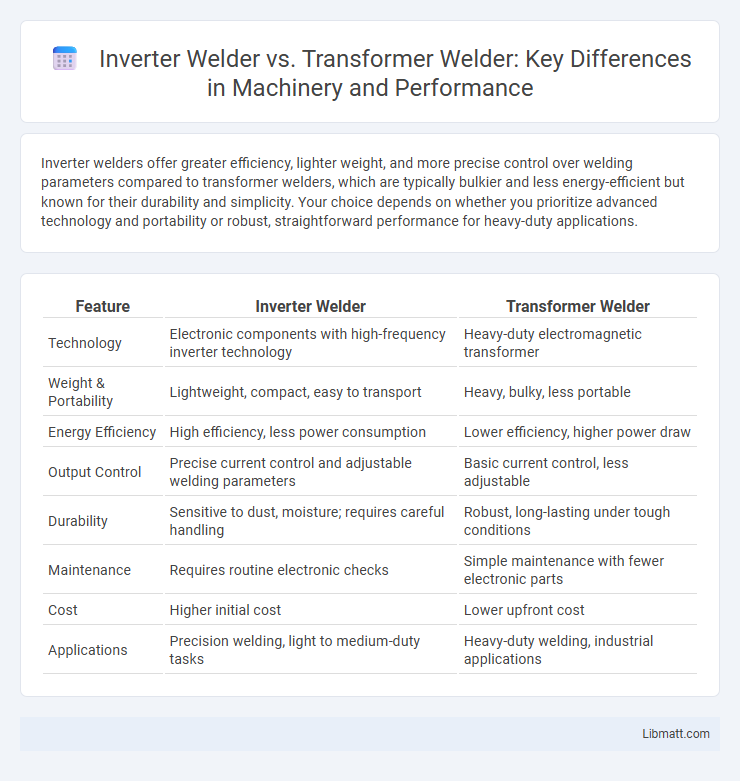
Inverter welders offer greater efficiency, lighter weight, and more precise control over welding parameters compared to transformer welders, which are typically bulkier and less energy-efficient but known for their durability and simplicity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize advanced technology and portability or robust, straightforward performance for heavy-duty applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inverter Welder | Transformer Welder |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Electronic components with high-frequency inverter technology | Heavy-duty electromagnetic transformer |
| Weight & Portability | Lightweight, compact, easy to transport | Heavy, bulky, less portable |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, less power consumption | Lower efficiency, higher power draw |
| Output Control | Precise current control and adjustable welding parameters | Basic current control, less adjustable |
| Durability | Sensitive to dust, moisture; requires careful handling | Robust, long-lasting under tough conditions |
| Maintenance | Requires routine electronic checks | Simple maintenance with fewer electronic parts |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | Precision welding, light to medium-duty tasks | Heavy-duty welding, industrial applications |
Introduction to Welding Technologies
Inverter welders use advanced electronic components to convert AC to DC, offering precise control, lightweight design, and energy efficiency compared to traditional transformer welders. Transformer welders rely on heavy iron-core transformers that provide durable and consistent voltage output but tend to be bulkier and less portable. Your choice depends on the need for mobility, power efficiency, and welding precision in various applications.
What Is an Inverter Welder?
An inverter welder uses advanced electronic circuitry to convert AC power into a lower voltage, high-frequency current, enabling more efficient and precise welding performance. Unlike traditional transformer welders, inverter welders are lighter, more portable, and offer better control over welding parameters, making them ideal for various applications. Your welding tasks can benefit from the energy efficiency and versatility that an inverter welder provides, especially in professional or hobbyist settings.
What Is a Transformer Welder?
A transformer welder operates using electromagnetic induction to convert high voltage, low current electricity into low voltage, high current output suitable for welding. It features heavy copper windings and a robust iron core, providing durability and reliability in industrial applications. Transformer welders are known for their simplicity, consistent performance, and ability to handle heavy-duty welding tasks efficiently.
Key Differences Between Inverter and Transformer Welders
Inverter welders use advanced IGBT technology to convert AC power into a stable DC output, resulting in lightweight, energy-efficient machines with precise control over welding parameters. Transformer welders rely on heavy magnetic copper coils to step down voltage, making them robust but bulky and less energy-efficient compared to inverters. The key differences include size, weight, energy consumption, control precision, and performance flexibility, with inverter welders offering greater portability and efficiency while transformer welders provide simplicity and durability.
Efficiency and Power Consumption Comparison
Inverter welders offer significantly higher efficiency and lower power consumption compared to transformer welders due to their advanced electronic circuitry that regulates voltage and current more precisely. Your energy savings can be substantial since inverter welders convert power at frequencies up to 20,000 Hz, reducing energy loss and heat generation, unlike transformer welders operating at the standard 50-60 Hz. This efficiency advantage makes inverter welders ideal for prolonged use and portable applications where power availability and consumption are critical factors.
Portability and Size: Inverter vs Transformer
Inverter welders are significantly more portable and compact than transformer welders due to their lightweight electronic components, making them ideal for job sites requiring mobility. Transformer welders are bulkier and heavier because they rely on large iron cores and copper windings, which limits ease of transport. The size advantage of inverters translates to greater efficiency in confined spaces and easier storage compared to traditional transformer models.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Inverter welders typically have higher upfront costs but offer lower maintenance expenses due to their solid-state components and enhanced energy efficiency. Transformer welders, while more affordable initially, often require more frequent maintenance and replacement of bulky parts, which can increase long-term costs. Evaluating your budget and usage frequency will help determine which welder offers the best value for your welding projects.
Welding Performance and Output Quality
Inverter welders provide superior welding performance with precise current control, resulting in consistent arc stability and high-quality welds suitable for delicate or intricate projects. Transformer welders deliver robust output but often produce less stable arcs, leading to variable weld quality, especially on thin or complex materials. The advanced electronics in inverter welders enable smoother starts, better penetration, and reduced spatter, enhancing overall output quality compared to the heavier, bulkier transformer models.
Suitability for Various Applications
Inverter welders offer superior versatility and portability, making them ideal for diverse applications such as automotive repairs, construction, and light manufacturing where precise control and ease of movement are crucial. Transformer welders excel in heavy-duty industrial tasks requiring high power output and durability, suitable for thick metal welding and prolonged use in harsh environments. Your choice depends on the specific application needs, balancing portability and advanced features of inverter welders against the robustness and simplicity of transformer welders.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Welder
Inverter welders offer lightweight, energy-efficient operation with precise control, making them ideal for detailed and portable welding tasks, while transformer welders provide robust durability and higher tolerance for heavy-duty industrial applications. Selecting the right welder depends on factors such as job complexity, workspace mobility, power availability, and budget considerations. Prioritizing specific welding needs ensures optimal performance and long-term cost-efficiency.
Inverter welder vs transformer welder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com