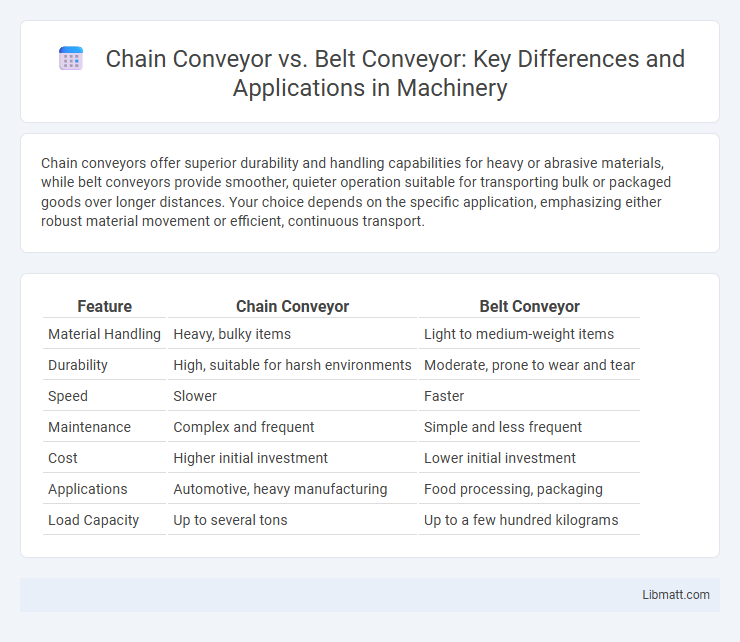
Chain conveyors offer superior durability and handling capabilities for heavy or abrasive materials, while belt conveyors provide smoother, quieter operation suitable for transporting bulk or packaged goods over longer distances. Your choice depends on the specific application, emphasizing either robust material movement or efficient, continuous transport.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chain Conveyor | Belt Conveyor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Handling | Heavy, bulky items | Light to medium-weight items |
| Durability | High, suitable for harsh environments | Moderate, prone to wear and tear |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Maintenance | Complex and frequent | Simple and less frequent |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Applications | Automotive, heavy manufacturing | Food processing, packaging |
| Load Capacity | Up to several tons | Up to a few hundred kilograms |
Introduction to Chain and Belt Conveyors
Chain conveyors use linked metal chains to move heavy or bulky materials, offering durability and strength for industrial applications. Belt conveyors employ continuous loops of rubber or fabric belts, ideal for transporting lighter, uniform items efficiently across various distances. Choosing the right conveyor depends on your material type, load capacity, and operational environment.
Key Differences Between Chain and Belt Conveyors
Chain conveyors use linked metal chains to move heavy loads over short distances, providing durability and resistance to high temperatures or abrasive materials, while belt conveyors utilize continuous rubber or fabric belts ideal for transporting lighter, bulkier, or fragile items smoothly over longer distances. The key differences lie in load capacity, maintenance needs, and suitable environments; chain conveyors excel in handling extreme conditions and heavy loads, whereas belt conveyors offer quieter operation and greater versatility in shape and incline. To choose the best option for your application, consider the weight, material type, and operational environment that impact conveyor efficiency and longevity.
How Chain Conveyors Work
Chain conveyors operate by using a series of linked metal chains that move over sprockets, enabling the transport of heavy loads across a production line. The chains directly engage with the carried items or are fitted with attachments to secure materials, offering higher durability and load capacity compared to belt conveyors. If your application involves moving bulky or abrasive materials, chain conveyors provide reliable performance and reduced maintenance needs.
How Belt Conveyors Operate
Belt conveyors operate by using a continuous loop of material, typically rubber or fabric, stretched over pulleys to transport goods efficiently across various distances. The belt is powered by electric motors that drive one or more pulleys, creating a smooth and consistent movement suitable for handling light to moderate loads. This system excels in transporting bulk materials, packaged goods, and unevenly shaped items with minimal maintenance requirements.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Chain conveyors offer higher durability and load-carrying capacity, making them ideal for transporting heavy or abrasive materials with minimal slippage. Belt conveyors excel in smooth and quiet operation, providing greater speed and energy efficiency when handling lighter loads and bulk materials. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, where chain conveyors deliver superior robustness and belt conveyors ensure consistent, efficient performance for lighter goods.
Common Applications of Chain Conveyors
Chain conveyors are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as automotive assembly lines, steel manufacturing, and warehouses handling bulky or abrasive materials. Their robust design enables them to transport heavy loads, pallets, and large containers efficiently, where belt conveyors may not withstand the weight or harsh conditions. Choosing the right conveyor system depends on your specific industry needs and the types of materials you need to move.
Typical Uses of Belt Conveyors
Belt conveyors are commonly used for transporting lightweight to medium-weight materials over long distances in industries such as mining, food processing, and packaging. Their smooth, continuous belt surface is ideal for moving bulk materials, boxes, and packaged products efficiently on flat or slightly inclined paths. Belt conveyors excel in applications requiring gentle handling and steady, high-speed transport of goods.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Chain conveyors require more frequent maintenance due to their complex mechanical components, including chains and sprockets that need regular lubrication and tension adjustments to prevent wear. Belt conveyors offer higher durability with fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain and ideal for transporting lighter materials. Your choice should consider the operational environment and maintenance resources to ensure long-term efficiency and minimal downtime.
Cost Analysis: Chain vs. Belt Conveyors
Chain conveyors generally incur higher initial costs due to robust construction and heavy-duty components, making them suitable for handling heavier loads and harsh environments. Belt conveyors offer lower upfront expenses and maintenance costs, ideal for transporting lighter, bulkier materials over longer distances with smooth operation. Your choice between chain and belt conveyors should consider factors like load weight, operational environment, and budget constraints to optimize cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Conveyor for Your Needs
Selecting the right conveyor system depends on the specific material handling requirements, load weight, and operating environment. Chain conveyors excel in transporting heavy or bulky items with durability and resistance to high temperatures, while belt conveyors offer smooth and quiet operation ideal for lightweight or delicate products. Evaluating factors such as throughput capacity, maintenance needs, and floor space will guide the optimal choice between chain and belt conveyors.
Chain conveyor vs belt conveyor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com