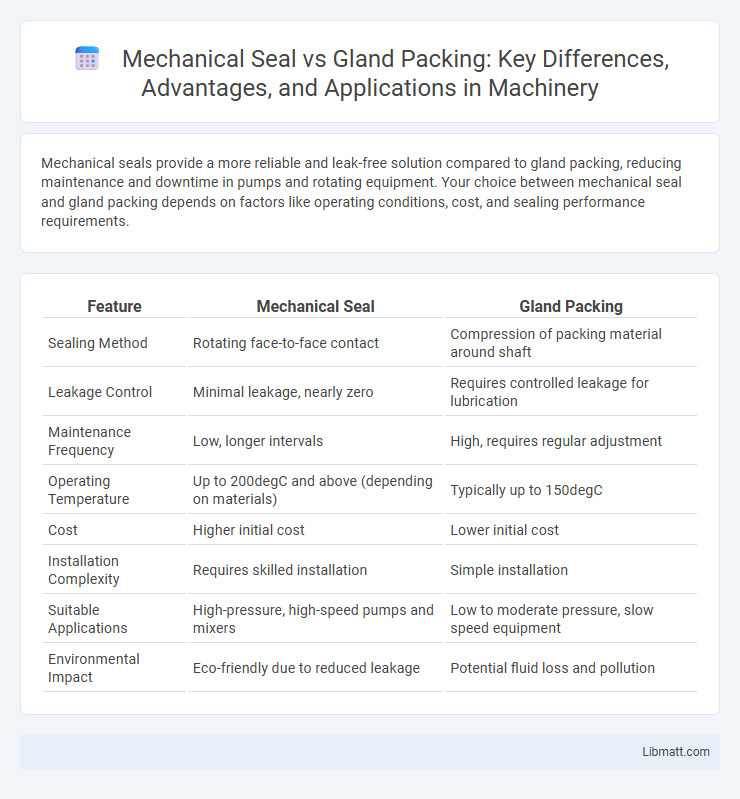
Mechanical seals provide a more reliable and leak-free solution compared to gland packing, reducing maintenance and downtime in pumps and rotating equipment. Your choice between mechanical seal and gland packing depends on factors like operating conditions, cost, and sealing performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Seal | Gland Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Rotating face-to-face contact | Compression of packing material around shaft |
| Leakage Control | Minimal leakage, nearly zero | Requires controlled leakage for lubrication |
| Maintenance Frequency | Low, longer intervals | High, requires regular adjustment |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 200degC and above (depending on materials) | Typically up to 150degC |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Installation Complexity | Requires skilled installation | Simple installation |
| Suitable Applications | High-pressure, high-speed pumps and mixers | Low to moderate pressure, slow speed equipment |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly due to reduced leakage | Potential fluid loss and pollution |
Introduction to Mechanical Seals and Gland Packing
Mechanical seals provide a modern and efficient method to prevent leakage in rotating equipment by using precise sealing faces and elastomers, offering superior reliability compared to traditional gland packing. Gland packing, consisting of braided or woven materials compressed around a shaft, offers a cost-effective sealing solution but requires frequent maintenance and adjustment to control leakage. Your choice between mechanical seals and gland packing depends on factors like equipment speed, pressure, and maintenance capabilities.
How Mechanical Seals Work
Mechanical seals operate by creating a seal between a rotating shaft and a stationary housing, using a pair of precisely machined sealing faces that remain in constant contact under spring or hydraulic pressure. These seals prevent fluid leakage by maintaining a thin film of lubricant between the faces, reducing friction and wear. Unlike gland packing, mechanical seals offer superior durability and minimize maintenance requirements due to their efficient sealing mechanism and resistance to pressure fluctuations.
How Gland Packing Operates
Gland packing operates by compressing a braided material, typically made from fibers such as graphite or PTFE, around the pump shaft within the stuffing box to create a seal that minimizes fluid leakage. This sealing method relies on the adjustable gland follower to maintain pressure on the packing, accommodating shaft movement and wear over time. You can control leakage rates manually by tightening the gland, but excessive compression risks increased shaft wear and energy loss due to friction.
Key Differences Between Mechanical Seals and Gland Packing
Mechanical seals provide a more reliable and leak-free solution compared to gland packing, which relies on compressible fibers to seal around the shaft. Mechanical seals offer longer service life and require less maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs, while gland packing often demands frequent adjustments and replacements due to wear. Your choice between these two options should consider factors such as pressure, temperature, shaft speed, and the nature of the fluid being sealed to ensure optimal performance.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Mechanical seals offer superior performance and efficiency compared to gland packing by providing a more reliable and leak-proof seal in rotating equipment. They reduce friction and wear, resulting in lower energy consumption and extended equipment lifespan. Gland packing, while simpler and less expensive initially, tends to have higher leakage rates and requires frequent maintenance, leading to decreased operational efficiency.
Leakage Control and Environmental Impact
Mechanical seals provide superior leakage control compared to gland packing by creating a tight, reliable seal that minimizes fluid loss and reduces the risk of contamination, enhancing operational efficiency. They are environmentally friendly due to their reduced leakage rates, which decrease hazardous emissions and prevent pollutant discharge into surrounding areas. Your choice of mechanical seals promotes sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations while ensuring optimal system performance.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Mechanical seals typically require less frequent maintenance than gland packing due to their advanced sealing technology, resulting in lower long-term operational costs. Gland packing demands regular adjustments and replacement, increasing both labor expenses and downtime. Your choice impacts overall maintenance budgets, with mechanical seals offering more cost-effective, reliable performance over time.
Suitability for Different Applications
Mechanical seals are highly suitable for high-pressure and high-speed applications due to their reliable sealing capability and low leakage rates, making them ideal for pumps, compressors, and mixers in industries such as chemical processing and oil refining. Gland packing works well in low-pressure, low-speed environments and is often preferred for simple, cost-sensitive applications like water pumps or valves where maintenance access is frequent. Your choice between the two should consider factors such as operating conditions, maintenance frequency, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Longevity and Reliability Factors
Mechanical seals offer superior longevity and reliability compared to gland packing due to their precise sealing mechanism and resistance to wear under high-pressure conditions. They minimize leakage and reduce maintenance frequency by maintaining consistent sealing performance over extended periods. Gland packing, while simpler and less expensive initially, tends to degrade faster, requiring frequent adjustments and replacements that compromise operational reliability.
Choosing the Right Sealing Solution
Mechanical seals offer superior leak prevention and longer service life compared to gland packing, especially in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Gland packing is a cost-effective choice for low-pressure systems but requires frequent maintenance and adjustment to prevent leaks and wear. Selecting the right sealing solution depends on factors such as operational pressure, temperature, shaft speed, and maintenance capabilities, ensuring optimal performance and reduced downtime.
Mechanical seal vs gland packing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com