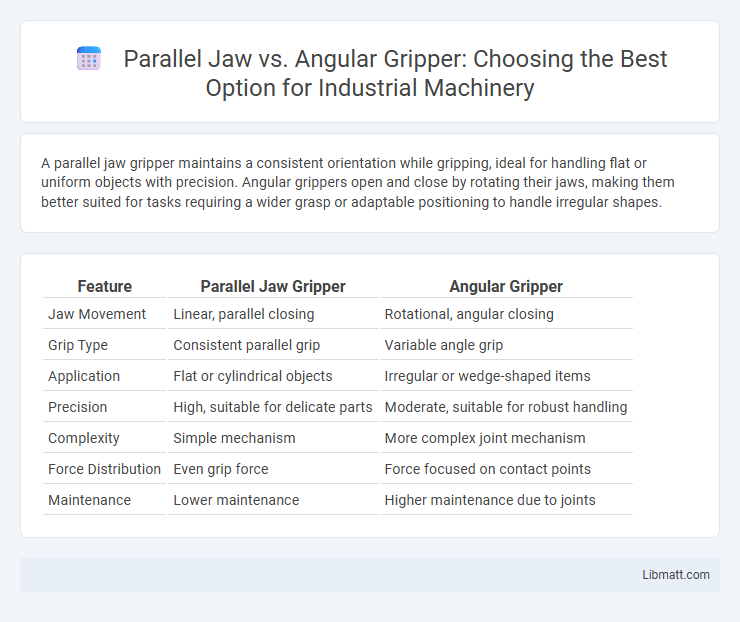
A parallel jaw gripper maintains a consistent orientation while gripping, ideal for handling flat or uniform objects with precision. Angular grippers open and close by rotating their jaws, making them better suited for tasks requiring a wider grasp or adaptable positioning to handle irregular shapes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parallel Jaw Gripper | Angular Gripper |
|---|---|---|
| Jaw Movement | Linear, parallel closing | Rotational, angular closing |
| Grip Type | Consistent parallel grip | Variable angle grip |
| Application | Flat or cylindrical objects | Irregular or wedge-shaped items |
| Precision | High, suitable for delicate parts | Moderate, suitable for robust handling |
| Complexity | Simple mechanism | More complex joint mechanism |
| Force Distribution | Even grip force | Force focused on contact points |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance | Higher maintenance due to joints |
Introduction to Robotic Grippers
Parallel jaw grippers feature two fingers that move symmetrically towards each other, providing stable and precise grasping ideal for uniform objects in automation tasks. Angular grippers operate with fingers rotating about a pivot, allowing a wider opening angle and adaptability to irregular shapes, often used in assembly lines where object variability is high. Both gripper types are essential in robotic end-effectors, optimized for specific applications requiring either consistent alignment or flexible grasping capabilities.
Overview of Parallel Jaw Grippers
Parallel jaw grippers feature two opposing fingers that move linearly in parallel to grasp objects with consistent force and precise alignment, making them ideal for handling a wide range of part sizes and shapes. Their straightforward design ensures reliable performance in automation tasks such as assembly, packaging, and material handling. These grippers excel in applications requiring secure gripping of flat or cylindrical components without angular misalignment.
Overview of Angular Grippers
Angular grippers operate by opening and closing their jaws through a pivoting or rotating motion, allowing them to grasp objects at varying angles, which is ideal for handling irregular or angled parts. These grippers typically provide a wider range of motion compared to parallel jaw grippers, making them suitable for applications requiring adaptive gripping and complex part orientations. You can benefit from angular grippers in tasks where flexible positioning and secure handling of asymmetrical objects are crucial.
Key Differences: Parallel Jaw vs Angular Gripper
Parallel jaw grippers offer consistent gripping force and maintain parallel alignment throughout the grasp, enabling precise and stable handling of flat or cylindrical objects. Angular grippers pivot open and closed at an angle, allowing for wider opening ranges and adaptability to irregularly shaped items, but may provide less uniform gripping pressure. The key difference lies in motion mechanics and grip consistency, where parallel jaws ensure parallelism and uniform force, while angular grippers emphasize wider range and adaptability.
Application Scenarios for Parallel Jaw Grippers
Parallel jaw grippers excel in applications requiring precise, stable, and repeatable gripping of flat or uniformly shaped objects such as electronic components, machined parts, or packaging materials. Their symmetrical and linear motion ensures secure handling in automated assembly lines, pick-and-place operations, and quality inspection processes. You can optimize your manufacturing workflow by selecting parallel jaw grippers for tasks demanding consistent gripping force and minimal object deformation.
Application Scenarios for Angular Grippers
Angular grippers excel in applications requiring precise angular movement to grasp objects in tight or irregular spaces, commonly found in assembly lines dealing with complex parts or tools. Their ability to open and close with a pivoting motion makes them ideal for handling oblong or asymmetrical workpieces, improving efficiency in packaging, electronics, and automotive industries. When your task involves gripping items at various angles or working within confined areas, angular grippers provide superior adaptability compared to parallel jaw grippers.
Performance Comparison: Force and Precision
Parallel jaw grippers deliver consistent gripping force with high precision due to their symmetrical clamping action, making them ideal for handling delicate or uniformly shaped objects. Angular grippers apply force through a pivoting motion, offering greater grip strength but less precision, which suits applications requiring powerful holds on irregular or angled surfaces. When balancing force and precision, parallel jaw grippers excel in accurate placement, while angular grippers provide superior clamping force for robust gripping tasks.
Gripper Selection Criteria
When selecting between parallel jaw and angular grippers, consider grip precision, object shape, and application speed. Parallel jaw grippers provide consistent, linear force ideal for rectangular or cylindrical objects, ensuring stable handling in precise automation tasks. Angular grippers offer wider opening angles suitable for irregular shapes and faster cycle times, enhancing performance in tasks requiring quick adaptability.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Type
Parallel jaw grippers offer precise, consistent grasping with uniform force distribution, making them ideal for handling delicate or flat objects; however, they may struggle with irregular shapes due to limited adaptability. Angular grippers provide a wider opening range and better accommodation of varied object geometries, enhancing versatility in complex tasks, but they often exert uneven gripping force and can be less precise. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements, balancing the need for precision with the complexity of the objects being handled.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Gripper
Selecting the right gripper depends on the specific application and object geometry; parallel jaw grippers excel in precision handling of uniform shapes, while angular grippers offer versatility for irregular or angled parts. Your choice should prioritize the gripping force requirements, object dimensions, and the need for repeatability in automated processes. Understanding these factors ensures optimal efficiency and reliability in robotic manipulation tasks.
Parallel jaw vs angular gripper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com