An air compressor increases air pressure by compressing and storing it, ideal for powering pneumatic tools and inflating tires, while a vacuum pump removes air to create a low-pressure environment for applications like refrigeration or laboratory work. Understanding the differences helps you select the right equipment based on whether you need to add pressure or create a vacuum.
Table of Comparison
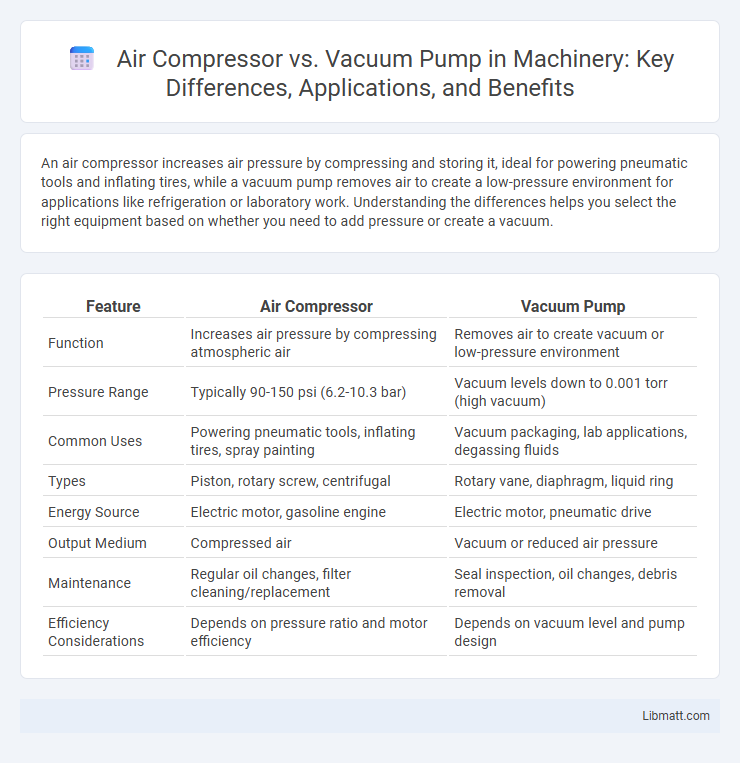
| Feature | Air Compressor | Vacuum Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Increases air pressure by compressing atmospheric air | Removes air to create vacuum or low-pressure environment |
| Pressure Range | Typically 90-150 psi (6.2-10.3 bar) | Vacuum levels down to 0.001 torr (high vacuum) |
| Common Uses | Powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, spray painting | Vacuum packaging, lab applications, degassing fluids |
| Types | Piston, rotary screw, centrifugal | Rotary vane, diaphragm, liquid ring |
| Energy Source | Electric motor, gasoline engine | Electric motor, pneumatic drive |
| Output Medium | Compressed air | Vacuum or reduced air pressure |
| Maintenance | Regular oil changes, filter cleaning/replacement | Seal inspection, oil changes, debris removal |
| Efficiency Considerations | Depends on pressure ratio and motor efficiency | Depends on vacuum level and pump design |
Introduction to Air Compressors and Vacuum Pumps
Air compressors convert power into potential energy stored as compressed air, widely used in pneumatic tools, HVAC systems, and industrial applications. Vacuum pumps create a vacuum by removing gas molecules from a sealed volume, essential for processes in manufacturing, laboratory environments, and medical devices. Both devices operate on distinct principles and serve critical roles in various engineering and scientific fields.
Core Functions: How Air Compressors and Vacuum Pumps Work
Air compressors convert power into potential energy by compressing air and storing it in a tank for various applications like powering pneumatic tools or inflating tires. Vacuum pumps remove air or gas molecules from a sealed volume, creating a partial vacuum used in processes such as medical suction, laboratory work, or packaging. Understanding your requirement for pressure increase or air removal helps determine whether an air compressor or a vacuum pump is the ideal device for Your operation.
Key Differences Between Air Compressors and Vacuum Pumps
Air compressors increase the pressure of air by compressing it into a smaller volume, while vacuum pumps reduce the air pressure by removing air molecules to create a vacuum. Air compressors are commonly used for powering pneumatic tools and inflating tires, whereas vacuum pumps are essential in applications like laboratory experiments, vacuum packaging, and medical suction. Your choice depends on whether you need to generate high pressure or create a low-pressure environment.
Applications of Air Compressors
Air compressors are essential in industries such as manufacturing, automotive repair, and construction for powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, and operating spray guns. Their capacity to deliver pressurized air makes them ideal for cleaning equipment and supporting HVAC control systems. Your choice of an air compressor depends on the specific pressure requirements and flow rates needed for efficient operation.
Applications of Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps are essential in industries requiring controlled environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals, where precise pressure regulation is critical. They enable the removal of gases and vapors, facilitating processes like vacuum distillation, freeze drying, and vacuum packaging to preserve product integrity. Your operations can benefit from vacuum pumps in applications demanding contamination-free conditions and efficient gas evacuation.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Air compressors typically achieve higher volumetric efficiency by converting electrical energy into compressed air with minimal losses, ideal for applications requiring consistent high pressure. Vacuum pumps often exhibit varied efficiency depending on the technology used, with liquid ring and rotary vane pumps providing reliable performance in low to medium vacuum ranges but consuming more energy under heavy load conditions. Performance comparisons highlight that air compressors excel in delivering continuous airflow at elevated pressures, while vacuum pumps are optimized for creating negative pressure environments, each tailored to their specific industrial uses.
Energy Consumption: Air Compressor vs Vacuum Pump
Air compressors typically consume more energy than vacuum pumps due to the higher power required to compress atmospheric air to the desired pressure levels. Vacuum pumps operate by removing air molecules from a sealed volume, often requiring less energy for generating negative pressure compared to the positive pressure produced by air compressors. Industry data shows vacuum pumps can achieve energy savings of up to 30-50% in applications where maintaining low pressure is critical, making them more efficient for specific vacuum processes.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance of an air compressor involves checking and replacing air filters, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting belts for wear to ensure optimal performance and extended lifespan. Vacuum pumps require consistent oil changes, seal inspections, and monitoring for leaks to prevent contamination and mechanical failure. Properly maintaining your equipment can significantly enhance longevity and reduce operational costs over time.
Cost Considerations
Air compressors generally have lower upfront costs compared to vacuum pumps, making them more accessible for budget-conscious projects. Maintenance expenses for air compressors tend to be less frequent but can vary significantly based on usage and model quality. When choosing equipment, consider your total cost of ownership, including initial purchase, energy consumption, and ongoing service, to ensure your investment meets operational needs efficiently.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting between an air compressor and a vacuum pump depends on your specific application requirements, such as pressure type and flow rate. Air compressors are ideal for delivering pressurized air for tools and machinery, while vacuum pumps provide suction for processes like material handling or laboratory use. Assessing factors like operating pressure, power consumption, and maintenance needs ensures you choose the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
Air compressor vs vacuum pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com