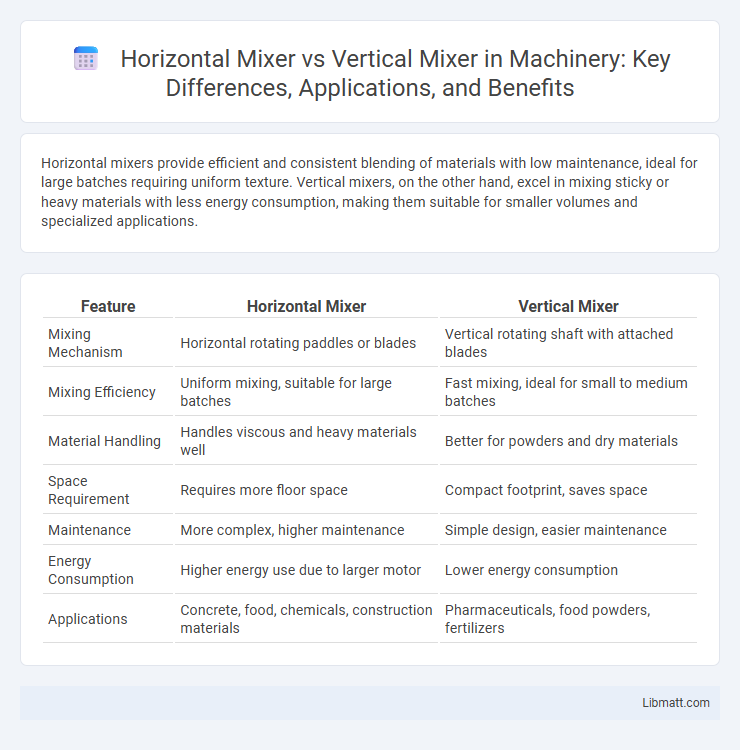
Horizontal mixers provide efficient and consistent blending of materials with low maintenance, ideal for large batches requiring uniform texture. Vertical mixers, on the other hand, excel in mixing sticky or heavy materials with less energy consumption, making them suitable for smaller volumes and specialized applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Horizontal Mixer | Vertical Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing Mechanism | Horizontal rotating paddles or blades | Vertical rotating shaft with attached blades |
| Mixing Efficiency | Uniform mixing, suitable for large batches | Fast mixing, ideal for small to medium batches |
| Material Handling | Handles viscous and heavy materials well | Better for powders and dry materials |
| Space Requirement | Requires more floor space | Compact footprint, saves space |
| Maintenance | More complex, higher maintenance | Simple design, easier maintenance |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to larger motor | Lower energy consumption |
| Applications | Concrete, food, chemicals, construction materials | Pharmaceuticals, food powders, fertilizers |
Introduction: Horizontal vs Vertical Mixers
Horizontal mixers offer efficient blending for large batches with a low center of gravity, ideal for consistent mixing of powders and granules. Vertical mixers excel in blending lightweight, fine materials and provide better vertical mixing dynamics for specialty applications. You can choose based on your material characteristics and production scale for optimal mixing performance.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Mixers
Horizontal mixers feature a horizontal drum with a rotating shaft that offers efficient blending and quicker processing times, ideal for large batch mixing. Vertical mixers have a vertical drum with a central agitator, better suited for gentle mixing and handling fragile materials without damaging them. Your choice depends on the desired mixing intensity, batch size, and material characteristics, with horizontal mixers excelling in heavy-duty tasks and vertical mixers providing precision for delicate blends.
Design and Construction Overview
Horizontal mixers feature a cylindrical drum with a horizontal axis, equipped with paddles or blades that rotate to achieve consistent material blending. Vertical mixers have a stationary vertical drum with a central agitator shaft designed for lifting and folding materials to improve uniformity. Your choice depends on the type of materials processed and the mixing efficiency required for your application.
Mixing Efficiency and Performance
Horizontal mixers deliver superior mixing efficiency by ensuring uniform particle distribution through their rotating horizontal blades, making them ideal for large-scale industrial applications requiring consistent blend quality. Vertical mixers excel in performance for light to medium mixing tasks, leveraging gravity-driven tumbling action that reduces power consumption but may produce less homogeneous mixtures in shorter cycles. Selection depends on material type and desired batch consistency, with horizontal models favored for dense, abrasive materials and vertical mixers suited for free-flowing powders.
Suitability for Different Materials
Horizontal mixers excel in blending dense or abrasive materials, offering uniform mixing for powders, granules, and pellets, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Vertical mixers are better suited for light, free-flowing, and fragile materials, ensuring gentler blending to preserve particle integrity and minimize degradation. Choice depends on material characteristics and processing requirements, with horizontal types optimizing intensive mixing and vertical models prioritizing material protection.
Space and Installation Requirements
Horizontal mixers require more floor space due to their elongated design, making installation challenging in compact facilities. Vertical mixers have a smaller footprint and utilize vertical height, optimizing space efficiency in constrained environments. Installation of vertical mixers is generally simpler, with less need for extensive structural modifications.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Horizontal mixers feature easily accessible blades and open designs that simplify cleaning and maintenance, reducing downtime in industrial settings. Vertical mixers often have a more compact structure, but their deeper mixing chambers can complicate thorough cleaning and require more frequent inspection of seals and bearings. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing ease of maintenance or space efficiency in production environments.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Horizontal mixers typically consume more energy due to their larger motor sizes and extended mixing cycles, making them less efficient for smaller batches. Vertical mixers operate with lower energy consumption by using a single vertical shaft and shorter processing times, which can reduce your overall power costs. Choosing the right mixer depends on your operational scale and energy efficiency priorities.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational Expenses
Horizontal mixers generally require higher initial investment due to their complex design and larger footprint, but they offer more efficient mixing for large-scale operations, reducing operational costs over time. Vertical mixers tend to have lower upfront costs and smaller space requirements, making them economical for smaller batches, though their mixing efficiency may lead to longer processing times and increased energy consumption. Evaluating both mixers' initial purchase price, maintenance expenses, energy usage, and production output is crucial for accurate cost analysis tailored to specific industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Application
Selecting the right mixer depends on your specific application needs, with horizontal mixers excelling in uniform blending of dry powders and granules for industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Vertical mixers offer advantages in space-saving design and efficient mixing of free-flowing materials and moist substances, ideal for smaller batch sizes or limited floor space. Evaluating factors such as material type, batch size, mixing time, and space constraints ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency for your production process.
Horizontal mixer vs vertical mixer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com