interaction through methods like phone calls, video conferences, and live chats, ensuring instant feedback and dynamic exchange. Asynchronous communication, such as emails, messages, and forum posts, allows participants to respond at their convenience without requiring simultaneous presence, enhancing flexibility in diverse time zones. Understanding the differences between these communication types is crucial for optimizing collaboration and productivity in both remote and in-office environments.
Defining Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication occurs when participants engage in real-time interactions, such as phone calls, video conferences, or face-to-face meetings, allowing immediate feedback and dynamic exchange of information. This type of communication is essential for urgent decision-making, collaborative teamwork, and situations requiring instant clarification. Understanding synchronous communication helps you optimize workflows that demand direct and timely responses.
Defining Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication allows information exchange without requiring participants to be present simultaneously, enabling flexibility in response times and locations. Common examples include emails, messaging apps, and discussion forums, where messages can be sent and read at any time. Your productivity increases by reducing interruptions and allowing thoughtful, measured replies in asynchronous communication environments.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Communication
Synchronous communication occurs in real-time, requiring participants to be present simultaneously, as seen in video calls and instant messaging. Asynchronous communication allows time gaps between responses, enabling flexibility through emails, forums, or recorded messages. Key differences involve immediacy, response latency, and the need for simultaneous participation, impacting collaboration efficiency and communication flow.
Advantages of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication offers real-time interaction that fosters immediate feedback and quick decision-making, enhancing collaboration and reducing misunderstandings. It is especially effective for complex discussions and brainstorming sessions where dynamic exchanges of ideas are crucial. Your team benefits from quicker resolution of issues and strengthened interpersonal connections, boosting overall productivity and engagement.
Benefits of Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication enhances productivity by allowing team members to respond at their own pace, reducing interruptions and enabling deeper focus on complex tasks. This communication style supports flexible work schedules and spans different time zones, fostering inclusivity and global collaboration. It also creates a documented trail of conversations, improving transparency and knowledge retention within organizations.
Common Tools for Synchronous Communication
Common tools for synchronous communication include video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet, which facilitate real-time interaction and collaboration across remote teams. Instant messaging applications such as Slack and Microsoft Teams enable quick text exchanges and immediate feedback during live discussions. Your choice of these tools can enhance productivity by ensuring timely responses and seamless team engagement.
Popular Platforms for Asynchronous Communication
Popular platforms for asynchronous communication include Slack, Microsoft Teams, and email services like Gmail and Outlook, which enable users to send messages and collaborate without requiring immediate responses. Tools like Trello, Asana, and Jira optimize project management by allowing team members to update tasks and share progress on their own schedules. These platforms enhance productivity by accommodating different time zones and work habits, making remote and distributed teamwork more efficient.
Choosing the Right Communication Method for Your Team
Choosing the right communication method for your team depends on project urgency, collaboration needs, and team dynamics. Synchronous communication, like video calls and instant messaging, fosters real-time interaction and immediate feedback, ideal for brainstorming and quick decision-making. Asynchronous communication, including emails and project management tools, allows flexibility and thoughtful responses, supporting teams across different time zones and reducing interruptions.
Future Trends in Workplace Communication
Future trends in workplace communication emphasize a hybrid approach combining synchronous methods like video calls and meetings with asynchronous tools such as collaborative platforms and messaging apps. Advances in AI-powered communication will enhance both real-time interactions and delayed responses, improving efficiency and clarity. Your organization can leverage these innovations to foster flexibility, accommodate diverse workstyles, and boost overall productivity.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous communication Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com