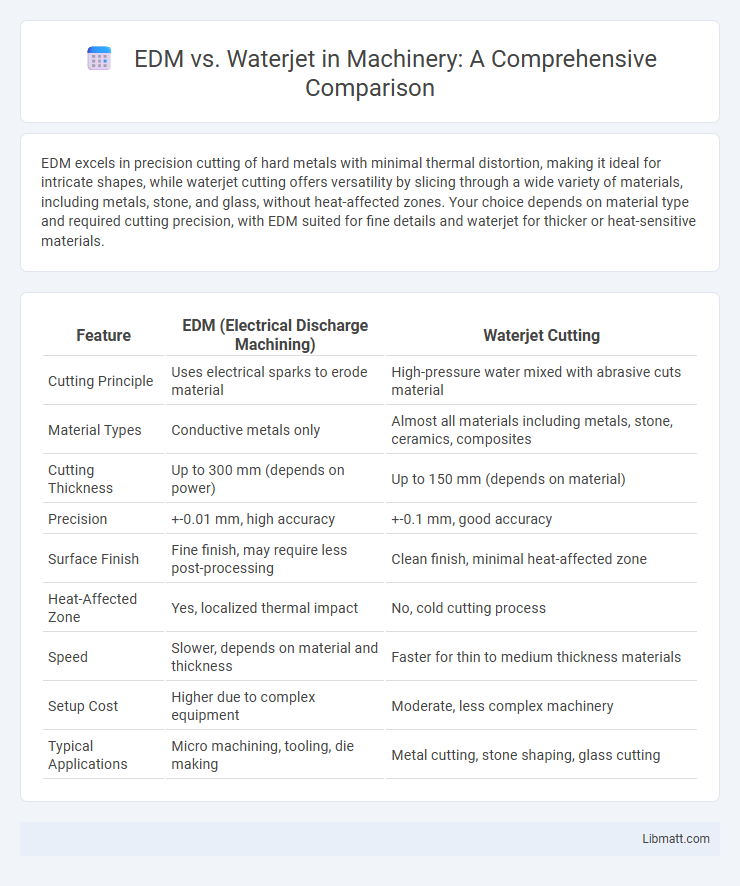
EDM excels in precision cutting of hard metals with minimal thermal distortion, making it ideal for intricate shapes, while waterjet cutting offers versatility by slicing through a wide variety of materials, including metals, stone, and glass, without heat-affected zones. Your choice depends on material type and required cutting precision, with EDM suited for fine details and waterjet for thicker or heat-sensitive materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Principle | Uses electrical sparks to erode material | High-pressure water mixed with abrasive cuts material |
| Material Types | Conductive metals only | Almost all materials including metals, stone, ceramics, composites |
| Cutting Thickness | Up to 300 mm (depends on power) | Up to 150 mm (depends on material) |
| Precision | +-0.01 mm, high accuracy | +-0.1 mm, good accuracy |
| Surface Finish | Fine finish, may require less post-processing | Clean finish, minimal heat-affected zone |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Yes, localized thermal impact | No, cold cutting process |
| Speed | Slower, depends on material and thickness | Faster for thin to medium thickness materials |
| Setup Cost | Higher due to complex equipment | Moderate, less complex machinery |
| Typical Applications | Micro machining, tooling, die making | Metal cutting, stone shaping, glass cutting |
Introduction to EDM and Waterjet Cutting
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) uses controlled electrical sparks to erode metal with high precision, ideal for intricate shapes and hard materials. Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive particles to slice through various materials without heat distortion. Your choice depends on the material type, desired precision, and thermal sensitivity.
How EDM Cutting Works
EDM cutting works by generating controlled electrical sparks between an electrode and the workpiece, eroding material with precision without physical contact. This process excels in machining hard metals and intricate shapes where conventional cutting methods struggle. Your choice of EDM ensures accurate, clean cuts, especially for complex geometries and delicate materials.
How Waterjet Cutting Works
Waterjet cutting operates by propelling a high-pressure stream of water, sometimes mixed with abrasive materials like garnet, at velocities reaching 60,000 psi, effectively eroding and slicing through a variety of materials including metal, stone, and composites. The process relies on the kinetic energy of the ultra-fine water jet to create precise, clean cuts without generating heat, thus minimizing thermal distortion or material stress. This cold-cutting technology is highly advantageous for cutting heat-sensitive substrates while offering flexibility in thickness and complex geometries compared to Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM).
Key Differences Between EDM and Waterjet
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) uses electrical discharges to erode material from electrically conductive workpieces, offering high precision for complex shapes and hard metals. Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles, to slice through a wide range of materials, including metals, composites, and ceramics, without causing heat-affected zones. The key differences lie in the cutting mechanism, suitable materials, and precision levels, with EDM excelling in intricate detail on conductive materials and waterjet providing versatility and cold cutting across diverse substrates.
Material Compatibility: EDM vs Waterjet
EDM excels at cutting hard, electrically conductive materials such as titanium, tool steel, and carbide with high precision, while waterjet offers versatile compatibility with virtually all materials, including metals, glass, ceramics, and composites. Your choice between EDM and waterjet depends on the material hardness, thickness, and sensitivity; waterjet is ideal for heat-sensitive or layered materials since it generates no heat-affected zones. For intricate cuts in tough metals, EDM provides superior accuracy, whereas waterjet ensures clean, stress-free cuts across a broader range of materials.
Precision and Tolerance Comparison
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) offers exceptional precision with tolerances reaching as tight as +-0.001 mm, making it ideal for intricate and detailed components. Waterjet cutting provides slightly lower precision, typically around +-0.1 mm, but excels in handling a wide variety of materials without heat-affected zones. For applications requiring ultra-fine detail and minimal dimensional deviation, EDM remains the preferred choice over waterjet technology.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
Wire EDM offers higher precision but operates at slower cutting speeds compared to waterjet machines, which excel in rapid material removal. Waterjet cutting provides superior efficiency for thicker or composite materials, minimizing thermal distortion and reducing the need for secondary processes. Your choice between EDM and waterjet depends on balancing the need for fine detail against throughput requirements.
Cost Factors: EDM vs Waterjet
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) generally incurs higher operational costs due to slower machining speeds, specialized electrodes, and greater power consumption compared to waterjet cutting. Waterjet machining offers cost efficiency with lower tooling expenses, minimal material waste, and reduced setup time, making it ideal for thicker or composite materials. Material type, thickness, and precision requirements significantly influence the cost-effectiveness between EDM and waterjet technologies.
Surface Finish and Edge Quality
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) delivers superior surface finish with minimal thermal distortion, producing precise, smooth edges especially on hard metals and complex geometries. Waterjet cutting excels in edge quality by providing clean, burr-free cuts without heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity. Both methods offer exceptional surface and edge results, but EDM is preferred for fine precision finishes, while waterjet is ideal for versatile, non-thermal cutting of varied materials.
Choosing the Right Cutting Technology
EDM and waterjet cutting are specialized technologies suited for different materials and applications; EDM excels in precision cutting of electrically conductive metals with complex geometries, while waterjet is versatile for cutting metals, composites, and ceramics without heat-affected zones. Your choice depends on factors like material type, thickness, desired edge quality, and production speed; waterjet offers cleaner cuts and minimal thermal distortion, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials. EDM provides superior accuracy for intricate internal shapes but is generally slower and limited to conductive materials, guiding your decision based on project requirements.
EDM vs waterjet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com