Helical springs provide high load capacity and excellent energy storage with uniform stress distribution, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring extended deflection. Wave springs offer compact design and reduced height, perfect for saving space in applications where Your assembly needs consistent load at lower deflections.
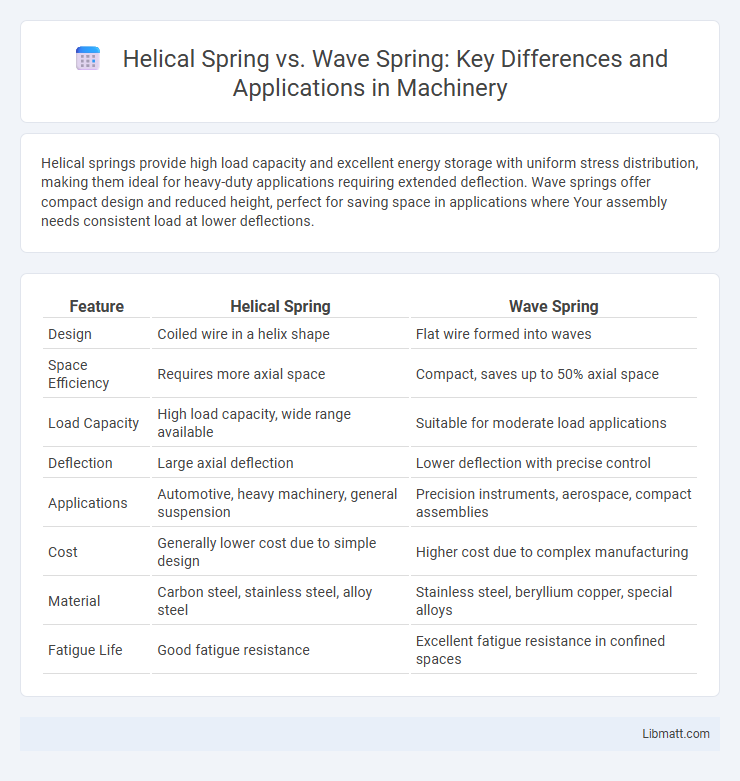
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Helical Spring | Wave Spring |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Coiled wire in a helix shape | Flat wire formed into waves |
| Space Efficiency | Requires more axial space | Compact, saves up to 50% axial space |
| Load Capacity | High load capacity, wide range available | Suitable for moderate load applications |
| Deflection | Large axial deflection | Lower deflection with precise control |
| Applications | Automotive, heavy machinery, general suspension | Precision instruments, aerospace, compact assemblies |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simple design | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing |
| Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel | Stainless steel, beryllium copper, special alloys |
| Fatigue Life | Good fatigue resistance | Excellent fatigue resistance in confined spaces |
Introduction to Helical Springs and Wave Springs
Helical springs, made from coiled wire, provide consistent compression and tension capabilities commonly used in automotive and industrial applications. Wave springs, composed of flat wire formed into a wave shape, offer space-saving benefits and precise load control ideal for compact assemblies. Understanding these differences helps you select the optimal spring type for your engineering design or machinery needs.
Definition and Basic Structure
A helical spring is a mechanical device made from coiled wire designed to store and release energy through axial compression or tension. It features a uniform cylindrical shape with consistent coil diameter and pitch, typically made from metal wire. Wave springs consist of a flat strip of metal shaped into a series of waves, allowing them to provide axial force in a smaller axial space compared to traditional helical springs.
Key Differences in Design
Helical springs feature a continuous wire coiled into a helix shape, optimizing for high load capacity and energy storage within a compact volume. Wave springs consist of a flattened wire formed into waves, providing reduced axial space while maintaining similar force characteristics. The primary design difference lies in the geometry, where helical springs excel in axial flexibility and wave springs offer space-saving benefits with minimal spring height.
Load and Deflection Characteristics
Helical springs provide a linear load-deflection curve with consistent stiffness, making them ideal for applications requiring straightforward load-bearing and energy storage. Wave springs offer similar load capacities but achieve deflection with a smaller solid height, allowing for more compact designs and reduced axial space requirements. The wave spring's multiple waves distribute load evenly, enabling improved space utilization without compromising performance compared to traditional helical springs.
Space and Weight Efficiency
Wave springs offer superior space and weight efficiency compared to helical springs by providing the same force and deflection with significantly reduced axial space. Helical springs require more coil turns and greater material volume, resulting in increased weight and bulk. Wave springs' compact design enables lightweight applications where minimizing space and weight is critical, such as aerospace and medical devices.
Common Applications
Helical springs are commonly used in automotive suspensions, industrial machinery, and aerospace systems due to their high load capacity and ability to store significant mechanical energy. Wave springs are preferred in compact spaces such as medical devices, electrical connectors, and precision instruments where space-saving and lighter weight are crucial. Your choice of spring depends on whether you require high load-bearing performance or compact design efficiency.
Material Choices and Durability
Helical springs are commonly made from high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and phosphor bronze, providing excellent durability for heavy-load applications and resistance to fatigue. Wave springs typically use stainless steel or Inconel alloys, offering superior performance in space-constrained environments due to their compact design and corrosion resistance. Your choice between the two depends on the material's compatibility with operating conditions and the required spring longevity.
Performance in Dynamic Environments
Helical springs offer reliable energy storage and consistent force in dynamic environments with high load variations, but they may experience greater fatigue due to their traditional coil structure. Wave springs provide superior space efficiency and improved vibration absorption, making them ideal for applications requiring compact design and reduced resonance. When optimizing your machinery's dynamic performance, consider wave springs for enhanced stability and longer service life in confined spaces.
Cost Comparison
Helical springs generally offer a lower initial cost due to simpler manufacturing processes and widespread availability, making them cost-effective for standard applications. Wave springs, while more expensive upfront, can reduce overall costs by saving space and weight, leading to smaller, lighter assemblies and lower material usage. Choosing between the two depends on your budget constraints and design requirements, balancing immediate expenses against long-term savings.
Choosing the Right Spring for Your Application
Helical springs provide high load capacity and energy storage in compact cylindrical shapes, ideal for applications requiring axial force and durability such as automotive suspensions and industrial machinery. Wave springs offer space-saving advantages with their coiled flat wire design, making them suitable for applications with limited axial space and moderate load requirements, including aerospace and medical devices. Selecting between helical and wave springs depends on factors like available space, load capacity, deflection requirements, and environmental conditions to optimize performance and longevity.
Helical spring vs wave spring Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com