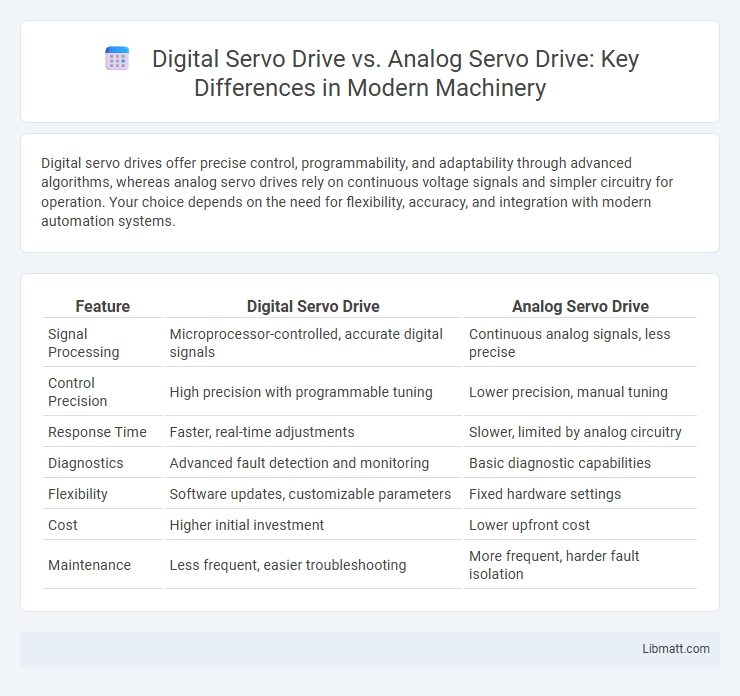
Digital servo drives offer precise control, programmability, and adaptability through advanced algorithms, whereas analog servo drives rely on continuous voltage signals and simpler circuitry for operation. Your choice depends on the need for flexibility, accuracy, and integration with modern automation systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Servo Drive | Analog Servo Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Microprocessor-controlled, accurate digital signals | Continuous analog signals, less precise |
| Control Precision | High precision with programmable tuning | Lower precision, manual tuning |
| Response Time | Faster, real-time adjustments | Slower, limited by analog circuitry |
| Diagnostics | Advanced fault detection and monitoring | Basic diagnostic capabilities |
| Flexibility | Software updates, customizable parameters | Fixed hardware settings |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Less frequent, easier troubleshooting | More frequent, harder fault isolation |
Introduction to Servo Drives
Servo drives control the motion of electric servomotors by regulating motor current, velocity, and position for precise performance. Digital servo drives utilize microprocessors and software algorithms to offer enhanced accuracy, programmability, and adaptive control compared to analog servo drives, which rely on continuous electrical signals for operation. The digital approach enables advanced diagnostics, network communication, and integration with automation systems, making it ideal for modern applications requiring high precision and flexibility.
Key Differences Between Digital and Analog Servo Drives
Digital servo drives utilize microprocessors for precise control and offer adaptive tuning, while analog servo drives rely on continuous voltage signals for simpler operation. Digital drives provide enhanced accuracy, programmability, and diagnostic capabilities, improving your machine's overall performance and maintenance ease. Analog drives excel in cost-effectiveness and lower electromagnetic interference but lack the flexibility and advanced features of digital counterparts.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Precision
Digital servo drives offer superior speed and precision compared to analog servo drives due to their advanced microprocessor-based control algorithms that enable faster response times and finer resolution in position feedback. They support high-frequency signal processing, which results in more accurate and stable motor control with minimal overshoot and oscillation. Analog servo drives, limited by their continuous signal components and simpler control schemes, generally exhibit slower response times and lower positioning accuracy.
Control Features and Functionality
Digital servo drives offer advanced control features such as programmable parameters, adaptive tuning, and real-time diagnostics, enabling precise and flexible motion control. Analog servo drives provide basic control functionalities with fixed parameters and limited adaptability, primarily relying on continuous voltage signals for operation. Your choice between these drives impacts system responsiveness, accuracy, and ease of integration with modern automation platforms.
Integration with Modern Automation Systems
Digital servo drives offer superior integration with modern automation systems due to their advanced communication protocols like EtherCAT and Modbus, enabling seamless connectivity and real-time data exchange. These drives support precise motion control through software-based tuning and diagnostics, enhancing your system's flexibility and efficiency. Analog servo drives lack such compatibility and adaptability, often requiring additional hardware for basic integration functions.
Advantages of Digital Servo Drives
Digital servo drives offer superior precision control and adaptability due to their ability to process complex algorithms and provide real-time feedback. They enable enhanced performance in automation systems through programmable parameters and easier integration with digital networks such as Ethernet/IP and PROFINET. Digital drives also improve diagnostics and reduce maintenance costs by facilitating advanced monitoring and fault detection capabilities.
Limitations of Analog Servo Drives
Analog servo drives face limitations including susceptibility to noise interference, limited accuracy due to signal drift, and difficulty in tuning for complex control algorithms. These drives often struggle with maintaining stable performance under varying load conditions and lack the flexibility and scalability found in digital servo drives. Your system may benefit from digital servo drives that offer enhanced precision, adaptive control, and easier integration with modern automation technologies.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Digital servo drives typically offer lower long-term maintenance costs due to self-diagnostic features and software updates, whereas analog servo drives may incur higher expenses from manual tuning and component wear. Initial costs for digital servo drives can be higher, but their efficiency and reduced downtime often result in overall cost savings. Your choice should weigh upfront investment against ongoing maintenance expenses to optimize operational budgets.
Application Suitability: Digital vs. Analog
Digital servo drives offer superior precision and adaptability, making them ideal for complex automation tasks in robotics, CNC machinery, and advanced manufacturing where high-speed responsiveness and programmable control parameters are crucial. Analog servo drives find their strengths in simpler, cost-effective applications with steady-state operations such as basic conveyor systems and traditional industrial machines where continuous and straightforward control is sufficient. The choice between digital and analog servo drives depends largely on the specific demands of the application, including required accuracy, flexibility, and integration with modern control systems.
Future Trends in Servo Drive Technology
Digital servo drives dominate future trends with enhanced precision, adaptive control algorithms, and real-time diagnostics, outperforming analog servo drives that rely on fixed, less flexible circuits. Integration of IoT connectivity and AI-driven predictive maintenance will further advance digital servo technology, enabling smarter, more efficient industrial automation systems. As industries demand higher performance and connectivity, digital drives will become the standard, phasing out analog systems due to their limited scalability and functionality.
Digital servo drive vs analog servo drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com