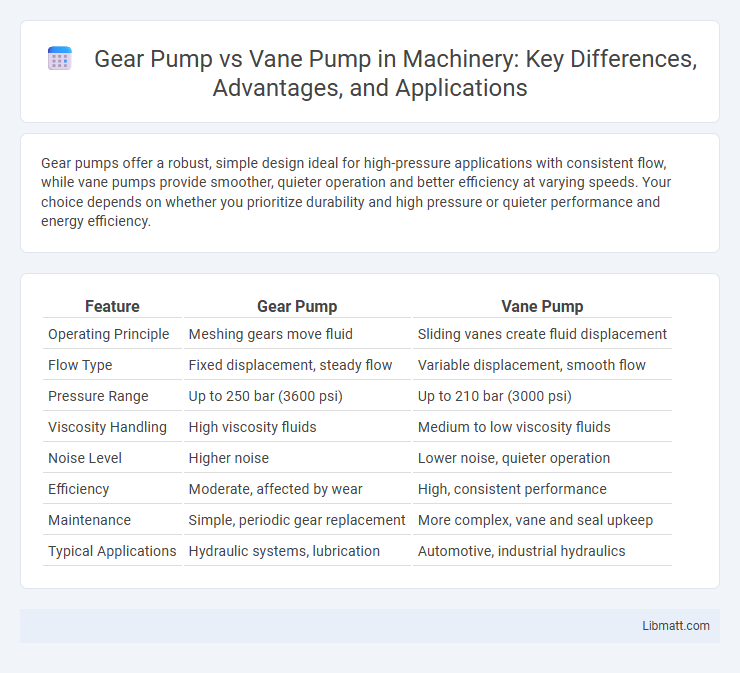
Gear pumps offer a robust, simple design ideal for high-pressure applications with consistent flow, while vane pumps provide smoother, quieter operation and better efficiency at varying speeds. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and high pressure or quieter performance and energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gear Pump | Vane Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Meshing gears move fluid | Sliding vanes create fluid displacement |
| Flow Type | Fixed displacement, steady flow | Variable displacement, smooth flow |
| Pressure Range | Up to 250 bar (3600 psi) | Up to 210 bar (3000 psi) |
| Viscosity Handling | High viscosity fluids | Medium to low viscosity fluids |
| Noise Level | Higher noise | Lower noise, quieter operation |
| Efficiency | Moderate, affected by wear | High, consistent performance |
| Maintenance | Simple, periodic gear replacement | More complex, vane and seal upkeep |
| Typical Applications | Hydraulic systems, lubrication | Automotive, industrial hydraulics |
Introduction to Gear Pumps and Vane Pumps
Gear pumps operate using meshing gears to transfer fluid, offering reliable performance in high-pressure hydraulic systems and applications requiring consistent flow rates. Vane pumps use a series of sliding vanes mounted on a rotor within a cam ring, providing smooth, low-pulsation flow ideal for lubrication and fuel transfer. Both pump types are widely employed in industrial hydraulics, but gear pumps excel in durability while vane pumps are preferred for quieter, more efficient fluid handling.
Working Principle of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps operate by meshing two gears together, where the rotation of the gears traps fluid between the teeth and the pump casing, creating a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump. The fluid is then carried around the outside of the gears to the discharge side, where the gears mesh again, forcing the fluid out under pressure. This positive displacement mechanism ensures a consistent flow rate regardless of pressure variations.
Working Principle of Vane Pumps
Vane pumps operate using a rotor with sliding vanes mounted inside a cavity, where centrifugal force pushes the vanes outward to maintain contact with the pump casing, creating sealed chambers. As the rotor turns, the volume of these chambers increases to draw fluid in and decreases to push fluid out, enabling smooth and efficient fluid transfer. This mechanism provides consistent flow and pressure, making vane pumps suitable for applications requiring moderate pressure and low pulsation.
Key Differences Between Gear and Vane Pumps
Gear pumps generate flow through the meshing of gears, providing high pressure and consistent performance in abrasive fluids. Vane pumps utilize sliding vanes within a rotor, offering smooth, low-pulsation flow ideal for hydraulic systems requiring variable displacement. Your choice between gear and vane pumps depends on factors like pressure requirements, fluid type, and the need for flow stability.
Efficiency Comparison: Gear Pump vs Vane Pump
Gear pumps typically offer higher volumetric efficiency at lower viscosities due to their robust design, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent flow rates under moderate pressure. Vane pumps excel in overall efficiency at variable displacements and higher pressures, providing smoother flow and better performance with shear-sensitive fluids. Performance differences in efficiency between gear and vane pumps depend heavily on operational conditions such as pressure, fluid type, and required flow consistency.
Application Areas of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are widely used in automotive lubrication systems, hydraulic machinery, and chemical processing due to their ability to handle high-viscosity fluids with consistent flow rates. They excel in applications requiring precise metering and pressure stability, such as fuel injection systems and oil transfer in manufacturing plants. Their robust design makes them suitable for industrial sectors like agriculture, marine engineering, and food processing, where reliable fluid movement is critical.
Application Areas of Vane Pumps
Vane pumps are widely utilized in applications requiring moderate pressure and smooth, pulse-free flow, such as hydraulic systems in automotive power steering, industrial machinery, and aircraft fuel systems. Their ability to handle variable displacement makes them suitable for refrigeration systems, HVAC units, and vacuum pumps. Vane pumps excel in environments demanding quiet operation and efficient fluid transfer of low-viscosity liquids.
Advantages of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps offer robust construction, ensuring high durability and the ability to handle viscous fluids efficiently. Their simple design provides reliable and consistent flow with minimal pulsation, making them ideal for precise hydraulic systems. You benefit from low maintenance requirements and a compact size, which allows easy integration into various industrial applications.
Advantages of Vane Pumps
Vane pumps offer superior efficiency and smoother flow compared to gear pumps due to their variable displacement design, which minimizes pulsation and noise in hydraulic systems. They provide better handling of low-viscosity fluids and improved volumetric efficiency under varying pressure conditions. Their compact size and ability to maintain performance with internal leakage make vane pumps ideal for precise, high-pressure applications in automotive and industrial hydraulics.
Choosing Between Gear Pump and Vane Pump
Choosing between a gear pump and a vane pump depends on your application's pressure requirements, fluid viscosity, and efficiency needs. Gear pumps excel in handling high-pressure, viscous fluids with robust, durable design, while vane pumps offer smoother flow and better efficiency in lower-pressure systems with cleaner fluids. Evaluating operational conditions and maintenance preferences helps determine whether the consistent displacement of gear pumps or the quieter, adjustable flow of vane pumps suits your system best.
Gear pump vs vane pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com