Synchronous belts offer precise timing and high efficiency for applications requiring exact speed ratios, while V-belts provide flexibility and cushioning, making them ideal for variable load transfers. Choosing the right belt depends on your machine's need for accuracy and load conditions.
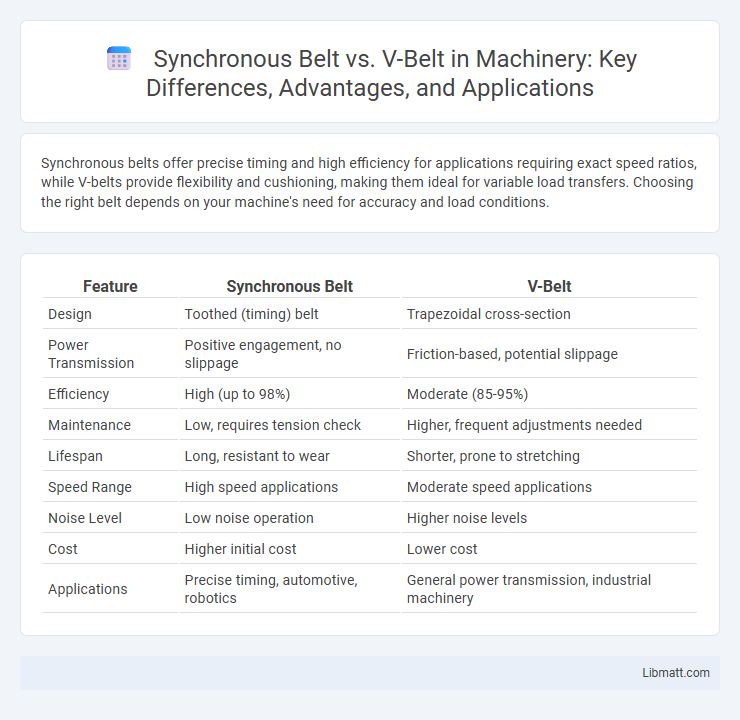
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synchronous Belt | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Toothed (timing) belt | Trapezoidal cross-section |
| Power Transmission | Positive engagement, no slippage | Friction-based, potential slippage |
| Efficiency | High (up to 98%) | Moderate (85-95%) |
| Maintenance | Low, requires tension check | Higher, frequent adjustments needed |
| Lifespan | Long, resistant to wear | Shorter, prone to stretching |
| Speed Range | High speed applications | Moderate speed applications |
| Noise Level | Low noise operation | Higher noise levels |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Precise timing, automotive, robotics | General power transmission, industrial machinery |
Introduction to Synchronous Belts and V-Belts
Synchronous belts, also known as timing belts, are designed with teeth that engage with corresponding grooves on pulleys to provide precise, slip-free power transmission in machinery. V-belts, characterized by their trapezoidal cross-section, rely on friction within pulley grooves to transfer motion and are widely used for their durability and ease of maintenance. Your choice between these belts depends on the need for accuracy versus flexibility in mechanical applications.
Working Principles: Synchronous vs. V-Belt
Synchronous belts operate using positive tooth engagement with pulleys, ensuring precise timing and minimal slippage in power transmission. V-belts rely on friction between the belt's trapezoidal cross-section and pulley grooves, allowing for smoother but less accurate power transfer. The synchronous belt's design is ideal for applications requiring exact synchronization, while V-belts suit variable-speed and shock-load conditions.
Key Structural Differences
Synchronous belts feature teeth on the inner surface that mesh precisely with pulleys, providing accurate timing and preventing slippage, while V-belts have a trapezoidal cross-section that wedges into pulley grooves for friction-driven power transmission. The structure of synchronous belts allows for high-efficiency power transfer and precise synchronization, making them ideal for timing-critical applications, unlike V-belts, which offer flexibility and vibration damping. Understanding these key structural differences helps you select the optimal belt type for your mechanical system's performance and reliability.
Efficiency and Power Transmission Comparison
Synchronous belts offer higher efficiency in power transmission due to their positive engagement with the pulley teeth, minimizing slippage and energy loss compared to V-belts, which rely on friction and can lose efficiency under load. The precise timing and reduced heat generation in synchronous belts make them ideal for applications demanding consistent speed and power, while V-belts perform well in less critical, lower torque environments. Choosing the right belt can improve your machinery's performance and reduce maintenance costs by optimizing power transfer efficiency.
Maintenance Requirements
Synchronous belts require minimal maintenance due to their durable construction and resistance to slippage, eliminating the need for regular tension adjustments common with V-belts. V-belts demand frequent inspection and tensioning to prevent wear and ensure optimal power transmission. Proper alignment and periodic replacement intervals are critical for both, but synchronous belts offer a more maintenance-efficient solution in high-precision applications.
Lifespan and Durability
Synchronous belts offer superior lifespan and durability compared to V-belts due to their reinforced materials and precise tooth engagement, which minimizes slippage and wear. V-belts, while generally easier to install, tend to suffer from faster degradation under heavy loads and high temperatures. To optimize your machinery's performance and reduce maintenance costs, selecting a synchronous belt can provide longer-lasting reliability.
Noise and Vibration Considerations
Synchronous belts generate less noise and vibration compared to V-belts due to their toothed design, which ensures positive engagement with pulleys and reduces slippage. V-belts tend to produce higher noise levels and vibrations caused by frictional slippage and belt tension variations during operation. For applications requiring quiet and smooth performance, synchronous belts are the preferred choice in minimizing acoustic emissions and mechanical vibrations.
Cost Implications and Investment
Synchronous belts generally have a higher upfront cost compared to V-belts due to their precise tooth engagement and advanced materials, which provide longer service life and reduced maintenance needs, potentially lowering total cost of ownership over time. V-belts are more cost-effective initially and widely available, making them suitable for lower-budget projects or applications with less demanding performance requirements. Investing in synchronous belts offers enhanced energy efficiency and torque capacity, which can justify the higher initial cost for industrial or high-precision operations.
Common Industrial Applications
Synchronous belts are widely used in precision machinery such as robotics, conveyors, and CNC equipment, where exact timing and reduced slippage are critical for performance and efficiency. V-belts dominate heavy-duty applications including industrial fans, compressors, and pumps, offering superior power transmission and durability under high stress. Your choice depends on the need for synchronization and load capacity in specific industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Belt for Your Needs
Choosing the right belt for your needs depends largely on the application's power transmission requirements and environmental conditions. Synchronous belts offer precise timing and high efficiency in machinery requiring accurate rotational synchronization, while V-belts provide greater flexibility, shock absorption, and easier installation in less timing-critical applications. Evaluating factors such as load capacity, speed, and maintenance will help you determine whether a synchronous belt or V-belt best suits your operational demands.
Synchronous belt vs V-belt Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com