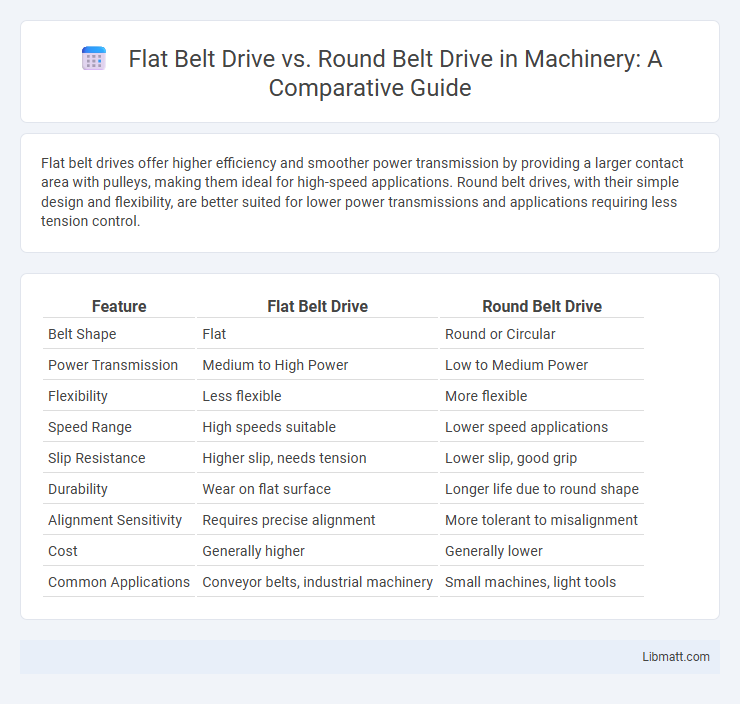
Flat belt drives offer higher efficiency and smoother power transmission by providing a larger contact area with pulleys, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Round belt drives, with their simple design and flexibility, are better suited for lower power transmissions and applications requiring less tension control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flat Belt Drive | Round Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Belt Shape | Flat | Round or Circular |
| Power Transmission | Medium to High Power | Low to Medium Power |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Speed Range | High speeds suitable | Lower speed applications |
| Slip Resistance | Higher slip, needs tension | Lower slip, good grip |
| Durability | Wear on flat surface | Longer life due to round shape |
| Alignment Sensitivity | Requires precise alignment | More tolerant to misalignment |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Common Applications | Conveyor belts, industrial machinery | Small machines, light tools |
Introduction to Flat and Round Belt Drives
Flat belt drives use wide, flat belts made of materials like leather or synthetic fabric to transmit power efficiently between pulleys, offering high speed and smooth operation with minimal slippage. Round belt drives consist of circular cross-section belts, typically made from rubber or polyurethane, designed for small pulley systems and lighter loads, providing flexibility and ease of installation. Understanding the differences in design and application helps you select the optimal belt drive for your machinery's performance and maintenance needs.
Key Differences Between Flat and Round Belt Drives
Flat belt drives provide higher power transmission efficiency and operate smoothly with less slippage, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Round belt drives, characterized by their circular cross-section, offer better flexibility and are suitable for smaller pulleys and lighter loads. Your choice depends on the specific mechanical demands, with flat belts excelling in heavy-duty, long-distance power transfer and round belts favoring compact, low-torque scenarios.
Design and Construction Features
Flat belt drives feature a broad, flat surface made of leather, rubber, or synthetic materials, designed to provide high friction and smooth power transmission over long distances, while round belt drives use a circular cross-section belt that fits into V-shaped or grooved pulleys for enhanced grip. The design of flat belts allows for flexibility and ease of alignment in various machinery layouts, whereas round belts excel in compact applications requiring minimal slippage and precise speed ratios. Your selection between the two should consider the specific mechanical requirements, such as load capacity, speed, and pulley compatibility, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Flat belt drives offer higher efficiency and smoother power transmission due to their greater contact surface area and reduced slippage, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Round belt drives, while simpler and easier to align, typically experience lower efficiency and power loss from increased friction and slippage. The choice between flat and round belts directly impacts machine performance, with flat belts preferred for maintaining consistent power delivery in industrial machinery.
Applications and Suitable Uses
Flat belt drives are ideal for high-speed, light to medium power transmission in industries such as textile, paper mills, and conveyors due to their smooth operation and ability to handle large center distances. Round belt drives are best suited for low-power applications like small machinery, agricultural equipment, and automotive accessories where flexibility, ease of installation, and vibration absorption are essential. Your choice between flat and round belts should consider the required power capacity, belt alignment tolerance, and the operating environment to ensure optimal performance.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Flat belt drives require precise alignment and tension adjustments during installation to ensure efficient power transmission, while round belt drives are generally easier to install due to their flexibility and ability to accommodate misalignment. Maintenance for flat belts often involves regular checks for wear, tracking, and tension, whereas round belts demand less frequent tension adjustments but need monitoring for surface wear and cracking. Both types benefit from routine inspection to prolong service life, but flat belts may incur higher maintenance time due to sensitivity to environmental factors like dust and moisture.
Performance in Different Operating Conditions
Flat belt drives deliver superior performance in high-speed and long-distance applications due to their higher frictional grip and lower slip rates compared to round belt drives. Round belts excel in environments requiring flexibility and alignment tolerance, performing better in lower speed or variable load conditions where shock absorption is critical. Your choice depends on the operating speed, load variability, and environmental factors affecting belt tension and wear.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Flat belt drives generally offer lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing and less material usage compared to round belt drives. Round belts often require higher investment in specialized pulleys and maintenance, increasing long-term expenses. Your choice should consider the overall economic impact, factoring in durability, maintenance frequency, and operational efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Flat belt drives offer high efficiency and smooth operation with minimal slippage, making them ideal for long-distance power transmission and variable speed applications. However, they require larger pulley diameters, precise alignment, and are prone to wear and distortion, limiting their use in dusty or high-torque environments. Round belt drives provide better flexibility, tolerate misalignment, and require smaller pulleys, but they generally have lower power transmission capacity and increased slippage compared to flat belts.
Choosing the Right Belt Drive for Your System
Choosing the right belt drive for your system depends on factors like power transmission efficiency, belt speed, and pulley design. Flat belt drives offer high efficiency and smooth operation best suited for high-speed, low-torque applications, while round belt drives excel in simple, low-power scenarios with easy alignment and tensioning. Your system's load requirements and maintenance preferences will guide the optimal choice between these two belt types.
Flat belt drive vs round belt drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com