Tapered roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads efficiently due to their angled rollers, making them ideal for applications with combined forces. Cylindrical roller bearings primarily support heavy radial loads and offer lower friction for high-speed operations, so choosing the right type depends on your load and speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
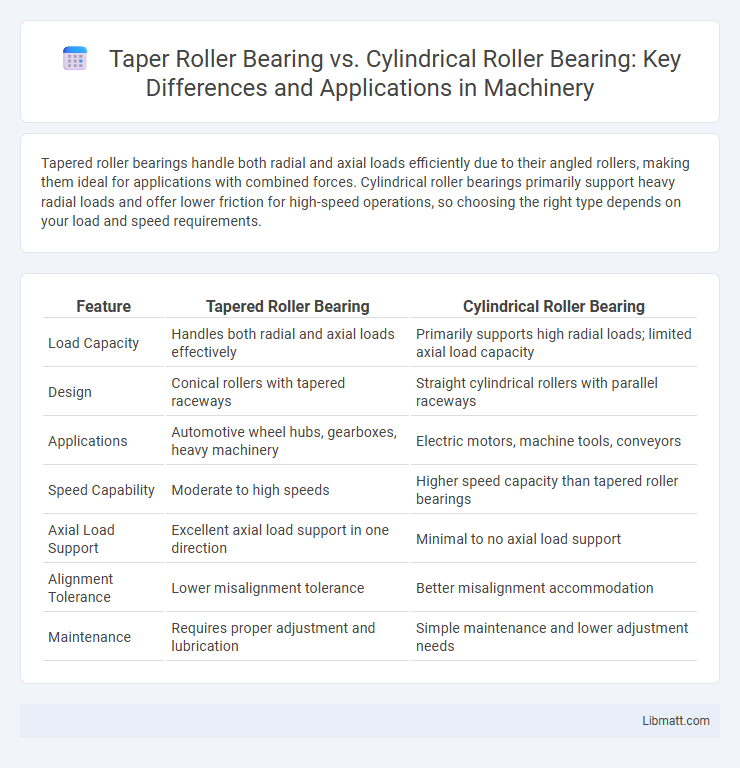
| Feature | Tapered Roller Bearing | Cylindrical Roller Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Handles both radial and axial loads effectively | Primarily supports high radial loads; limited axial load capacity |
| Design | Conical rollers with tapered raceways | Straight cylindrical rollers with parallel raceways |
| Applications | Automotive wheel hubs, gearboxes, heavy machinery | Electric motors, machine tools, conveyors |
| Speed Capability | Moderate to high speeds | Higher speed capacity than tapered roller bearings |
| Axial Load Support | Excellent axial load support in one direction | Minimal to no axial load support |
| Alignment Tolerance | Lower misalignment tolerance | Better misalignment accommodation |
| Maintenance | Requires proper adjustment and lubrication | Simple maintenance and lower adjustment needs |
Introduction to Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings and cylindrical roller bearings are critical components designed to support radial and axial loads in machinery. Tapered roller bearings feature conical rollers that handle combined loads effectively, while cylindrical roller bearings with straight rollers excel at managing high radial loads. Understanding these differences helps you select the optimal roller bearing for your specific mechanical application, ensuring durability and performance.
Overview of Taper Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings feature conically shaped rollers that handle both radial and axial loads efficiently, making them suitable for applications with combined loading conditions. Their design allows for high load-bearing capacity and durability in automotive and industrial machinery. You can rely on tapered roller bearings when precise alignment and support for thrust and radial forces are critical.
Overview of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings feature rollers with a high length-to-diameter ratio that enable them to support heavy radial loads and moderate axial loads, making them ideal for applications requiring high-speed performance and precise shaft alignment. Their design involves multiple rollers arranged parallel to the shaft, which reduces friction and increases load-carrying capacity compared to other types of bearings. You can rely on cylindrical roller bearings in electric motors, gearboxes, and machine tool spindles where durability and efficient load distribution are critical.
Key Design Differences
Tapered roller bearings feature conical rollers designed to handle both radial and axial loads, making them ideal for applications requiring high thrust capacity. Cylindrical roller bearings utilize straight rollers, optimized primarily for radial loads with minimal axial load tolerance. Your choice depends on load direction needs, as tapered bearings excel in combined loading scenarios while cylindrical bearings provide superior radial load performance.
Load Handling Capabilities
Tapered roller bearings excel in handling combined radial and axial loads due to their conical geometry, which allows efficient distribution of forces along the roller length. Cylindrical roller bearings primarily support high radial loads but have limited capacity for axial loads because of their straight roller design. Engineers often select tapered roller bearings for applications requiring robust axial load handling in addition to substantial radial loads.
Axial vs Radial Load Support
Tapered roller bearings excel in supporting both axial and radial loads due to their angled roller design, which effectively manages combined forces in mechanical systems. Cylindrical roller bearings primarily focus on radial load support and offer limited axial load capacity, making them ideal for applications where high radial forces dominate. Understanding your equipment's load requirements is crucial when choosing between these bearing types to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Friction and Efficiency Comparison
Tapered roller bearings exhibit higher friction levels due to their angled contact surfaces, which generate axial and radial load handling but increase resistance during operation. Cylindrical roller bearings feature straight rollers that reduce friction, enhancing efficiency and suitability for high-speed applications where minimal energy loss is critical. You should choose cylindrical roller bearings when maximizing efficiency and minimizing friction is essential for your machinery performance.
Common Applications
Tapered roller bearings are commonly used in automotive wheel hubs, gearboxes, and heavy machinery where they support combined radial and axial loads. Cylindrical roller bearings find frequent application in electric motors, machine tool spindles, and industrial gearboxes due to their high radial load capacity and ability to accommodate thermal expansion. Your choice between the two depends on the load conditions and operational requirements of your equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Tapered roller bearings excel in handling both radial and axial loads due to their conical geometry, making them ideal for applications requiring combined load support, but they generally have higher friction and require more precise alignment than cylindrical roller bearings. Cylindrical roller bearings offer higher radial load capacity and lower friction under pure radial loads, enhancing rotational speed and efficiency, yet they lack significant axial load handling, limiting their use in thrust load conditions. The choice depends on application-specific requirements, such as load direction, speed, and alignment tolerance.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Needs
Tapered roller bearings are ideal for applications requiring combined axial and radial load support, offering high durability and precise alignment in automotive and heavy machinery. Cylindrical roller bearings excel in handling heavy radial loads with lower friction and higher speed capabilities, commonly used in electric motors and gearboxes. Understanding your operational load types and speed requirements is essential for selecting the right bearing to optimize performance and longevity.
Taper roller bearing vs cylindrical roller bearing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com