Oil cooled transformers offer superior cooling efficiency and are ideal for high-capacity applications requiring enhanced thermal management, while dry type transformers provide safer operation with reduced fire hazards and lower maintenance needs, making them suitable for indoor environments and sensitive installations. Your choice depends on factors like site safety, cooling requirements, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
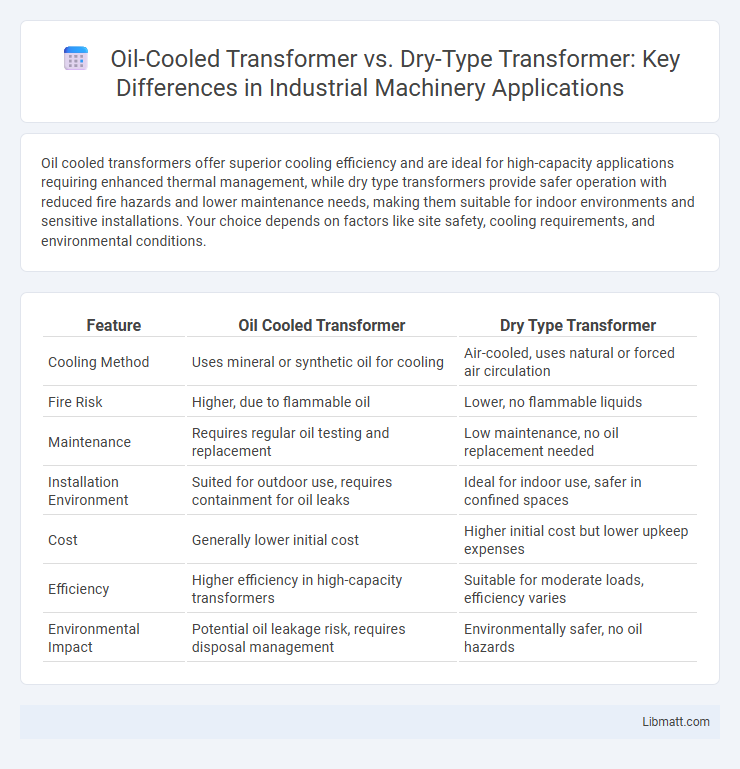
| Feature | Oil Cooled Transformer | Dry Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Uses mineral or synthetic oil for cooling | Air-cooled, uses natural or forced air circulation |
| Fire Risk | Higher, due to flammable oil | Lower, no flammable liquids |
| Maintenance | Requires regular oil testing and replacement | Low maintenance, no oil replacement needed |
| Installation Environment | Suited for outdoor use, requires containment for oil leaks | Ideal for indoor use, safer in confined spaces |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but lower upkeep expenses |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency in high-capacity transformers | Suitable for moderate loads, efficiency varies |
| Environmental Impact | Potential oil leakage risk, requires disposal management | Environmentally safer, no oil hazards |
Introduction to Oil Cooled and Dry Type Transformers
Oil cooled transformers use mineral or synthetic oil as an insulating and cooling medium, enhancing heat dissipation and allowing higher power capacity. Dry type transformers rely on air or other non-liquid insulations such as epoxy resin, making them suitable for indoor and environmentally sensitive areas. The choice between these transformers depends on factors like cooling efficiency, maintenance requirements, fire risk, and installation environment.
Basic Working Principles of Each Transformer
Oil-cooled transformers use mineral or synthetic oil to insulate and cool the windings by circulating the oil to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring efficient operation under heavy loads. Dry-type transformers rely on air circulation around the windings for cooling, often employing resin encapsulation to protect the coils while minimizing fire hazards. Understanding these basic working principles helps you select the right transformer based on cooling requirements and environmental safety considerations.
Key Differences in Construction
Oil-cooled transformers use liquid insulating oil for cooling and insulation, featuring a sealed tank containing windings immersed in oil to dissipate heat efficiently. Dry-type transformers rely on air cooling with windings encapsulated in epoxy resin or varnish, eliminating the need for oil and reducing fire hazards. Your choice depends on factors like environmental safety, maintenance requirements, and installation location.
Cooling Mechanisms Explained
Oil cooled transformers use mineral or synthetic oil as a cooling medium, which absorbs heat generated by the core and windings and dissipates it through natural convection or forced circulation. Dry type transformers rely on air circulation, either naturally or via fans, to cool the windings and core, making them suitable for indoor or environmentally sensitive installations. Understanding these cooling mechanisms helps you select the most efficient transformer based on operational environment and maintenance requirements.
Efficiency Comparison
Oil-cooled transformers typically offer higher efficiency due to improved heat dissipation, which reduces electrical losses during operation. Dry type transformers generally have slightly lower efficiency, as their resin-coated windings and air cooling limit heat transfer, leading to increased resistance. Choosing the right transformer for Your application depends on balancing efficiency requirements with maintenance and environmental considerations.
Safety and Fire Risk Factors
Oil-cooled transformers contain mineral oil that can pose a significant fire hazard due to its flammability, increasing the risk of fire in case of leaks or faults. Dry-type transformers use air for cooling and have epoxy resin or cast coil insulation, which drastically reduces fire risk and enhances safety in indoor or environmentally sensitive locations. Safety regulations often favor dry-type transformers in public or confined spaces to minimize the potential for fire-related accidents and environmental damage.
Installation Requirements and Flexibility
Oil-cooled transformers require specialized installation environments with proper ventilation and fire safety measures due to their liquid insulation, making them less flexible for indoor or confined spaces. Dry type transformers offer greater installation flexibility as they can be safely installed indoors without the need for additional fire containment systems. Your choice depends on space constraints, safety regulations, and specific application needs.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity
Oil-cooled transformers require regular maintenance, including oil testing and replacement, to prevent insulation degradation and overheating, contributing to a typical lifespan of 25-30 years. Dry type transformers, with sealed insulation systems, demand less frequent maintenance and offer improved safety in fire-prone environments, often achieving comparable longevity of 20-30 years. The choice between the two depends on operational conditions, maintenance capabilities, and environmental considerations impacting their durability and performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational
Oil-cooled transformers generally have higher initial costs due to the complexity of oil-filled insulation and cooling systems, but they offer better efficiency and longevity, reducing operational expenses over time. Dry type transformers have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance requirements, making them cost-effective for indoor or environmentally sensitive applications; however, their operational costs may increase due to shorter lifespan and potential cooling limitations. When analyzing total cost of ownership, oil-cooled transformers tend to be more economical in high-load, outdoor environments, whereas dry type transformers are preferred for lower power ratings and locations demanding enhanced safety and minimal fire risk.
Ideal Applications for Each Transformer Type
Oil-cooled transformers are ideal for outdoor installations, heavy industrial applications, and environments requiring superior cooling efficiency and longer service life due to their oil-based insulation and heat dissipation. Dry type transformers suit indoor settings, commercial buildings, and locations with strict fire safety regulations, as they use air for cooling, reducing the risk of fire hazards. Your choice depends on the installation environment's safety requirements and cooling needs.
Oil cooled transformer vs dry type transformer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com